40 aerobic cellular respiration diagram
Cells that have a high-energy demand such as nerve cells and muscle cells contain a large number of mitochondria to maximise ATP production by aerobic respiration. A muscle cell contains ... Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration - an equation, an output description and an illustration. 1) Equation: C 6 H 12 O 6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 O 2 = 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + 36 ATP (ENERGY) carbohydrate + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + ATP energy 2) Description of the molecules created in all three stages of cellular respiration:
Cellular Respiration: (2 kinds—Aerobic and Anaerobic) •Cellular respiration is the process by which the energy of glucoseis released in the cell to be used for life processes (movement, breathing, blood circulation, etc…)
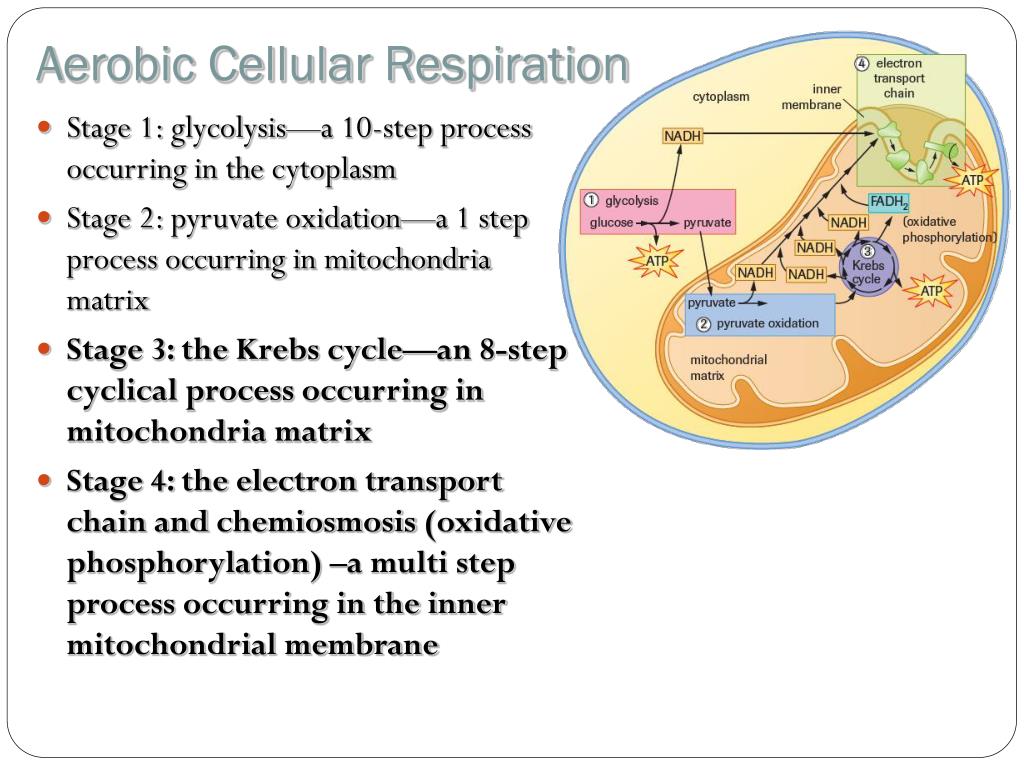
Aerobic cellular respiration diagram
Cellular respiration has 4 distinct processes, which drive the creation of atp. The process of this conversion is known as aerobic respiration and it is the reason why humans need to. While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration. Aerobic cellular respiration requires an adequate supply of. A. carbon dioxide. B. oxygen. C. ethyl alcohol. D. starch. 9. Which statement regarding cellular respiration is correct? A. Cellular respiration in plants occurs only during the day. B. All living organisms carry out some form of cellular respiration. C. Fungi and bacteria carry out aerobic cellular respiration only. D. Only plants ... 1. Aerobic respiration is the aerobic catabolism of carbohydrate to carbon dioxide, water, and energy. 2. The overall aerobic respiration can be mentioned by following chemical reaction. C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 → 6 C O 2 + 6 H 2 O. 3. This type of cellular respiration is seen in aerobes and facultative anaerobes. 4.
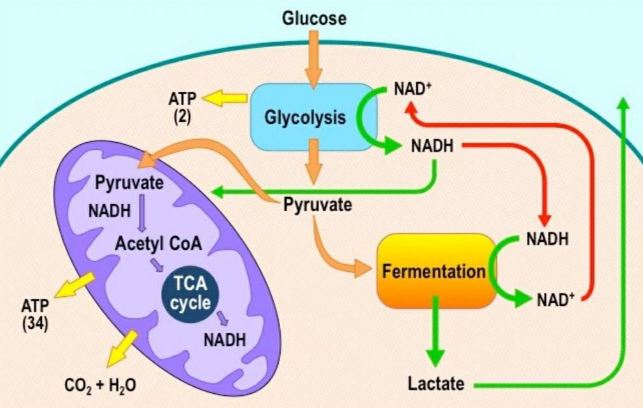
Aerobic cellular respiration diagram. Cellular respiration 2 Aerobic respiration Aerobic respiration (red arrows) is the main means by which both plants and animals utilize energy in the form of organic compounds that was previously created through photosynthesis (green arrow). Aerobic respiration requires oxygen in order to generate energy (ATP). Although carbohydrates, fats, and ... Aerobic implies that the process requires oxygen. In contrast, anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen. The Venn diagram compares aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. mcjpg Which statement could b Get the answers you need. The by-product of this process produces carbon dioxide along with ATP - the energy currency of the cells. 12.06.2021 · Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, “biological machines” also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell. 19.07.2021 · Diagram. The equation for aerobic cellular respiration is: oxygen + glucose = carbon dioxide + water + ATP . Cells get the reactants, or the starting materials, for cellular respiration from ...
