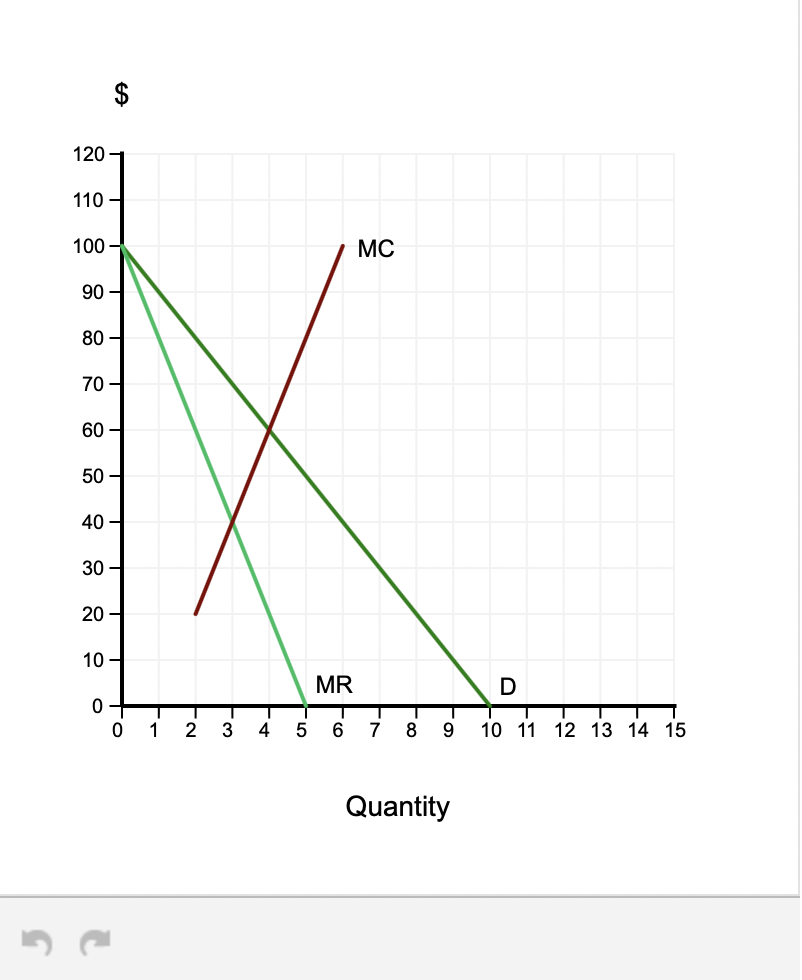
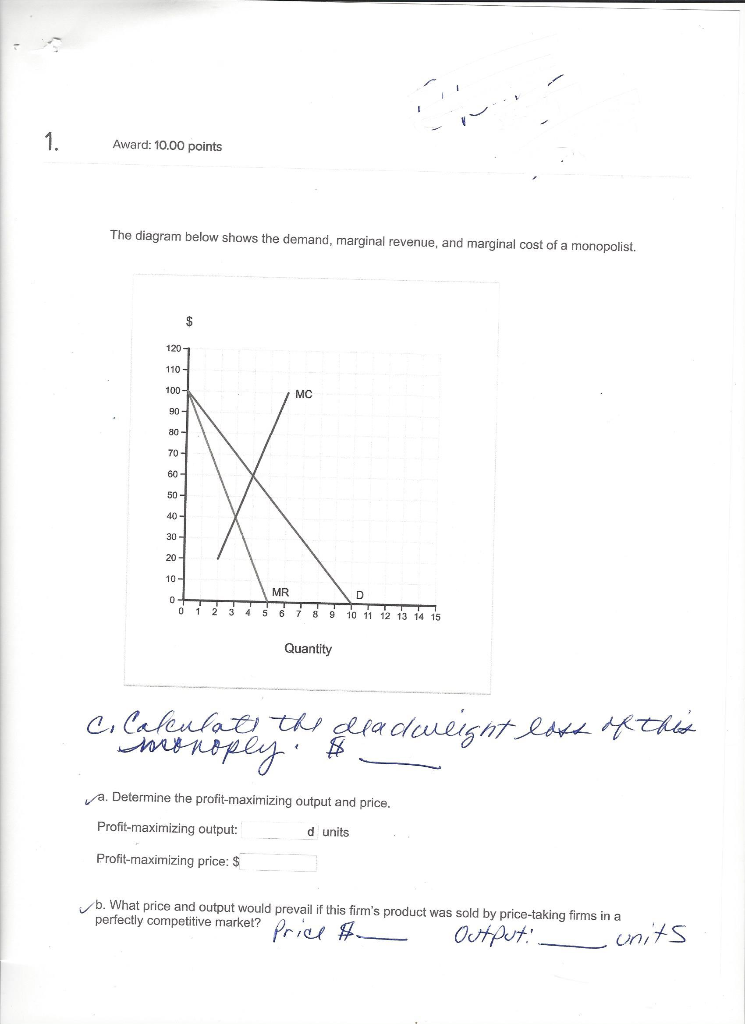
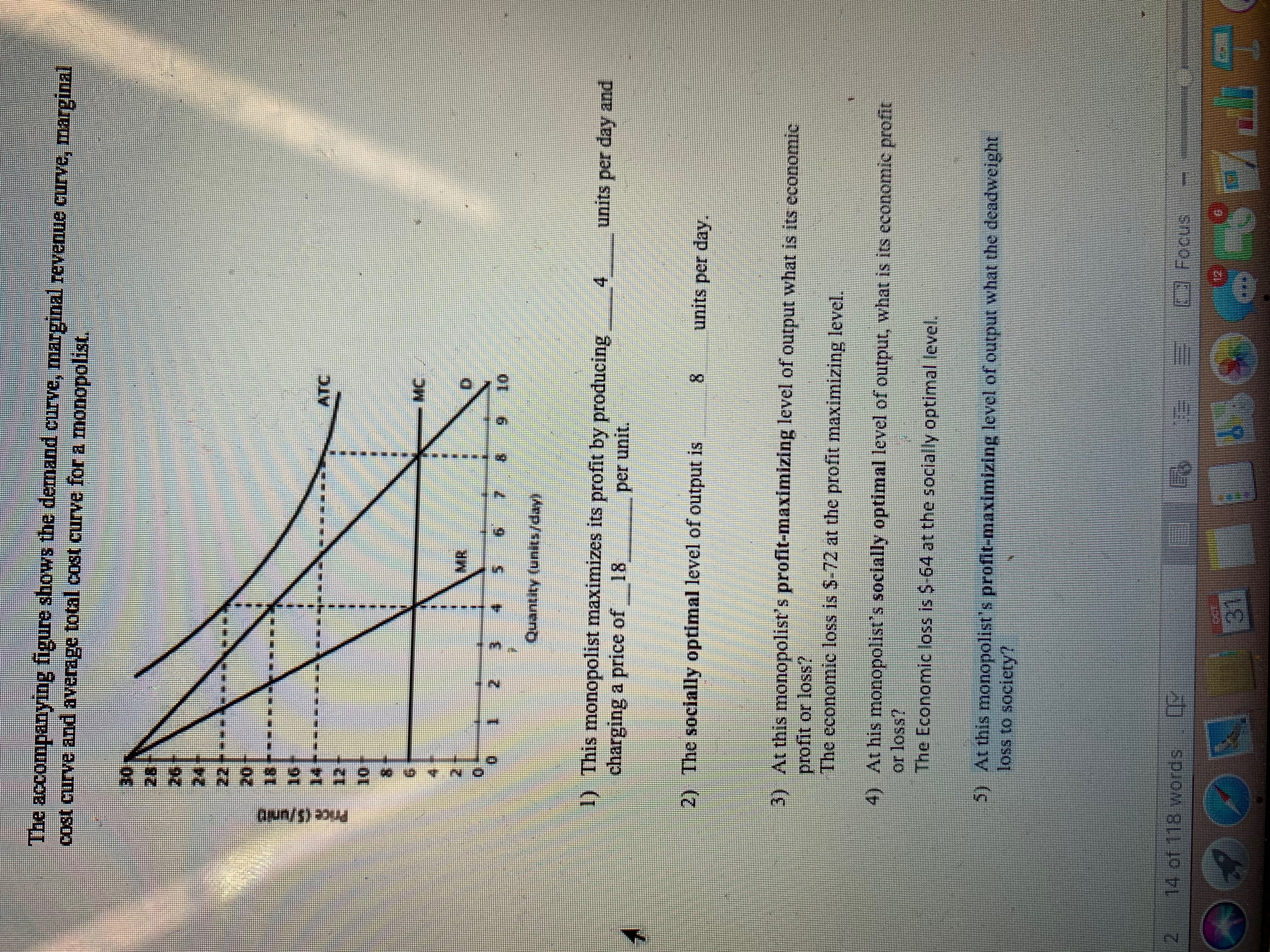
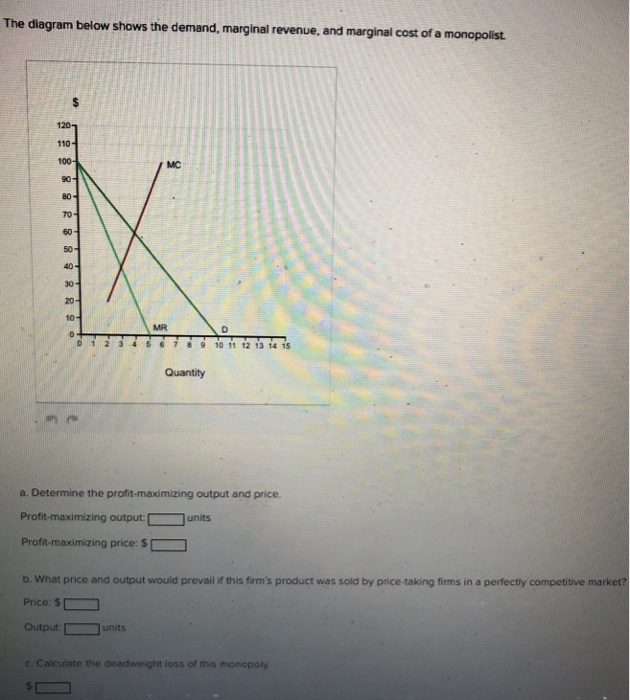
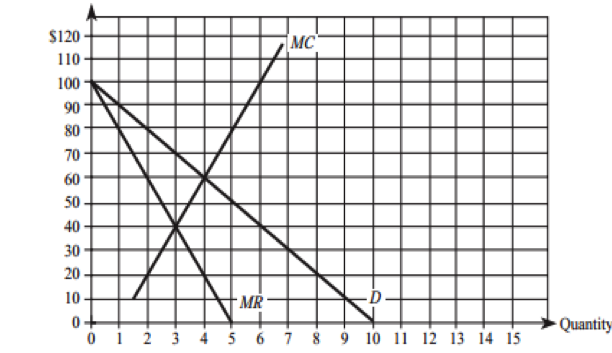
40 the diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist.
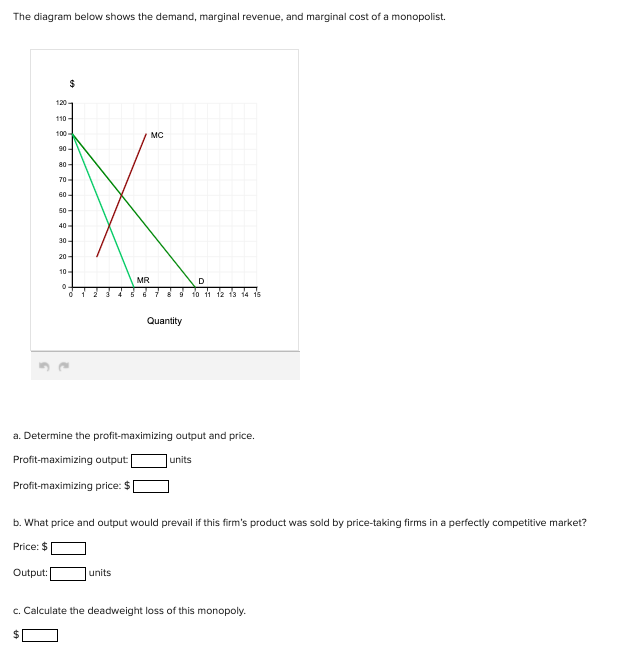
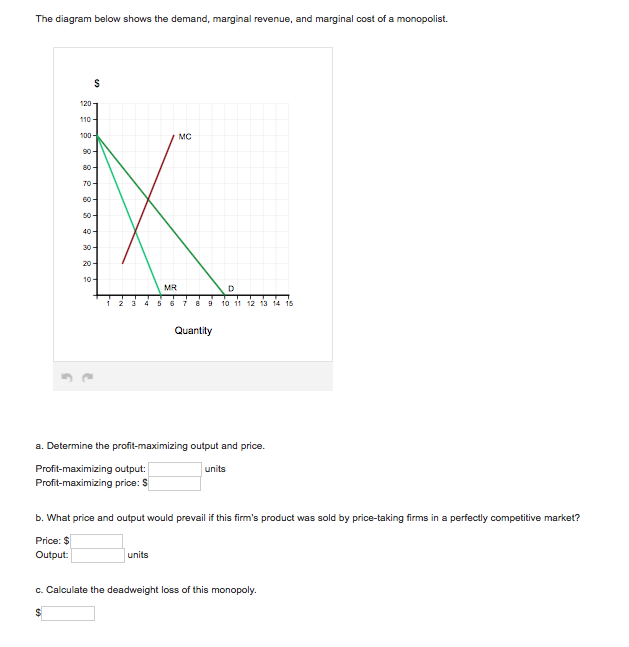
The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist.(PLEASE SEE ATTACHED) a. Determine the profit-maximizing output and price. b. What price and output would prevail if this firm's product was sold by price-taking firms in a perfectly competitive market? c. Calculate the deadweight loss of this monopoly. "We Offer Paper […]
The figure below shows the market for one hour of economics tutoring at your college. Imagine that the market for economics tutoring could be perfectly competitive, controlled by a monopolist who charges a single price or a monopolist who charges each customer a different price. Use the information in the diagram to answer the questions below.
