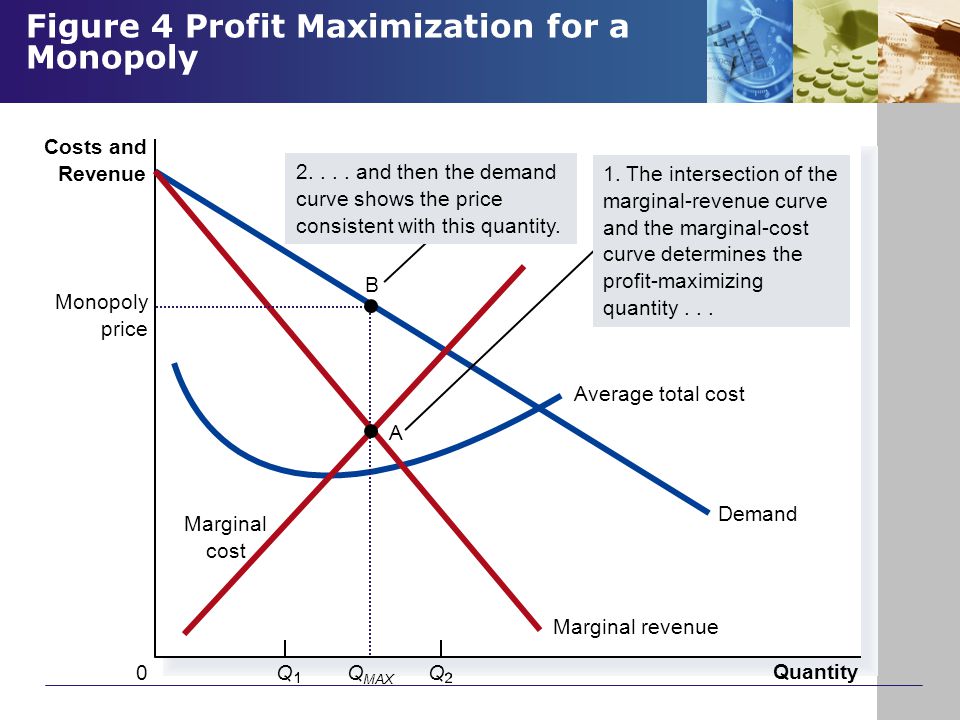
41 4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram
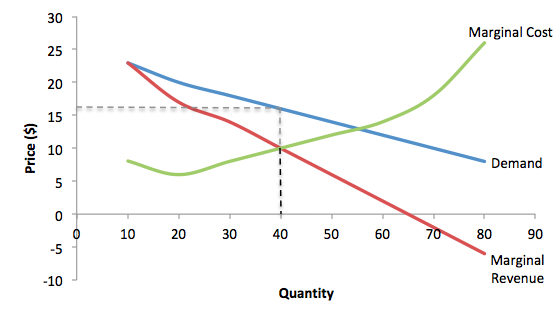
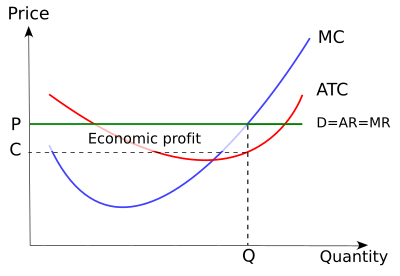
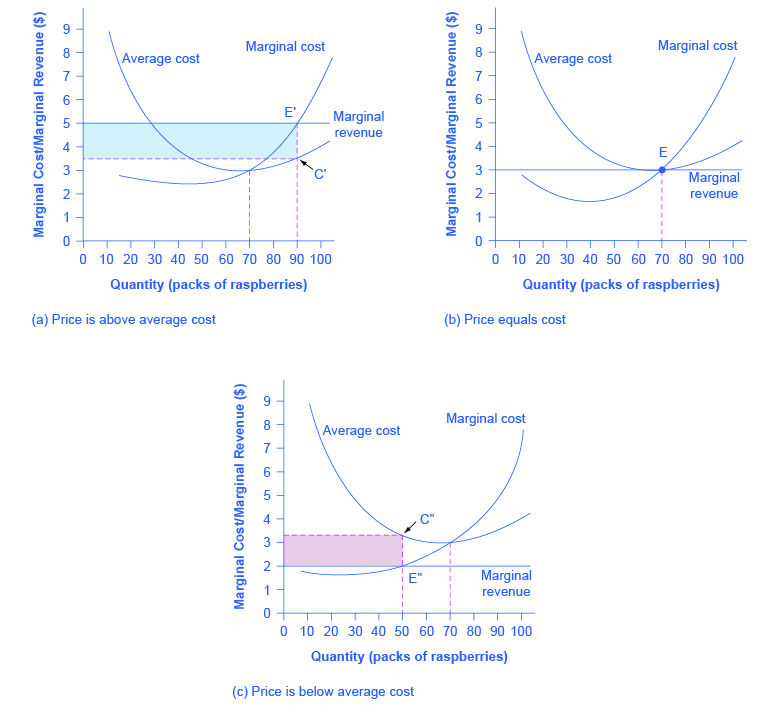
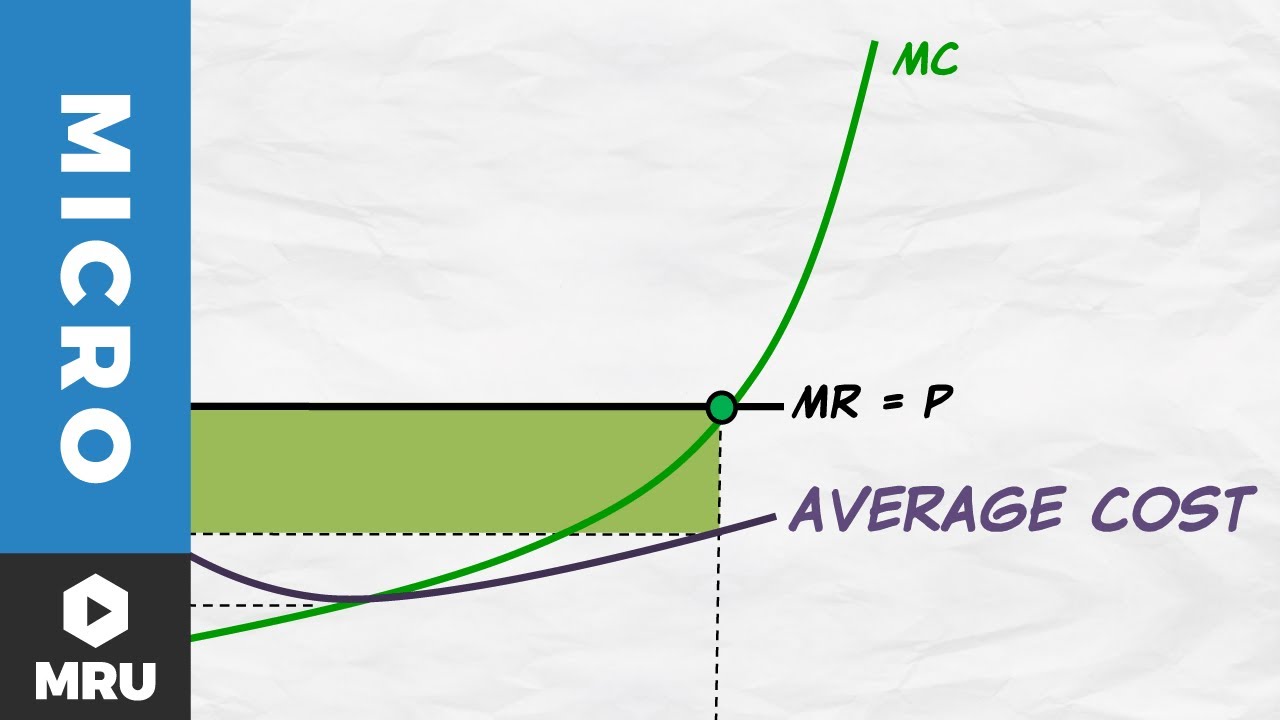
Profit (producer surplus) is the area below the equilibrium price and above the supply curve. The supply curve is the same thing as the Marginal Cost curve for the firm. Figure 5.2 Supply and Demand diagram showing profit (producer surplus) The rule for a profit-maximizing perfectly competitive firm is to produce the level of output where Price = MR = MC, so the raspberry farmer will produce a ...
