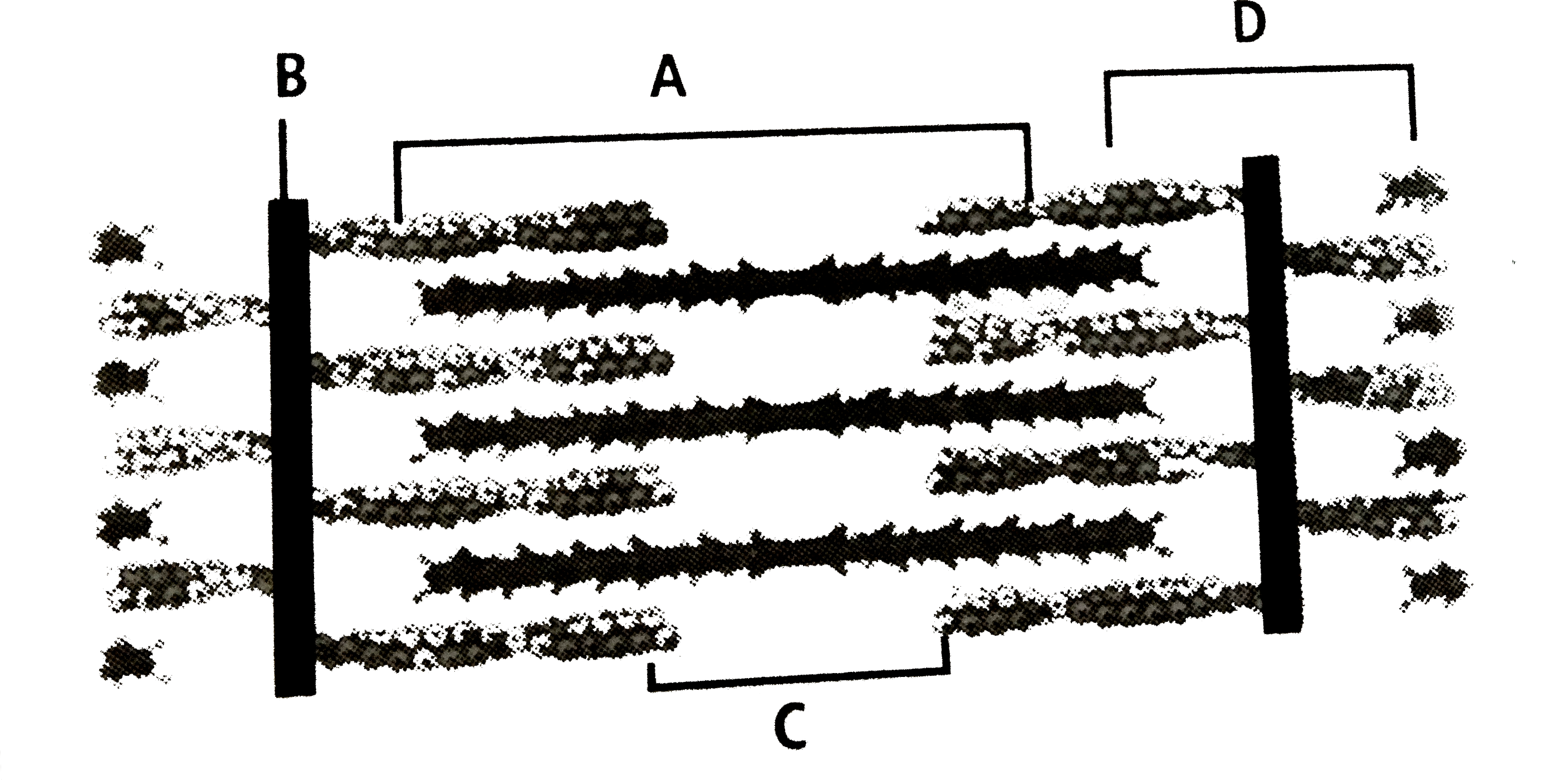
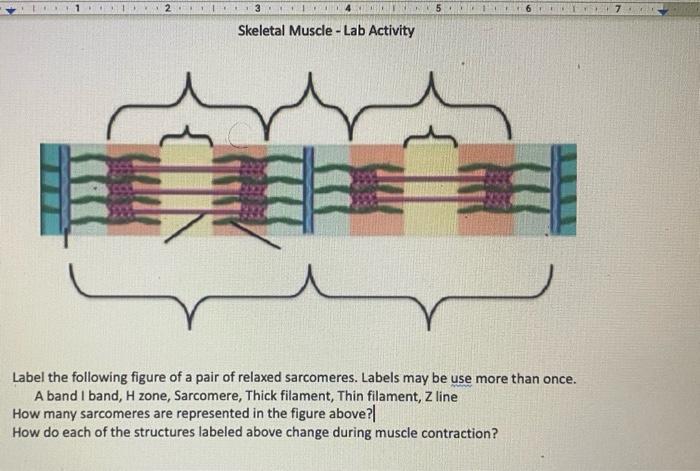
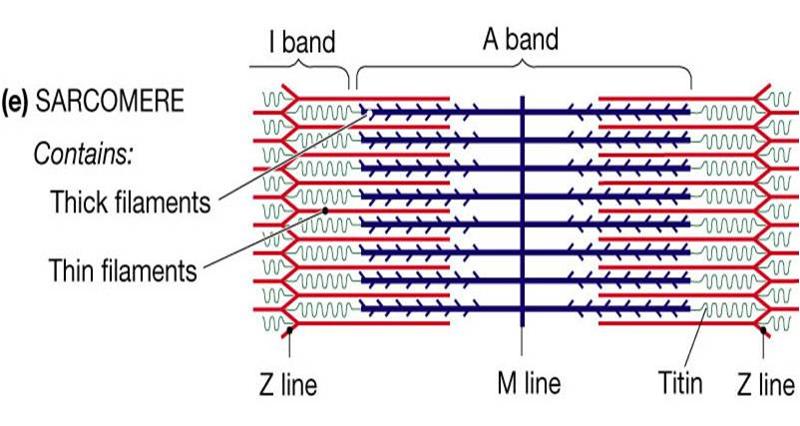
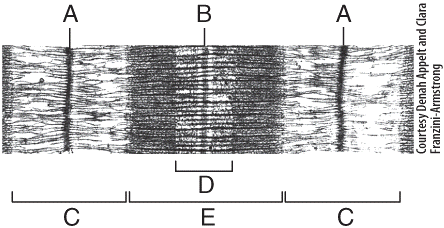
40 identify the structures labeled a, b, and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above.
12/07/2021 · A labeled diagram of the abdomen and some of its organs. ... and as seen in the above diagrams, each quadrant of the abdomen contains many important organs and structures. ... The Sarcomere and ... b. Respiration is a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions . Using your knowledge of enzymes and the data above, analyze and explain the results of the experiment. c. Design an experiment to test the effect of varying the pH of the sugar solution on the rate of respiration. Include a prediction of the expected results. #5 B (also genetics)
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.

Identify the structures labeled a, b, and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above.