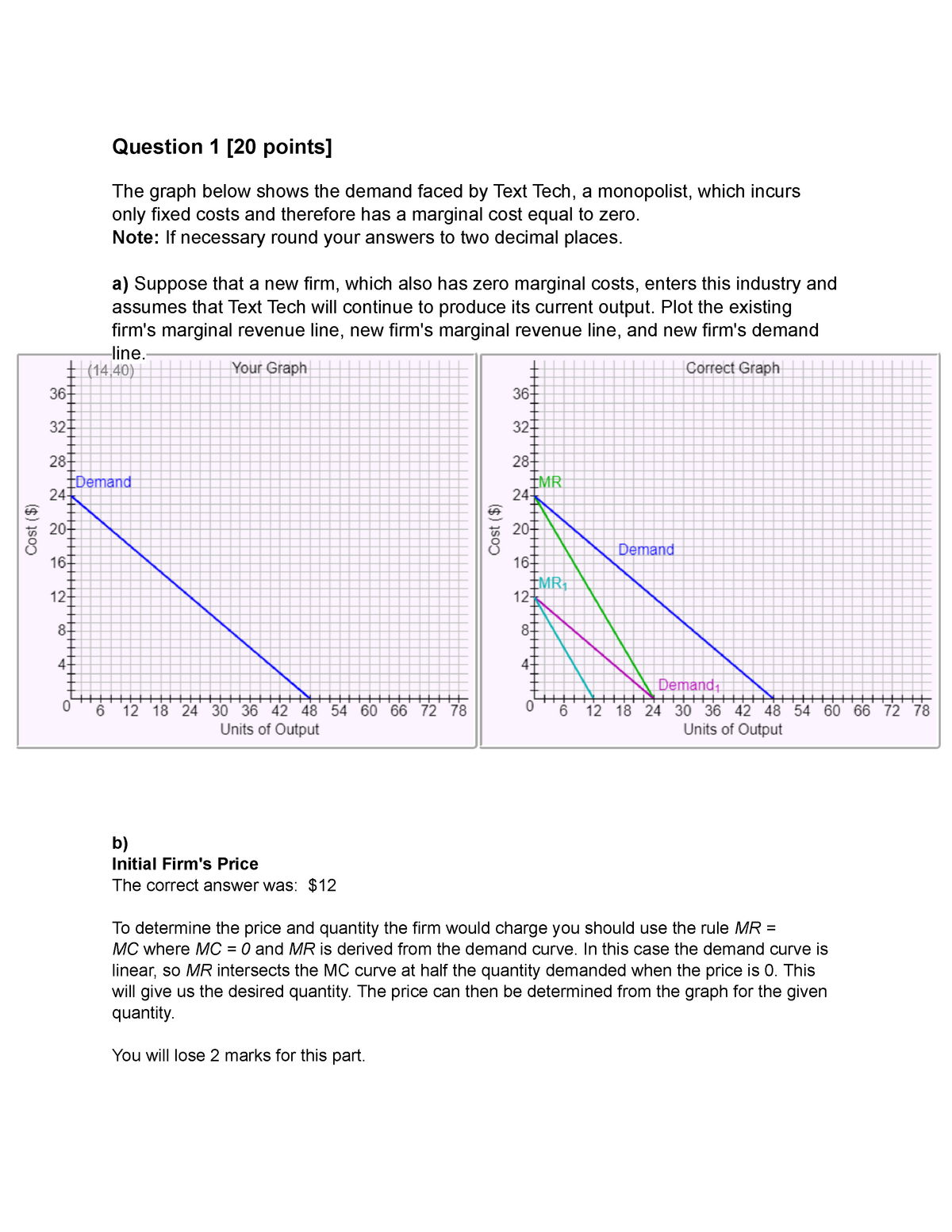
A monopolist faces the demand curve P = 11 - Q, where P is measured in dollars per unit and Q in thousands of units. The monopolist has a constant average cost of $6 per unit. a. Draw the average and marginal revenue curves, and the average arid marginal cost curves.