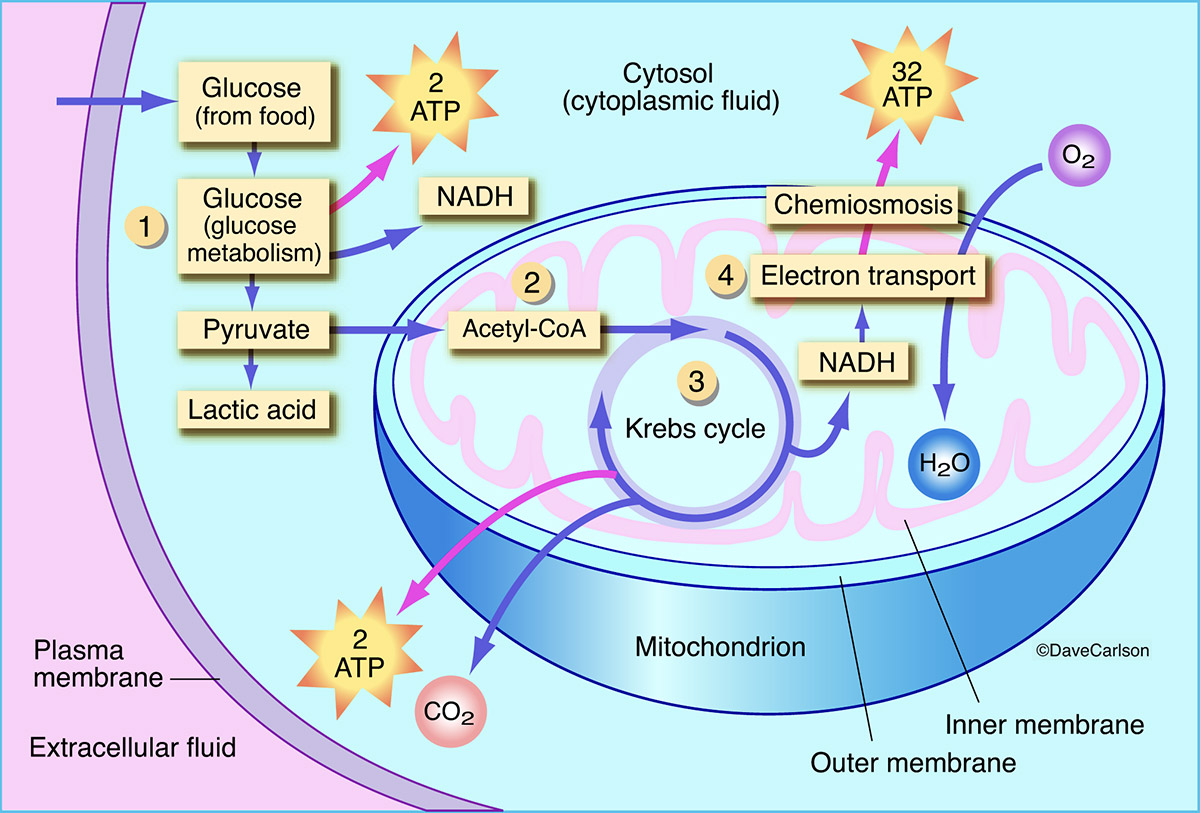
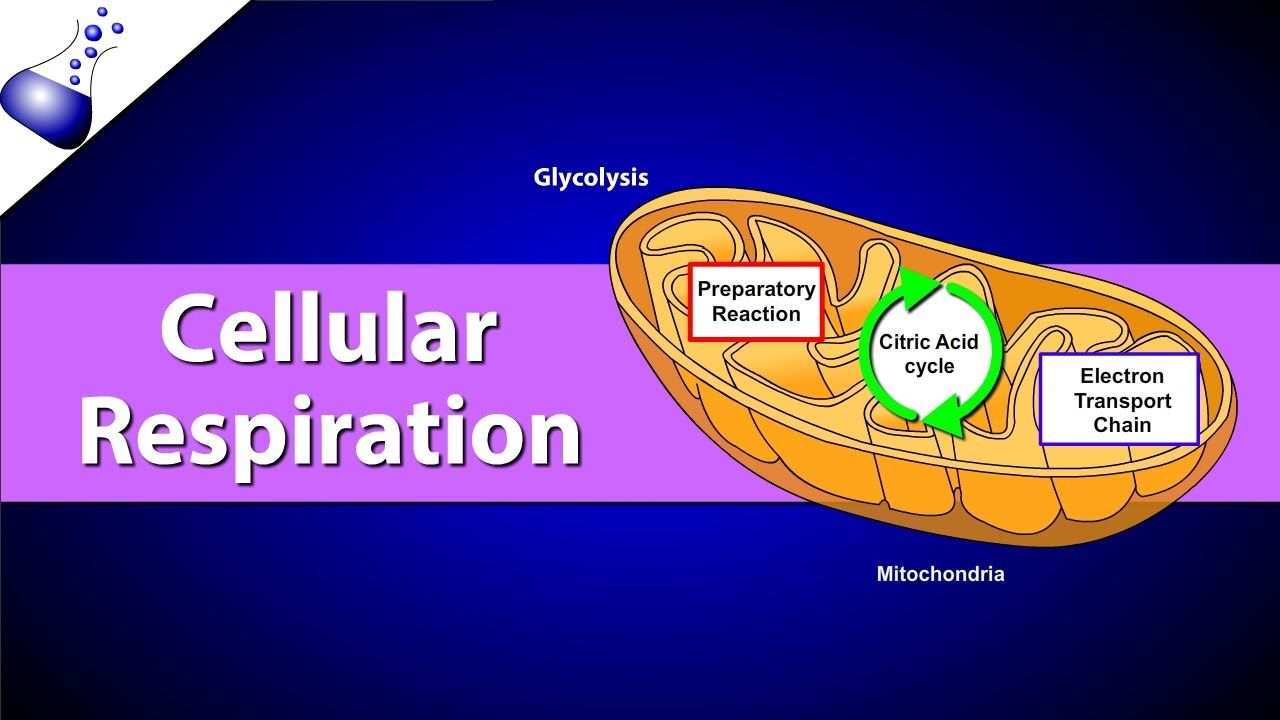
8.1.3 Draw and label a diagram showing the structure of a mitochondrion as seen in electron micrographs. Figure 8.1.2 - Labelled diagram of a mitochondrion. 8.1.4 Explain aerobic respiration, including the link reaction, the Krebs cycle, the role of NADH + H +, the electron transport chain and the role of oxygen. Aerobic Respiration 07.09.2011 · Cellular Respiration 13. Is cellular respiration aerobic or anaerobic? Explain. 14.____ When living cells break down the bonds holding molecules together, energy is a. stored as ADP. c. released as heat. b. stored as ATP. d. changed into glucose 15.____ In cellular respiration, the most energy is transferred during a. glycolysis. c. the Krebs ... Aerobic cellular respiration refers to the process by which living organisms convert nutrients into energy for the body to use via the oxidization of nutrients. During aerobic respiration, catabolic reactions convert larger complex organic molecules into ATP, the chemical that drives most physiological processes in the body.In other words, respiration is the key way that a cell gets chemical ... Start studying AEROBIC CELLULAR RESPIRATION (DIAGRAM). Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