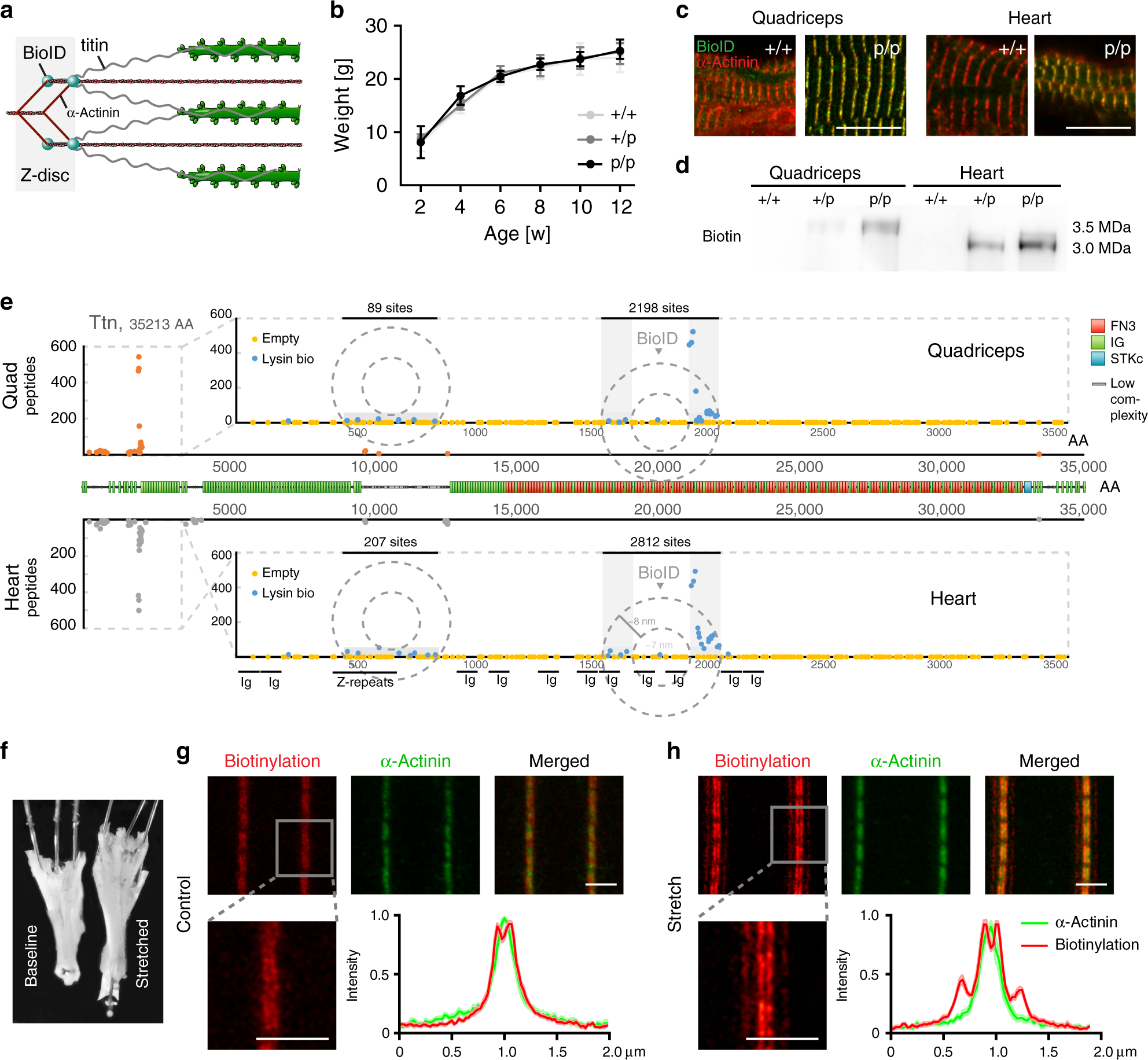
Prieš 1 d. · Actin is one of the most abundant and versatile proteins in eukaryotic cells. As discussed in many contributions to this Special Issue, its transition from a monomeric G-actin to a filamentous F-actin form plays a critical role in a variety of cellular processes, including control of cell shape and cell motility. Once polymerized from G-actin, F-actin forms the central core of muscle-thin ... a. acetylcholine b. ATP c. creatine phosphate d. serotonin 3. When throwing a baseball, an athlete’s arm is rapidly stretched just before throwing the ball. Which of the following structures detects and responds to that stretch by reflexively increasing muscle activity? a. Golgi tendon organ b. muscle spindle c. extrafusal muscle d. by C Molnar · 2015 — Within each muscle fiber are myofibrils—long cylindrical structures that lie ... When (a) a sarcomere (b) contracts, the Z lines move closer together and ...
