40 crystal field theory diagram
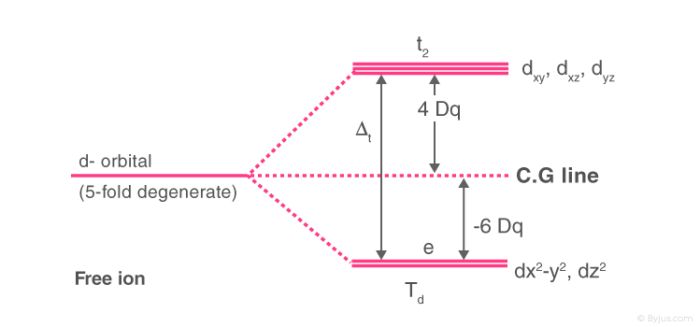
ions in tetrahedral fields, only that the diagram for a 3d10-N ion has to be utilized. In addition, the crystal field strength is reduced from its octahedral value. For instance, a 3d3 ion in tetrahedral symmetry has an identical diagram as a 3d7 ion in octahedral symmetry with the reduced value of D q. The parameters D q Semiconductors are materials with conductivity between conductors and insulators. Understand the properties, applications, uses and types of semiconductors with examples.
Jun 22, 2006 · The diagram depicts the relations between different theories, where Non-Relativistic Quantum Field Theory is not a historical theory but rather an ex post construction that is illuminating for conceptual purposes. ... Algebraic Quantum Field Theory (AQFT) ... such as the stress tensor for a crystal. A field is therefore specified by a time ...
Crystal field theory diagram
Crystal field theory (CFT) describes the breaking of degeneracies of electron orbital states, usually d or f orbitals, due to a static electric field produced by a surrounding charge distribution (anion neighbors). This theory has been used to describe various spectroscopies of transition metal coordination complexes, in particular optical spectra (colors). Crystal field stabilization is applicable to the transition-metal complexes of all geometries. The reason that many d 8 complexes are square-planar is the very large amount of crystal field stabilization that this geometry produces with this number of electrons. Square planar CFT splitting. Electron diagram for square planer d subshell splitting. Bonding: valence bond, crystal field theory, MO Spectrochemical series Crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) Electronic Spectra Magnetic Properties. 2 Limitations of VB Theory 3d 4s 4p Vacant orbitals available to accept ligand electrons Cr(III) 3d d2sp3 Vacant orbitals available to accept ligand electrons
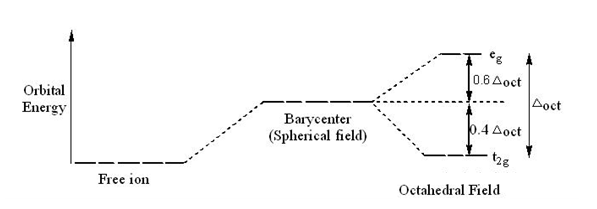
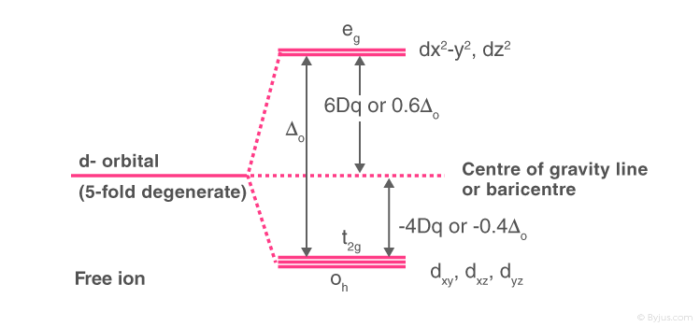
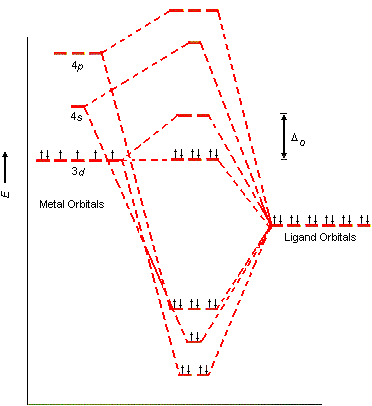
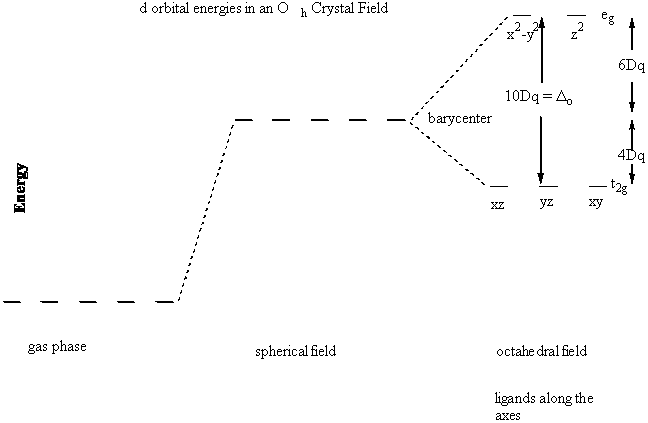
Crystal field theory diagram. Using crystal field theory, sketch the energy-level diagram for the d orbitals in an octahedral field; then fill in the electrons for the metal ion in each of the following complexes. How many unpaired electrons are there in each case? a [V(CN) 6] 3− b [Co(C 2 O 4) 3] 4− (high-spin). c [Mn(CN) 6] 3− (low-spin) Tetrahedral Crystal Field Splitting barycenter (spherical field) t 2 orbitals point more directly at ligands and are destabilized. e orbitals point less directly at ligands and are stabilized. x y z M L opposite splitting of octahedral field L L L Δ t < Δ o because only 4 ligands and d orbitals point between ligands We are used to using a theory like VSEPR theory to predict molecular geometry, but unfortunately with coordination compounds, things are not so simple, becau... Aug 15, 2020 · Crystal Field Splitting Energy. Within Crystal Field Theory, the interaction of the metal and ligand arise from the positive charge of the metal and negative charge on the ligands.The theory is developed by looking at the five degenerate d-orbitals and how the energies are changed on being surrounded by the negative point charges of the ligands.
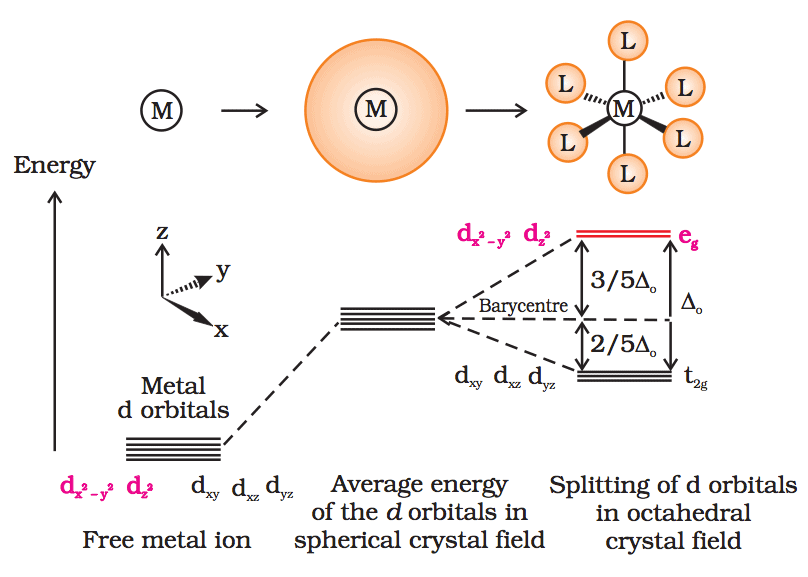