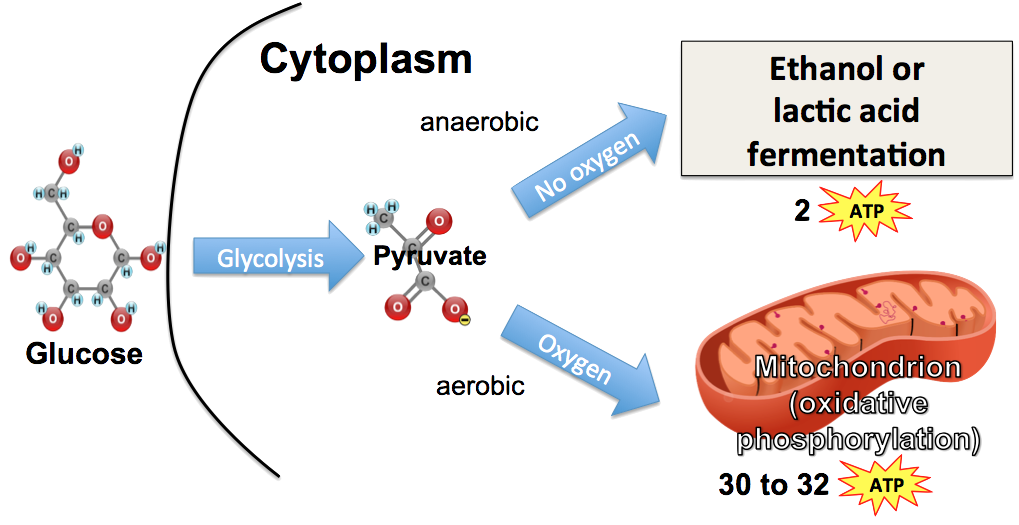
Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Stages, Equation & Products Aerobic cellular respiration occurs when cells break down food molecules to create ATP, or energy molecules, in the presence of oxygen. Aerobic Cellular Respiration- Carried out by organisms in oxic (oxygen containing) environment. •2. Anaerobic Cellular Respiration-Anoxic (no-oxygen containing) environment. •3. ... The diagram is a simplified view of stage 2 and stage 3 of aerobic respiration. 1. Circle the part of the diagram that shows pyruvate oxidation. Cellular Respiration The term cellular respiration refers to the biochemical pathway by which cells release energy from the chemical bonds of food molecules and provide that energy for the essential processes of life. All living cells must carry out cellular respiration. It can be aerobic respiration in the presence of oxygen or anaerobic respiration. Prokaryotic cells carry out cellular ... Aerobic respiration is a biological process that takes energy from glucose and other organic compounds to create a molecule called Adenosine TriPhosphate (ATP). ATP is then used as energy by nearly every cell in the body -- the largest user being the muscular system.