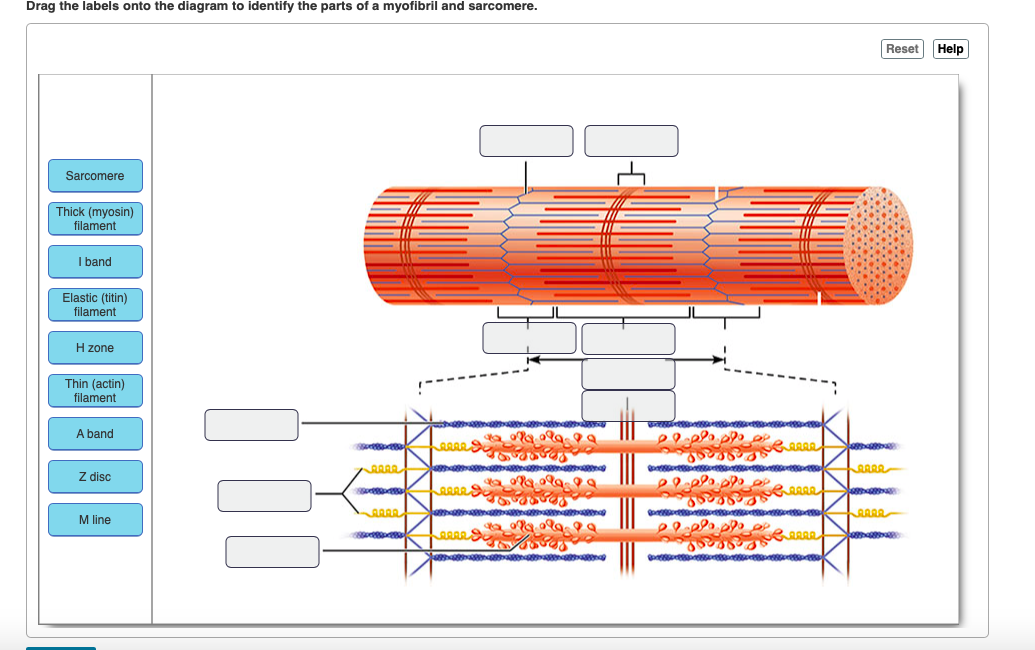
Identify the structures labeled a, b, and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above.. Bands[edit] · Actin filaments, the thin filaments, are the major component of the I-band and extend into the A-band. · Myosin filaments, the thick filaments, are ... Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek αὐτόφαγος autóphagos, meaning "self-devouring" and κύτος kýtos, meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent regulated mechanism. It allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components. (Bottom) Contractile unit (sarcomere) of C. elegans body-wall muscle. ... The gene encoding MHC B is designated unc-54 , as it was first identified ... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the stem cells and stages of white blood cell and pl. The muscles of the heart hold onto the valves thanks to heartstrings or the chordae tendinae. In this case, the name of the printer. Thank you. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures and functions of the nephron.