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into crystal field theory. It explains how to draw the crystal field splitting diagram of transi... Crystal Oscillator Circuit Diagram Crystal Oscillator Working. The crystal oscillator circuit usually works on the principle of the inverse piezoelectric effect. The applied electric field will produce a mechanical deformation across some materials. May 06, 2021 · Basic Concept. In Crystal Field Theory, it is assumed that the ions are simple point charges (a simplification). When applied to alkali metal ions containing a symmetric sphere of charge, calculations of bond energies are generally quite successful. Crystal field theory often termed as ligand field theory. Overview of Crystal Field Theory. In order to understand clearly the crystal field interactions in transition metal complexes, it is necessary to have knowledge of the geometrical or spatial disposition of d orbitals. The d-orbitals are fivefold degenerate in a free gaseous metal ion.
Crystal field theory was developed by considering two compounds: manganese (II) oxide, MnO, and copper (I) chloride, CuCl. Octahedral Crystal Fields. Each Mn 2+ ion in manganese (II) oxide is surrounded by six O 2- ions arranged toward the corners of an octahedron, as shown in the figure below. MnO is therefore a model for an octahedral complex ... SURVEY. 60 seconds. Q. When the ligands move along the x, y and z axes of d orbital in metal ion (tetrahedral geometry), none of the five d orbitals is directly in their path. Name the d orbitals that lower energy. answer choices. dz2 and dx2- y2. dxy, dxz and dyz. Quantum field theory emerged from the work of generations of theoretical physicists spanning much of the 20th century. Its development began in the 1920s with the description of interactions between light and electrons, culminating in the first quantum field theory—quantum electrodynamics.A major theoretical obstacle soon followed with the appearance and persistence of various infinities in ... In this presentation, the effective mass theory (EMT) for the electron in the crystal lattice will be introduced. The dynamics of the electron in free space and in the lattice will be compared. The E-k diagram for direct band gap semiconductors will be studied and …
Bonding: valence bond, crystal field theory, MO Spectrochemical series Crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) Electronic Spectra Magnetic Properties. 2 Limitations of VB Theory 3d 4s 4p Vacant orbitals available to accept ligand electrons Cr(III) 3d d2sp3 Vacant orbitals available to accept ligand electrons
Crystal field stabilization is applicable to the transition-metal complexes of all geometries. The reason that many d 8 complexes are square-planar is the very large amount of crystal field stabilization that this geometry produces with this number of electrons. Square planar CFT splitting. Electron diagram for square planer d subshell splitting.
Crystal field theory (CFT) describes the breaking of degeneracies of electron orbital states, usually d or f orbitals, due to a static electric field produced by a surrounding charge distribution (anion neighbors). This theory has been used to describe various spectroscopies of transition metal coordination complexes, in particular optical spectra (colors).
Which Of These Ions Will Have A Zero Crystal Field Splitting Energy In An Octahedral Complex Socratic