The diagram represents some processes occurring in the leaf of a plant. Which letters indicate substances needed by the leaf to carry out the process of aerobic cellular respiration? answer choices . A and C. B and C. C and D. B and D . Tags: Question 17 . SURVEY . 30 seconds .
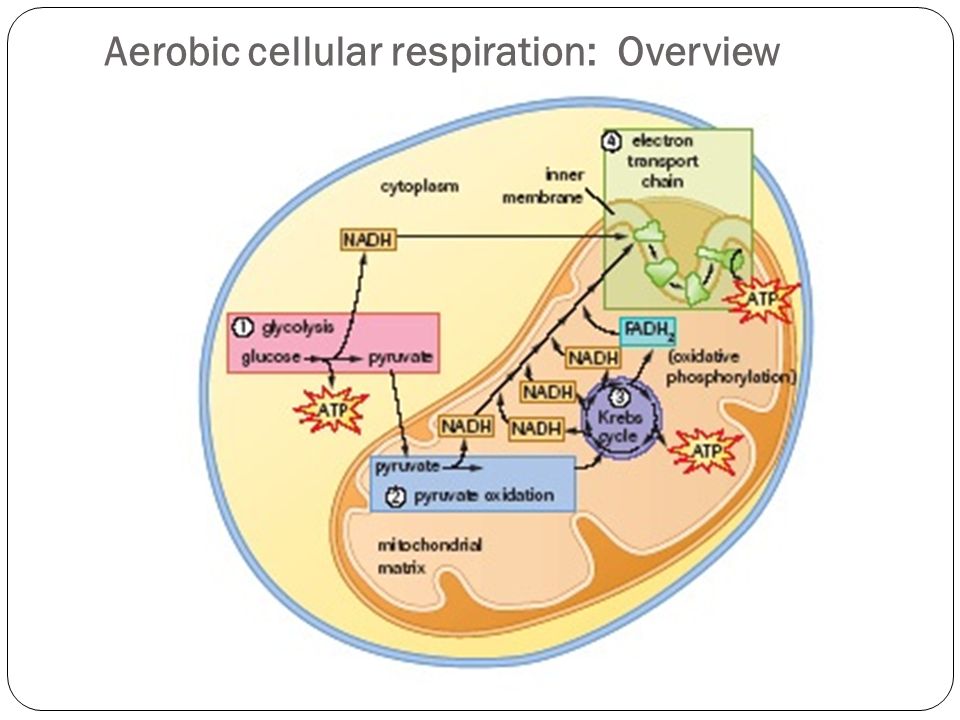
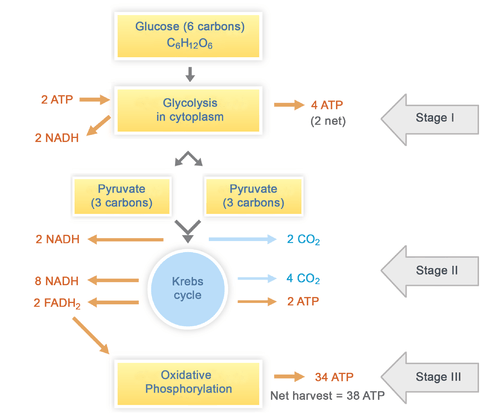
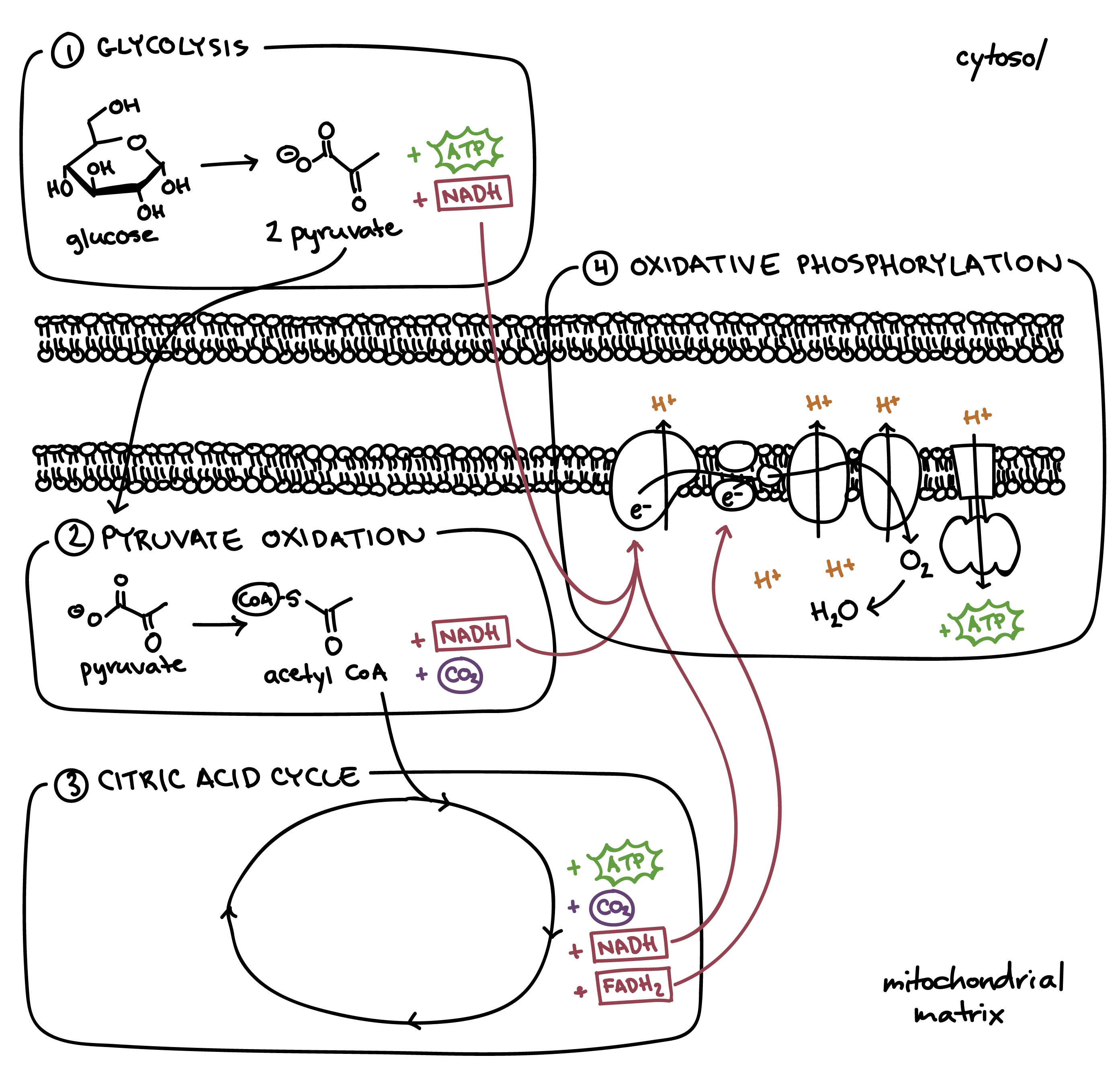
Steps of cellular respiration. Overview of the steps of cellular respiration. Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol. Pyruvate oxidation. Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to ...