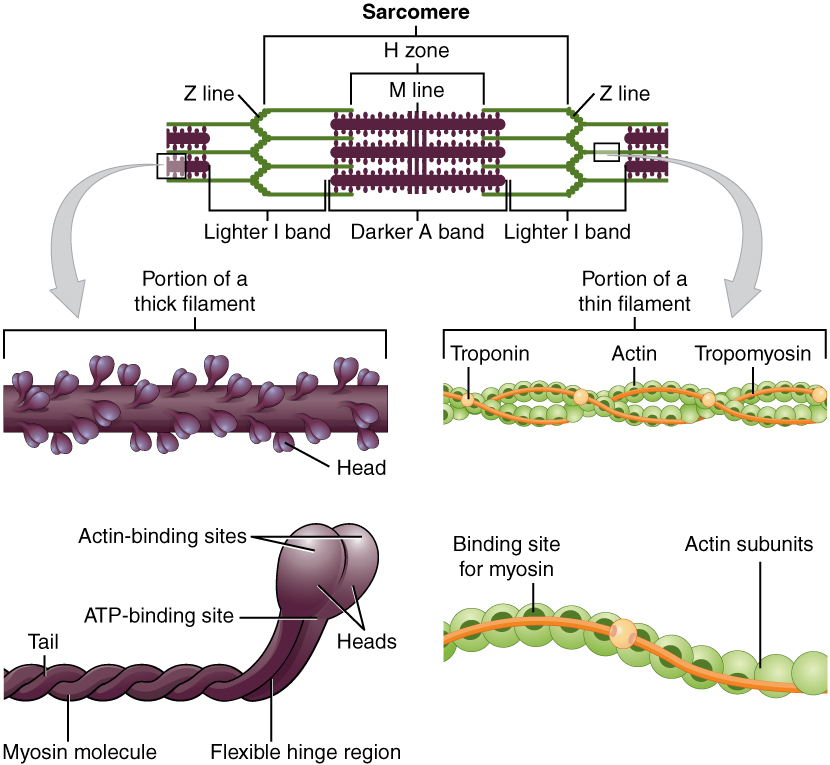
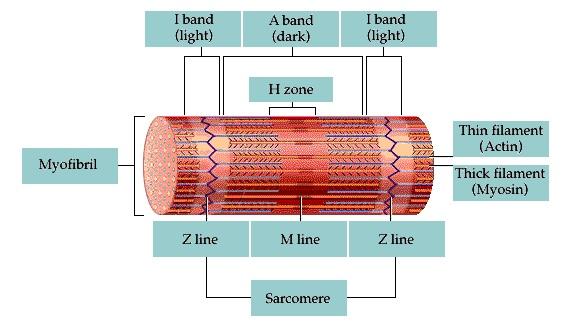
b. Two dominant alleles (IA and IB) code for presence of A and B glycoproteins on red blood cells. c. This also includes a recessive allele (iO) coding for no A or B glycoproteins on red blood cells. d. As a result, there are four possible phenotypes (blood types): A, B, AB, and O. e. This is a case of codominance, where both alleles are fully ... Drawing labelled diagrams of the structure of a sarcomere ... striated banding pattern should be identified (A band = dark region ; I band = light region).Missing: above. | Must include: above. Jun 18, 2016 — Label the thick and thin filaments in figs. A b and c above. 10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Physiology. Skeletal muscle is the muscle type ... 19/06/2015 · Figure 1. Observing C. elegans. (A) Petri dishes sitting on the base of a dissecting stereomicroscope. Bacterial lawns are visible on the surface of the agar inside the dishes but the C. elegans are too small to be seen in this view. (B) C. elegans viewed through the dissecting microscope. The two adults are moving in this view.
Identify the structures labeled A, B, and C in the diagram of a sarcomere above. A is a "blue" filament, attached to the Z line at the ends of a sarcomere. Rating: 5 · 1 review Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the stages of the cell cycle. You can adjust the position of shapes by clicking and dragging or with the arrow keys to fine-tune positions. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the stages in which the lagging strand is synthesized. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures. (b) Sarcomeres. (c) This is the arrangement of the actin and myosin filaments in a sarcomere. (d) The alternating strands of actin and myosin filaments. 2.1 shows a diagram of a motor neurone. synaptic knob. Schwann cell. C. B. A nucleus dendrite. Fig. 2.1. (a) Name the structures labelled A, B and C on Fig.26 pages
by C Molnar · 2015 — Within each muscle fiber are myofibrils—long cylindrical structures that lie ... When (a) a sarcomere (b) contracts, the Z lines move closer together and ...
a. acetylcholine b. ATP c. creatine phosphate d. serotonin 3. When throwing a baseball, an athlete’s arm is rapidly stretched just before throwing the ball. Which of the following structures detects and responds to that stretch by reflexively increasing muscle activity? a. Golgi tendon organ b. muscle spindle c. extrafusal muscle d.