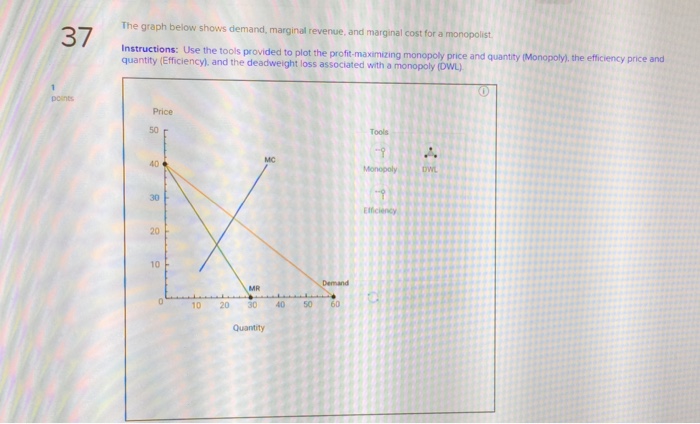
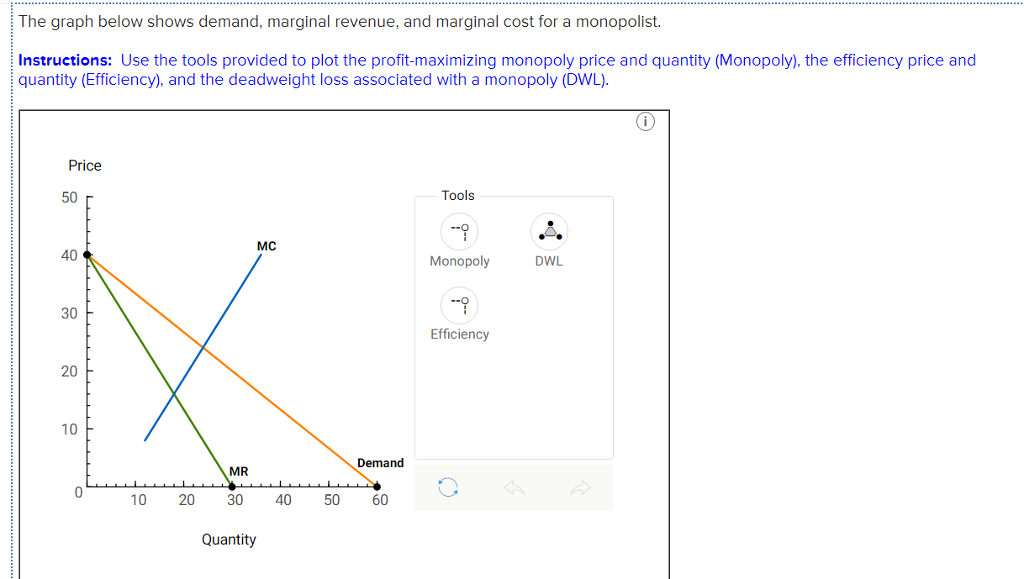
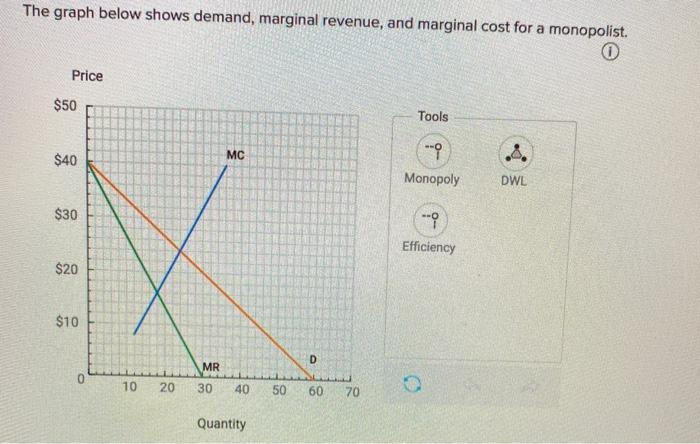
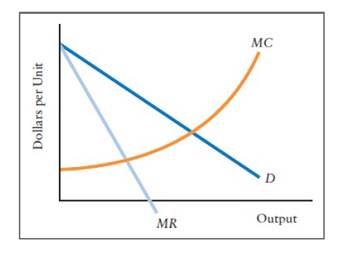
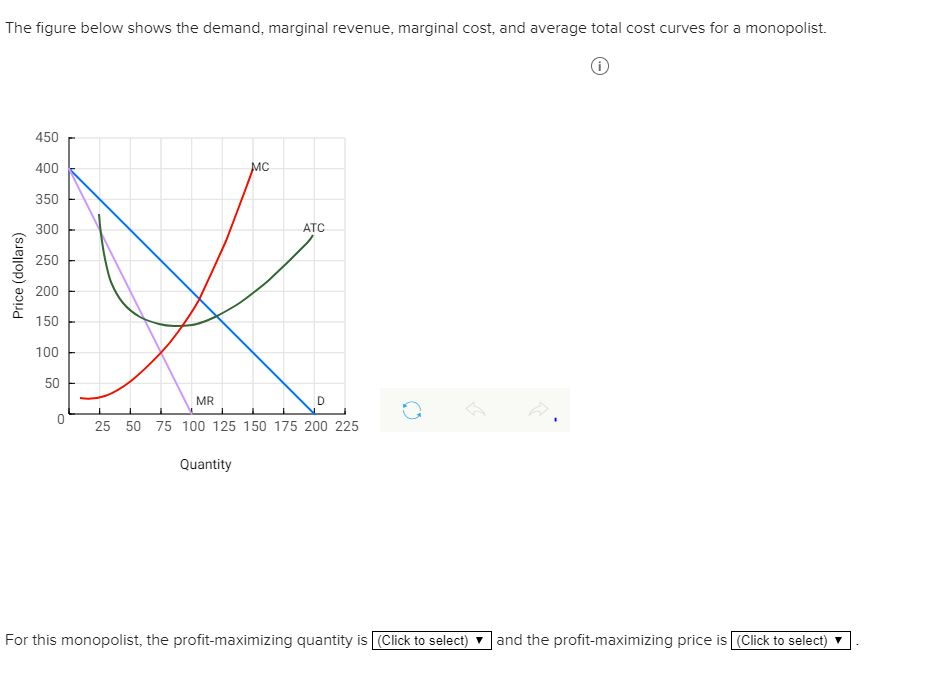
The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist.
The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist. (PLEASE SEE ATTACHED) a. Determine the profit-maximizing output and price. b. What price and output would prevail if this firm's product was sold by price-taking firms in a perfectly competitive market?
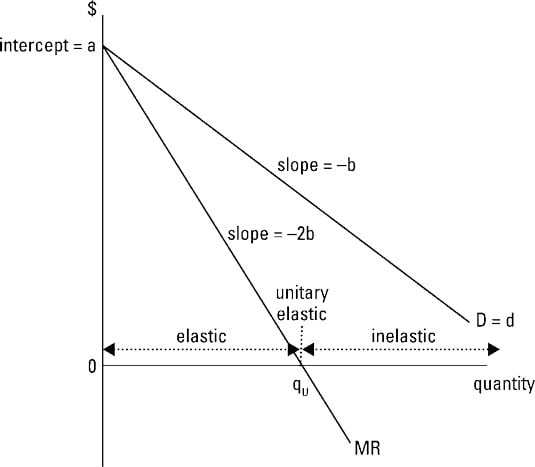
Question 1: Carefully explain why we believe that a linear demand curve will always be associated with a marginal revenue curve that has twice the slope of the demand curve in question.. A true supply curve shows the relationship between price and quantity supplied. For the monopolist, the key issue to consider is that the monopolist does not make quantity decisions based on price, but rather ...