#Introduction As I write this, I am living in Canada in the last few days before our 2019 federal election (this post happened to come out on election night), and while since the start of the campaign there have been twists and turns that any election has, the main issue has been climate change. Being in the rural area that I am in, the Liberal Trudeau government's carbon taxation program is very unpopular. Even among progressive young people it's viewed as a half-measure compared to the option...

4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram
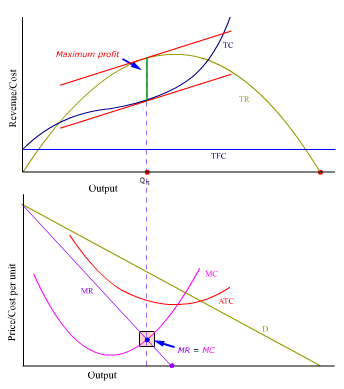
In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that lead to the highest profit. Neoclassical economics, currently the mainstream approach to microeconomics, usually models the firm as maximizing profit. An example diagram of Profit Maximisation: Chapter 9: Profit Maximization Profit Maximization The basic assumption here is that firms are profit maximizing. Profit is defined as: Profit = Revenue – Costs Π(q) = R(q) – C(q) To maximize profits, take the derivative of the profit function with respect to q and set this equal to zero. 1 answer4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for frying. Answer. Find step-by-step answers from expert tutors to questions asked ...
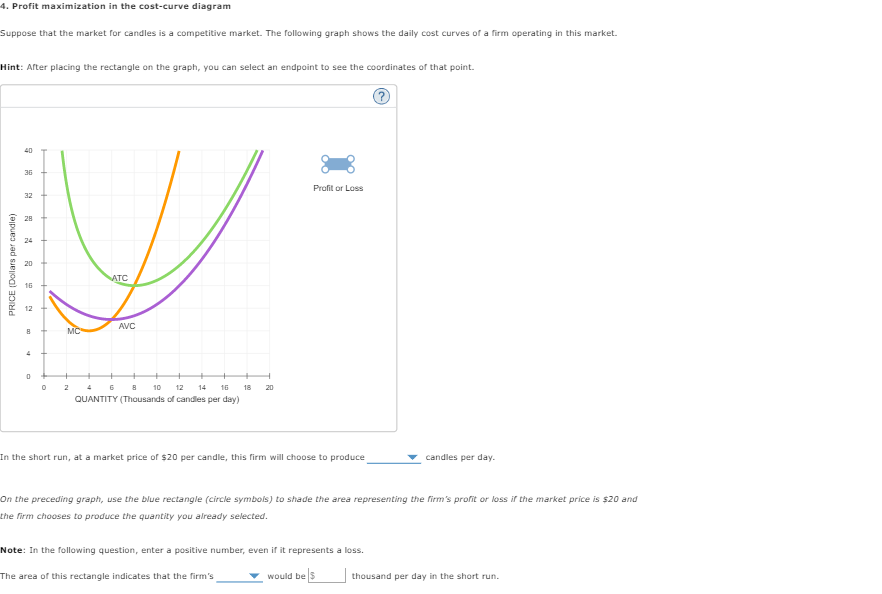
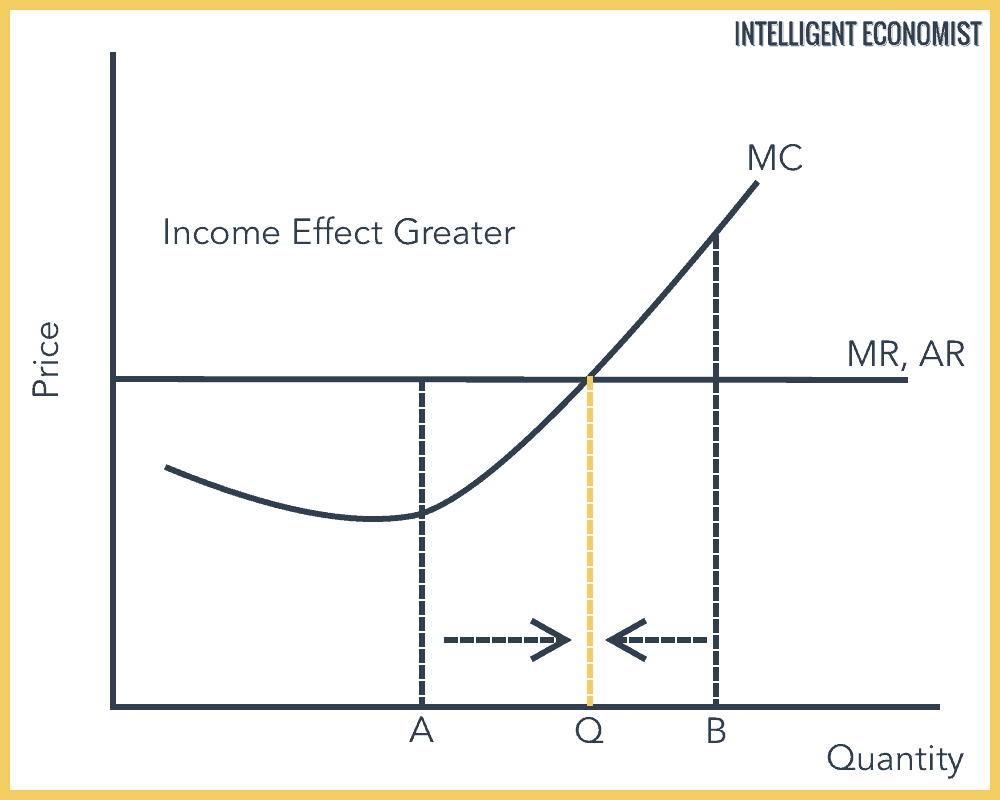
4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a ... Suppose that the market for wind chimes is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After ...2 answers · Top answer: As Figure 1 shows, an upward sloping marginal cost (MC) curve is the firm's supply curve. Therefore, ... We call the point where the marginal cost curve crosses the average cost curve, at the minimum of the average cost curve, the “zero profit point.” If the market price that a perfectly competitive firm faces is below average variable cost at the profit-maximizing quantity of output, then the firm should shut down operations immediately. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves ...