Metabolic pathways that contribute to the production of ATP molecules in cells are collectively referred to as cellular respiration. When a molecule of glucose undergoes aerobic cellular respiration, 36 molecules of ATP are produced. Glucose is an energy-rich molecule. The breakdown of glucose results in the formation of low-energy molecules and energy.
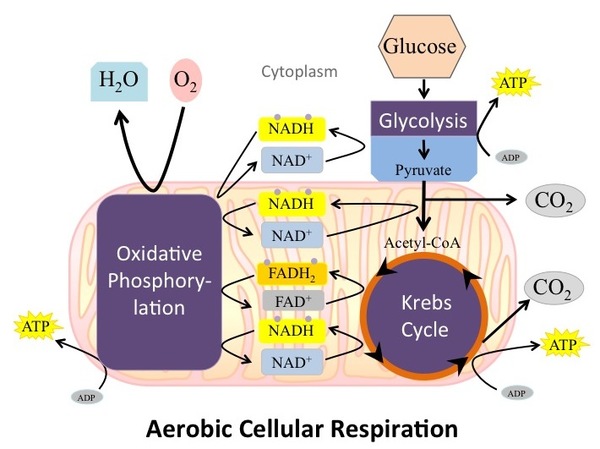
Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration is a series of chemical reactions which begin with the reactants of sugar in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products. This process occurs in the mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell. Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Water +ATP C 6H 12O