The following equations describe the monopolist's demand, marginal revenue, total costs and marginal costs: Demand: P = 10 - Q. Marginal revenue: MR = 10 - 2Q. Total costs: TC = 3 + Q + 0.5Q2. Marginal costs: MC = 1 + Q. a) How many units of the output does the monopolist produce? b) At what price are they sold? c) What is the monopolist ...
The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist..
Question. For a firm in perfect competition, a diagram shows quantity on the horizontal axis and both the firm's marginal cost (MC) and its marginal revenue (MR) on the vertical axis. The firm's profit-maximizing quantity occurs at the point where the A) MC curve intersects the MR curve from above, going from left to right.
The reason this statement is true is due to: (a) the law of demand (b) the law of diminishing marginal utility. The Demand curve, Average Total Cost curve, Marginal Cost Curve, and Marginal Revenue Curve for this firm are shown in the picture below. The government decides to regulate this market using marginal cost pricing.
The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist. a. Determine the profit-maximizing output and price. b. What price and output would prevail if this firm's product was sold by price-taking firms in a perfectly competitive market? c. Calculate the deadweight loss of this monopoly.
Question 1: Carefully explain why we believe that a linear demand curve will always be associated with a marginal revenue curve that has twice the slope of the demand curve in question.. A true supply curve shows the relationship between price and quantity supplied. For the monopolist, the key issue to consider is that the monopolist does not make quantity decisions based on price, but rather ...
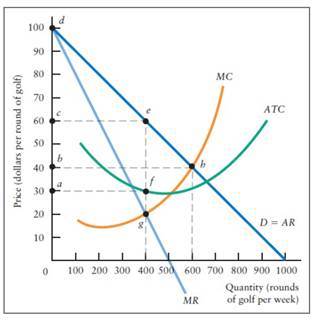
Demand, marginal revenue and cost curves. Just from $10/Page. Order Essay. Note: Make sure your name and student number are included on your assignment. Question 1. The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue and cost curves for Jingyi who owns the only golf course in her community. a.
If a perfectly competitive firm sells its product at the market price of $14 per unit, _____. its average revenue is $14 and its marginal revenue is also $14. Refer to Exhibit 8.4, which shows the demand and the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm. The firm will earn zero economic profit ____. at a price of P2.
Relationship between tax revenue and dead weight loss in a monopoly - Deadweight loss Weight loss Too high a tax rate would then suspend some transactions that could have continued, and the government itself would have become a victim.
The diagram shows the demand curve for kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity, the company's marginal revenue (MR) curve, its marginal cost (MC) curve, and its average total cost (ATC) curve. The government wants to regulate the monopolist by imposing a price ceiling. Diagram 1. a. In diagram 2., the government does not regulate this monopolist.
M6 If the demand curve is downward sloping, the monopolist's marginal revenue curve is. Above the demand curve. Always above its average cost curve. The same as the demand curve. Always below the marginal cost curve. Below the demand curve. M7 A monopolist maximizes profits by producing at a price and output where. P = MC. P = AC. MR = MC.
(d)Plot 4 curves, the Demand Curve, the Marginal Revenue Curve, the Average unit cost Curve, and the Marginal Cost Curve. Fully label your diagram including the three prices in (a), (b), (c) above. (Study page 298), Figure 11- 10). 7 Marks Optional Team Assignment No. 2A: 70 Marks - 13%, Due December 12, 2021, 11:59 pm Page 11 of 11
Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: Answer cannot be determined from the information given. will be ae per unit sold. will be bc per unit sold. will be ac per unit sold. 2.667 points Question 2 A profit-maximizing monopolist will set its price: Answer as far above ATC as possible. along the elastic portion of.
Question 1. The diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue and cost curves for Jingyi who owns the only golf course in her community. a. If Jingyi is a single-price monopolist, what is Jingyi's the profit maximizing quantity and price? [2 marks] b. What is the average total cost at the profit maximizing level of output? [2 marks] c.
The diagram shows the demand curve for kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity, the company's marginal revenue (MR) curve, its marginal cost (MC) curve, and its average total cost (ATC) curve. The government wants to regulate the monopolist by imposing a price ceiling. Diagram 1. a. In diagram 2., the government does not regulate this monopolist.










![Solved] The diagram below shows the demand curve, marginal ...](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.question.images/image/images9/702-B-E-D-S(1373).png)


0 Response to "40 the diagram below shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist."
Post a Comment