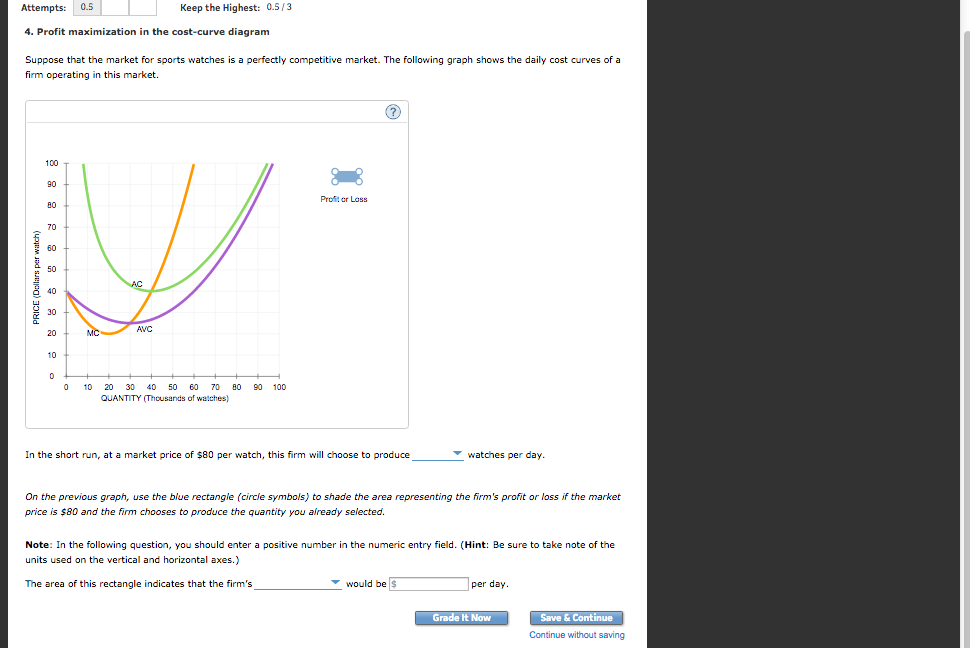
Answer to: Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for sports watches is a competitive market. The following graph...1 answer · Top answer: In the short run, at a market price of $80 per watch, this firm will choose to produce 52 watches per day. As noted above, the firm will maximize... 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. Suppose that the market for dress shirts is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. Profit Maximization Questions and Answers. Get help with your Profit maximization homework. Access the answers to hundreds of Profit maximization questions that are explained in a way that's easy ... Maximize profit calculator
1 answer4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for frying. Answer. Find step-by-step answers from expert tutors to questions asked ... Chapter 9: Profit Maximization Profit Maximization The basic assumption here is that firms are profit maximizing. Profit is defined as: Profit = Revenue – Costs Π(q) = R(q) – C(q) To maximize