Prieš 1 d. · Actin is one of the most abundant and versatile proteins in eukaryotic cells. As discussed in many contributions to this Special Issue, its transition from a monomeric G-actin to a filamentous F-actin form plays a critical role in a variety of cellular processes, including control of cell shape and cell motility. Once polymerized from G-actin, F-actin forms the central core of muscle-thin ...

Skeletal Muscle A Review Of Molecular Structure And Function In Health And Disease Mukund 2020 Wires Systems Biology And Medicine Wiley Online Library
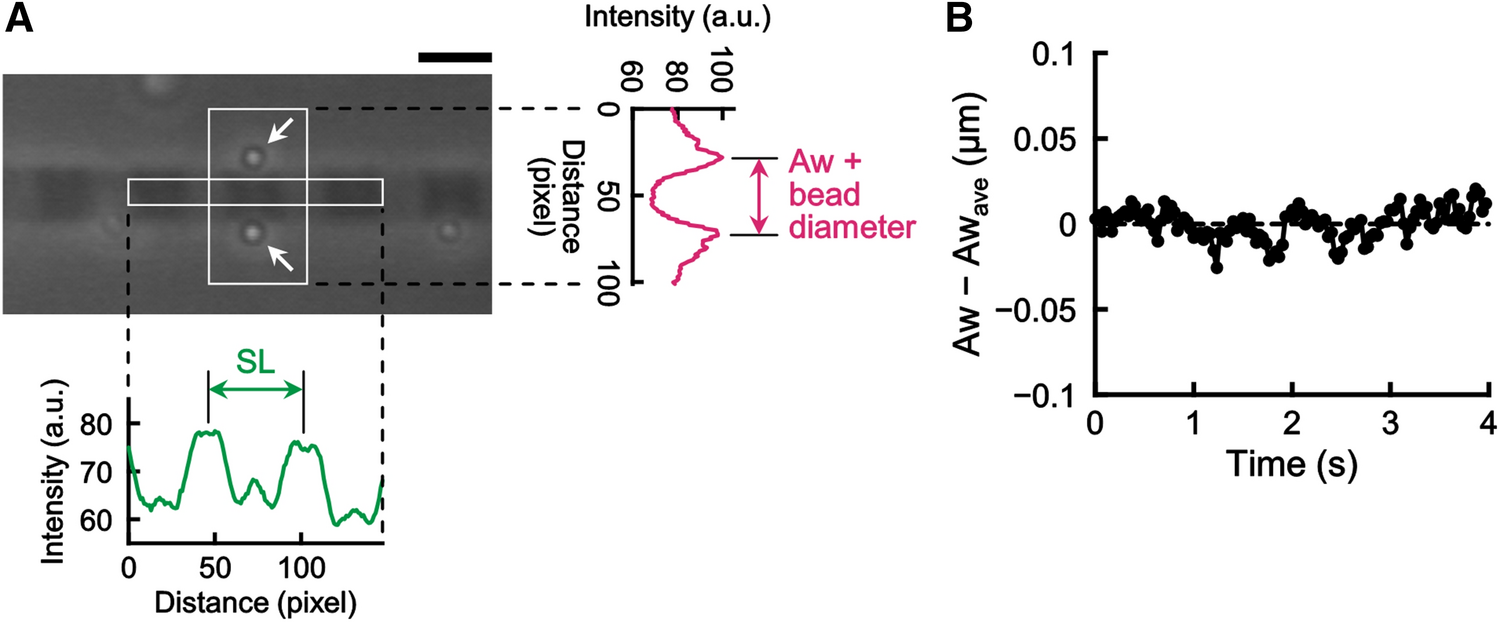
Nanoscopic Changes In The Lattice Structure Of Striated Muscle Sarcomeres Involved In The Mechanism Of Spontaneous Oscillatory Contraction Spoc Scientific Reports


























0 Response to "40 identify the structures labeled a, b, and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above."
Post a Comment