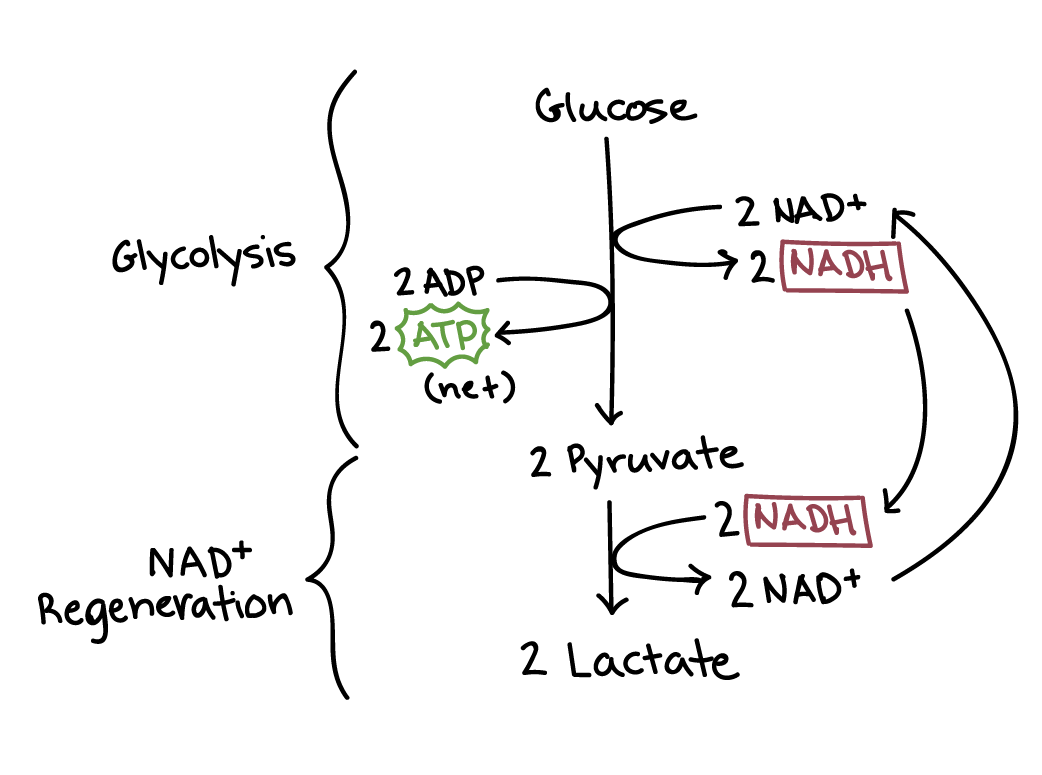
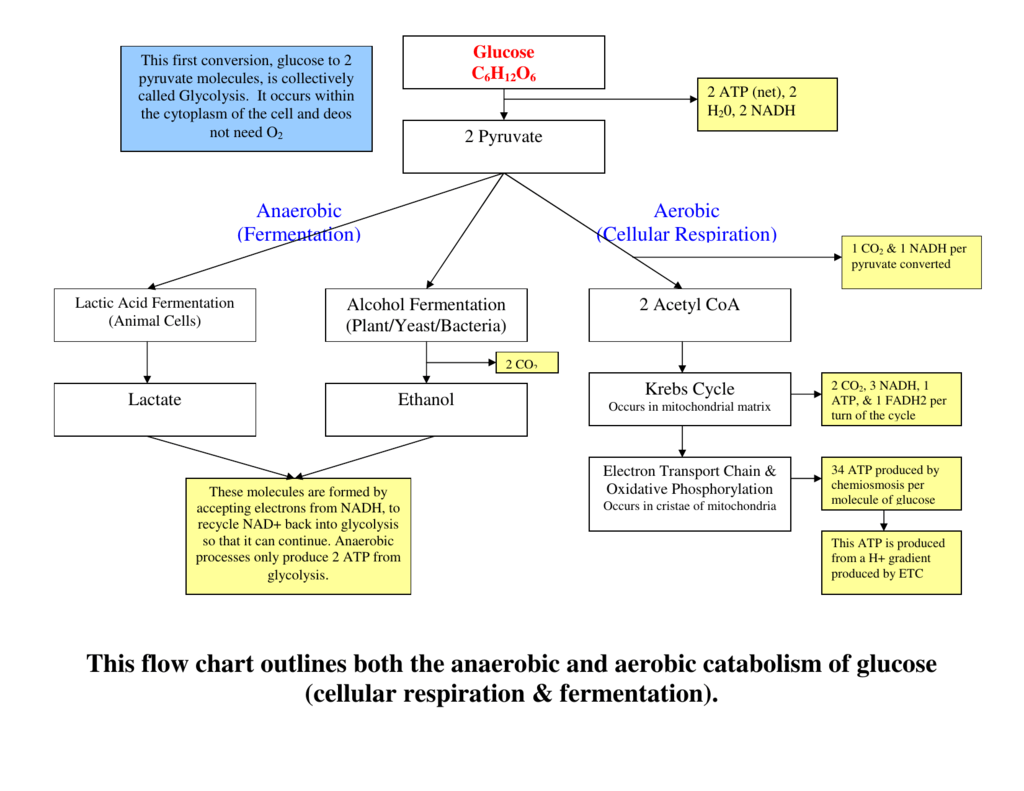
Aerobic Respiration and Fermentation (With Diagram) The reactions of glycolysis have no specific requirement for oxygen. Oxidation reactions do occur, such as the removal of two hydrogen's from glyceraldehyde- 3-phosphate, and NAD + is reduced to NADH, but oxygen per se is not consumed.
Aerobic cellular respiration is a part of cellular respiration, and it plays an important role in producing the energy that is required for various functions of a cell. All organisms are made up of tiny cells which carry out various functions. Energy is required for processing these functions. This energy is provided by the cells, and is ...