profits, take the derivative of the profit function with respect to q and set this equal to zero. In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that lead to the highest profit. Neoclassical economics, currently the mainstream approach to microeconomics, usually models the firm as maximizing profit. An example diagram of Profit Maximisation:
Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Aa Aa El Consider A Perfectly Competitive Market For Teddy Bears The Following Graph Shows The Daily Course Hero
3 Prot Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Suppose That The Market For Frying Pans Is A Competitive Market The Following Graph Shows The Daily Course Hero

Profit Maximization Using Total Cost And Total Revenue Curves 2 Docx 3 Profit Maximization Using Total Cost And Total Revenue Curves Suppose Dina Runs Course Hero

4 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Aa Aa Consider A Perfectly Competitive Market For Teddy Homeworklib

4 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagramsuppose That The Market For Black Sweaters Is A Competitive Homeworklib

Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Suppose That The Market For Sports Watches Is A Competitive Market The Following Graph Shows The Daily Cost Curves Of A Firm Operating In This Market

4 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Suppose That The Market For Polo Shirts Is A Homeworklib

Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Suppose That The Market For Wind Chimes Is A Competitive Market The Following Graph Shows The Daily Course Hero
Profit Maximization And Increasing Returns To Scale Marketplace Economics By Mohan Krishnamurthy Ph D Medium

Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagramsuppose That The Market For Candles Is A Competitive Market The Following Graph Shows The Daily Cost Course Hero





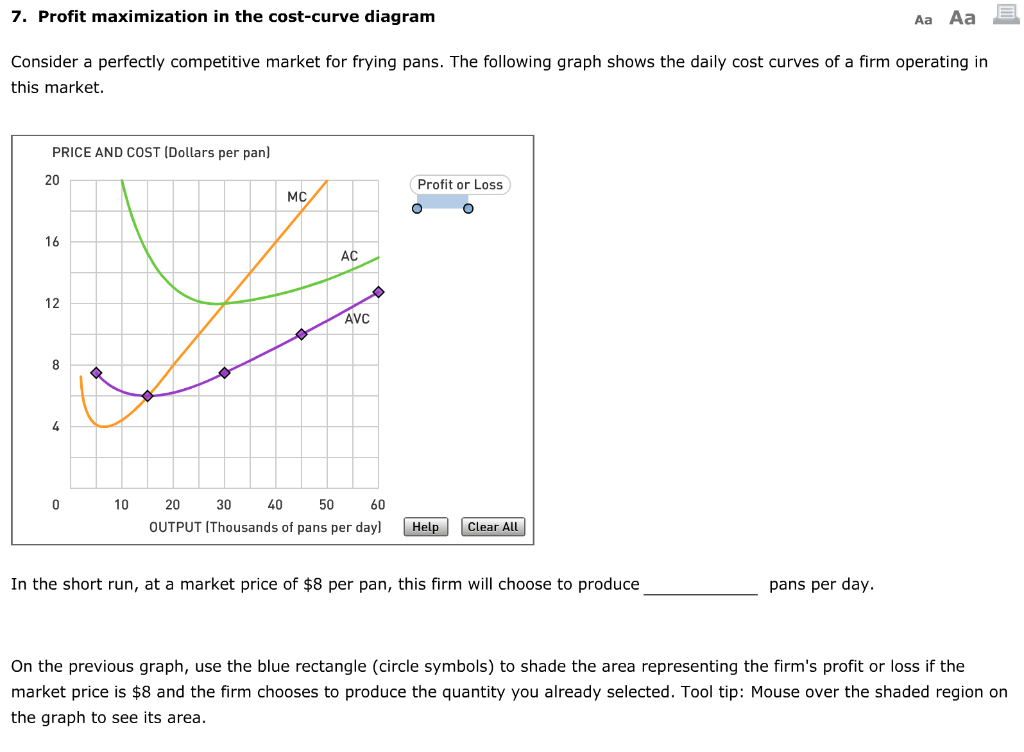
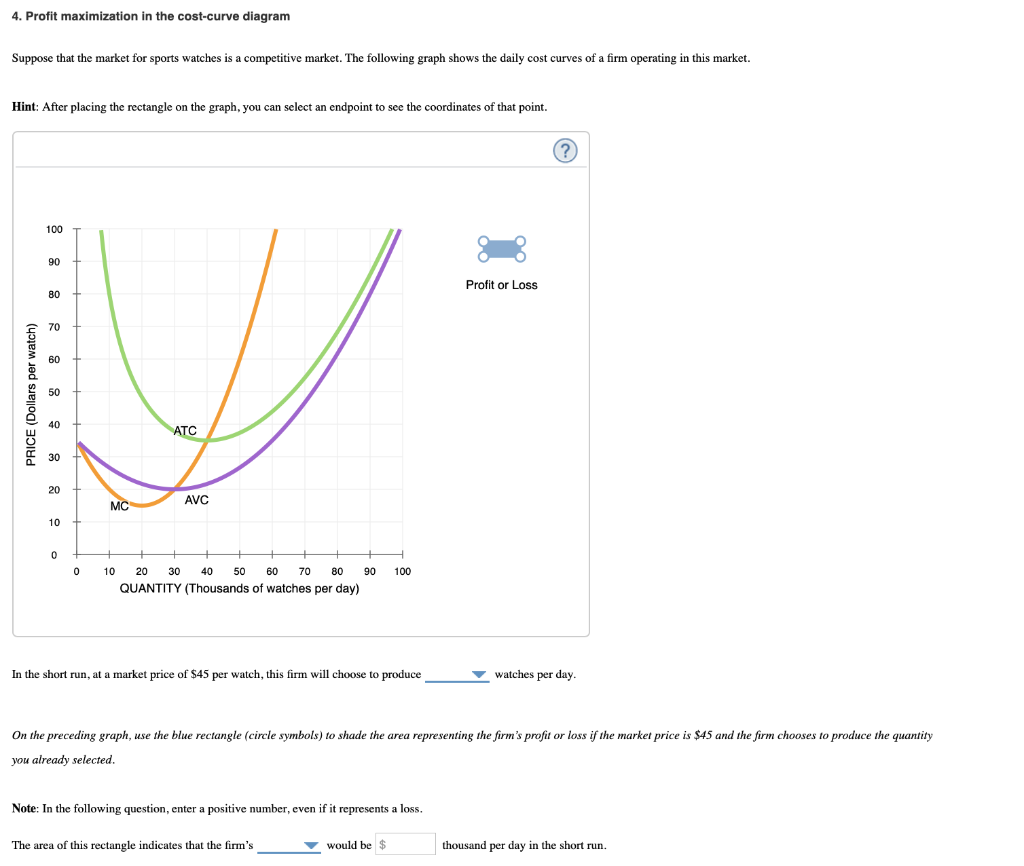

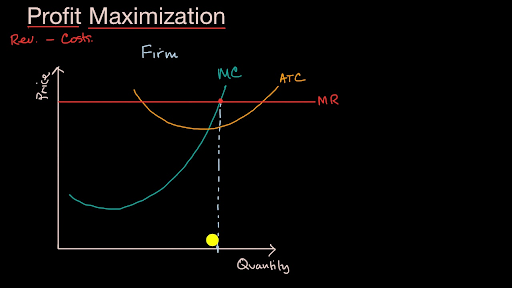

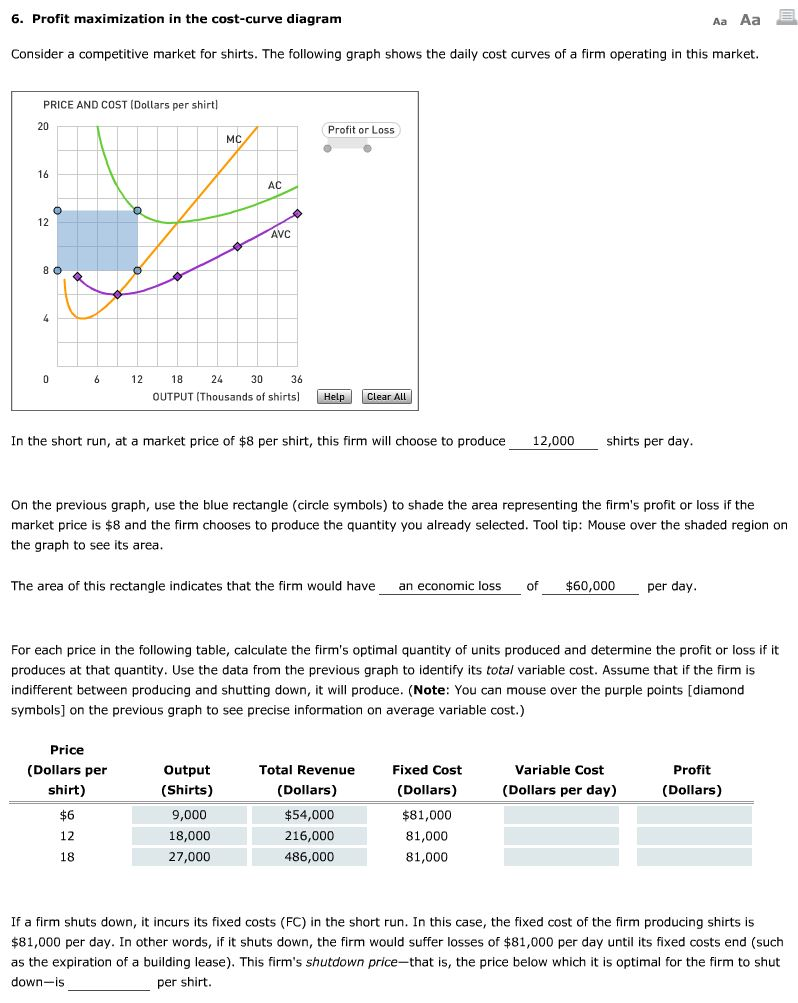








0 Response to "41 4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram"
Post a Comment