Figure 1 From Hydration Of Copper Ii New Insights From Density Functional Theory And The Cosmo Solvation Model Semantic Scholar

Ppt Bonding In Complexes Of D Block Metal Ions Crystal Field Theory Powerpoint Presentation Id 6724687

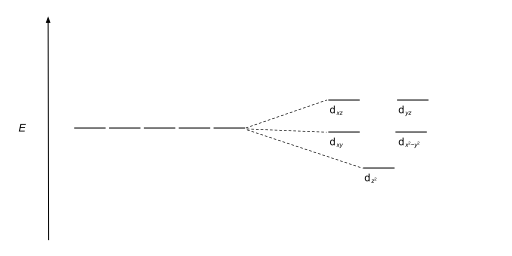
What Does The Crystal Field Splitting Diagram For Trigonal Planar Complexes Look Like Chemistry Stack Exchange

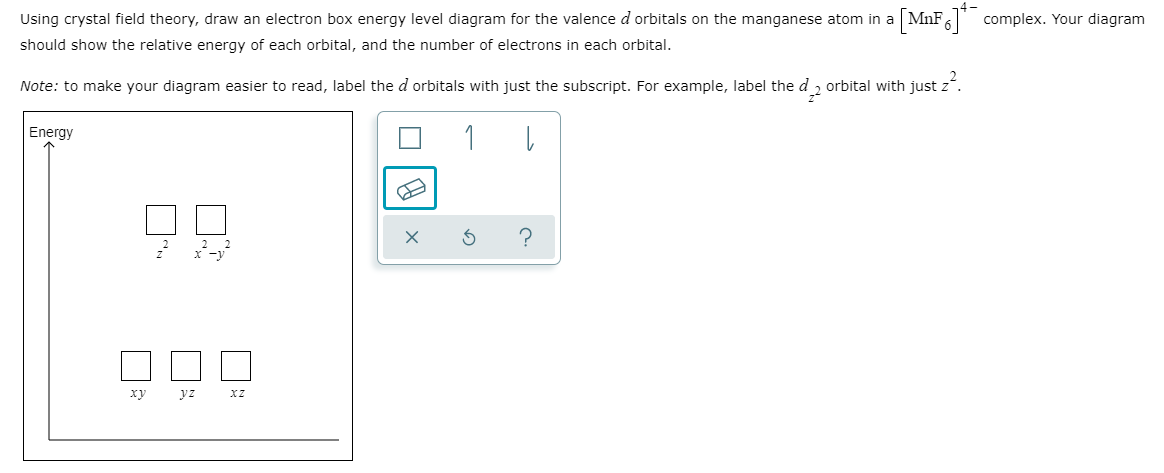
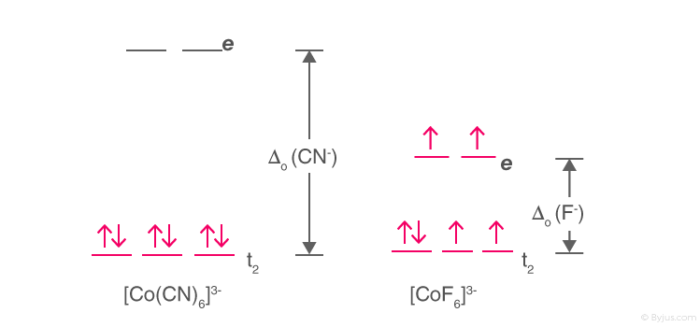
Using Crystal Field Theory Draw Energy Level Diagram Write Electronic Configuration Of The Central Metal Atom Ion And Determine The Magnetic Moment Value In The Following A Cof 6 3 Co H 2 O 6 2 Co Cn 6 3 B Fef 6 3













/Octahedral_crystal-field_splitting-589932a85f9b5874ee4e3368.png)






0 Response to "40 crystal field theory diagram"
Post a Comment