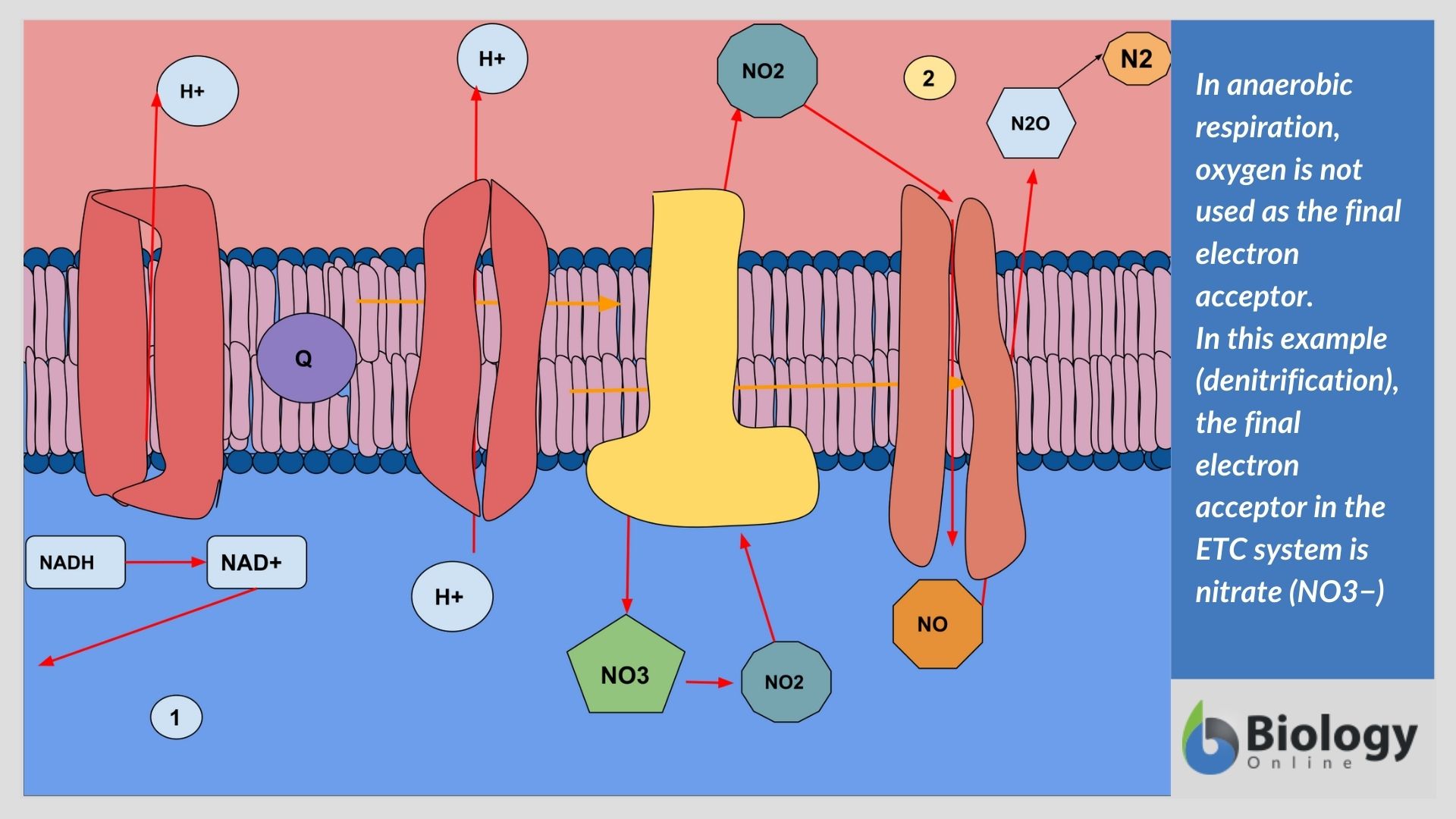
Aerobic Respiration: It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. Anaerobic Respiration: It is a process which takes place in the absence of oxygen ...
The main result of aerobic respiration is the A. conversion of radiant energy into chemical energy B. production of lactic acid as an end product C. storage of energy in a polysaccharide D. production of ATP from the breakdown of glucose 3. Which substance is needed for aerobic cellular respiration to occur? A. oxygen B. carbon dioxide
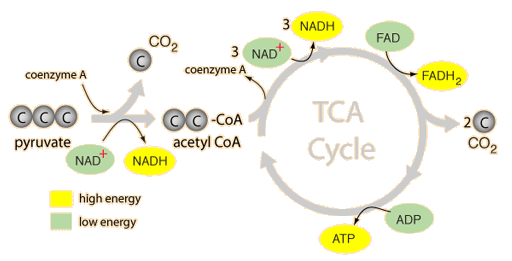
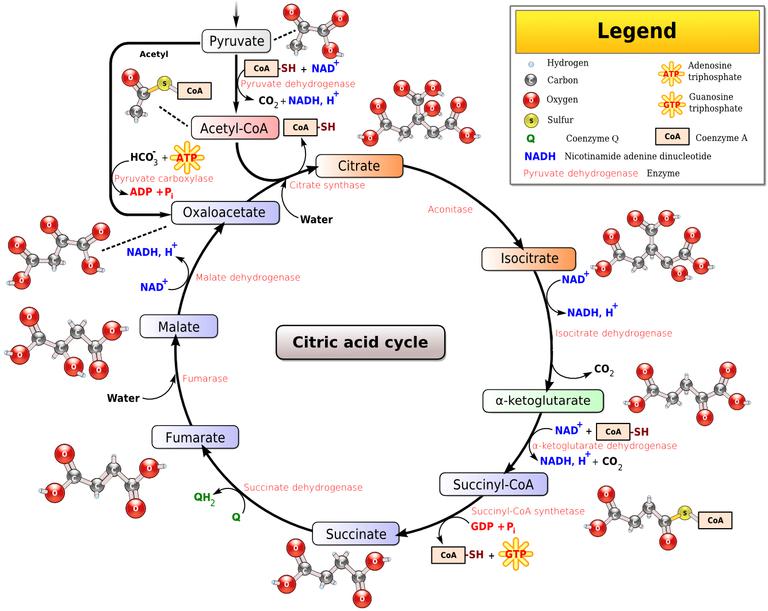
Organelle found in eukaryotic organisms that is the site of aerobic cellular respiration. Krebs Cycle Step in aerobic respiration that takes pyruvate from glycolysis to produce carbon dioxide and high energy electrons.
What is Cellular Respiration? Cellular or Aerobic (in air) Respiration is a series of chemical reactions in the mitochondrion where molecules of glucose are broken down to make CO 2, water, and ATP. C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 → 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + glucose oxygen carbon dioxide water 38 ATP
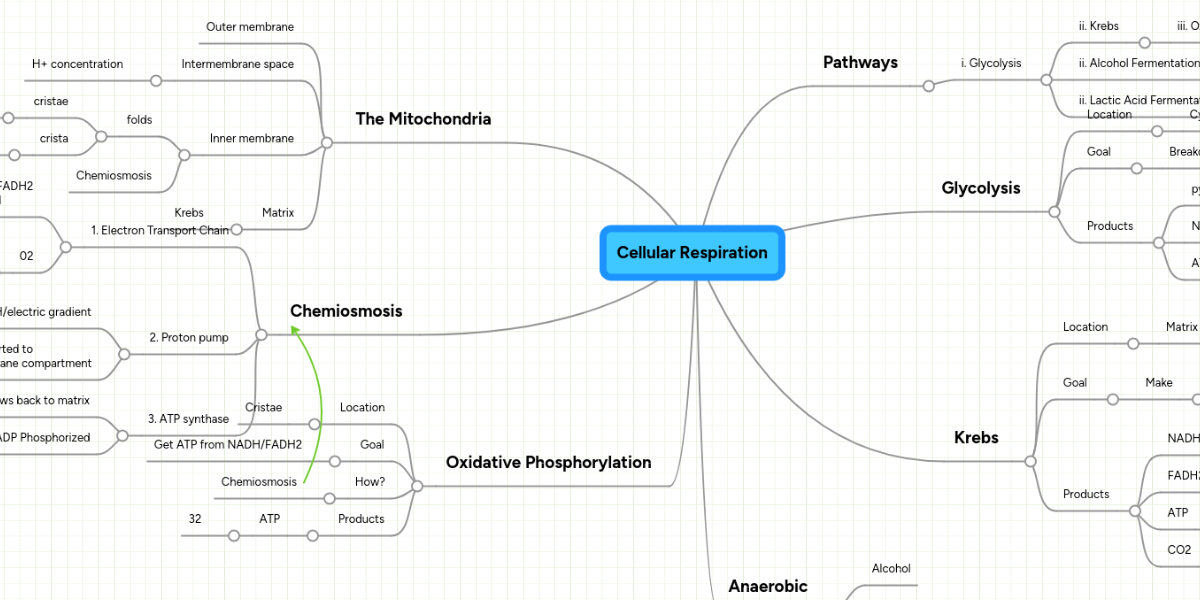
Unit Learning Goal Scale 4 - You can compare/contrast all components of photosynthesis & cellular respiration in terms of energy, organic and inorganic molecules as well as accurately diagram all the processes as part of the flow of energy and matter through all levels of organization in an ecosystem.
Aerobic implies that the process requires oxygen. If there is no oxygen present after glycolysis, a process called fermentation may occur. We will discuss this in the next lesson. Take a close look at the diagram below. Identify the areas where each step of aerobic cellular respiration occurs:
The chemical reaction of cellular Respiration is ... Aerobic Respiration. To know more about cellular respiration and photosynthesis, visit BYJU’S. Test your Knowledge on difference between photosynthesis and respiration. Q 5. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin! Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button ...
Aerobic Respiration, Part 1: Glycolysis You have read that nearly all of the energy used by living things comes to them in the bonds of the sugar, glucose. Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cell metabolism. Many living organisms carry out glycolysis as part of their metabolism.
Aerobic Respiration: The Krebs Cycle ª Review: During glycolysis, one molecule of glucose is split to form two pyruvate molecules, with a net profit of two ATP. The two pyruvate molecules then enter the mitochondria, where they are converted to acetyl CoA.
The cellular respiration can be classified into two types, depending upon the availability of oxygen: Aerobic Respiration: It is the process in which the oxidation of the carbohydrate molecule, glucose, takes place in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic Respiration: It is the process in which the oxidation of glucose takes place in the absence of ...
1. Aerobic respiration is the aerobic catabolism of carbohydrate to carbon dioxide, water, and energy. 2. The overall aerobic respiration can be mentioned by following chemical reaction. C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 → 6 C O 2 + 6 H 2 O. 3. This type of cellular respiration is seen in aerobes and facultative anaerobes. 4.
Aerobic cellular respiration requires an adequate supply of. A. carbon dioxide. B. oxygen. C. ethyl alcohol. D. starch. 9. Which statement regarding cellular respiration is correct? A. Cellular respiration in plants occurs only during the day. B. All living organisms carry out some form of cellular respiration. C. Fungi and bacteria carry out aerobic cellular respiration only. D. Only plants ...
Cellular respiration has 4 distinct processes, which drive the creation of atp. The process of this conversion is known as aerobic respiration and it is the reason why humans need to. While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration.







/Cellular-Respiration-58e52b113df78c5162b38dca.jpg)








0 Response to "40 aerobic cellular respiration diagram"
Post a Comment