40 plant cell cytoskeleton diagram
Plant Cytoskeleton, Crosslinking Factor. 1. Introduction. The cytoskeleton is a three-dimensional reticular structure The structural diagram of microtubules is shown in Figure 1. 16 in transgenic plant cells is accelerated the free assembly of MF and MT and the change of cytoskeleton dynamics...
4. Which cell lack a cytoskeleton? A. All types of cells including animal cells, plant cells, unicellular, prokaryotes and eukaryotes contain cytoskeleton. No cell lacks a cytoskeleton. 5. Which protein makes microfilaments? A. Microfilamntes are small fibres made up of actin protein.
of a cell. However, in plants the cytoskeleton is probably. more analogous to a scaffold, being directly involved in the. along with. a. schematic diagram empha-. sizing. the. the Plant Cell Cytoskeleton. 3. reorientation of microtubules, but not actin microfilaments
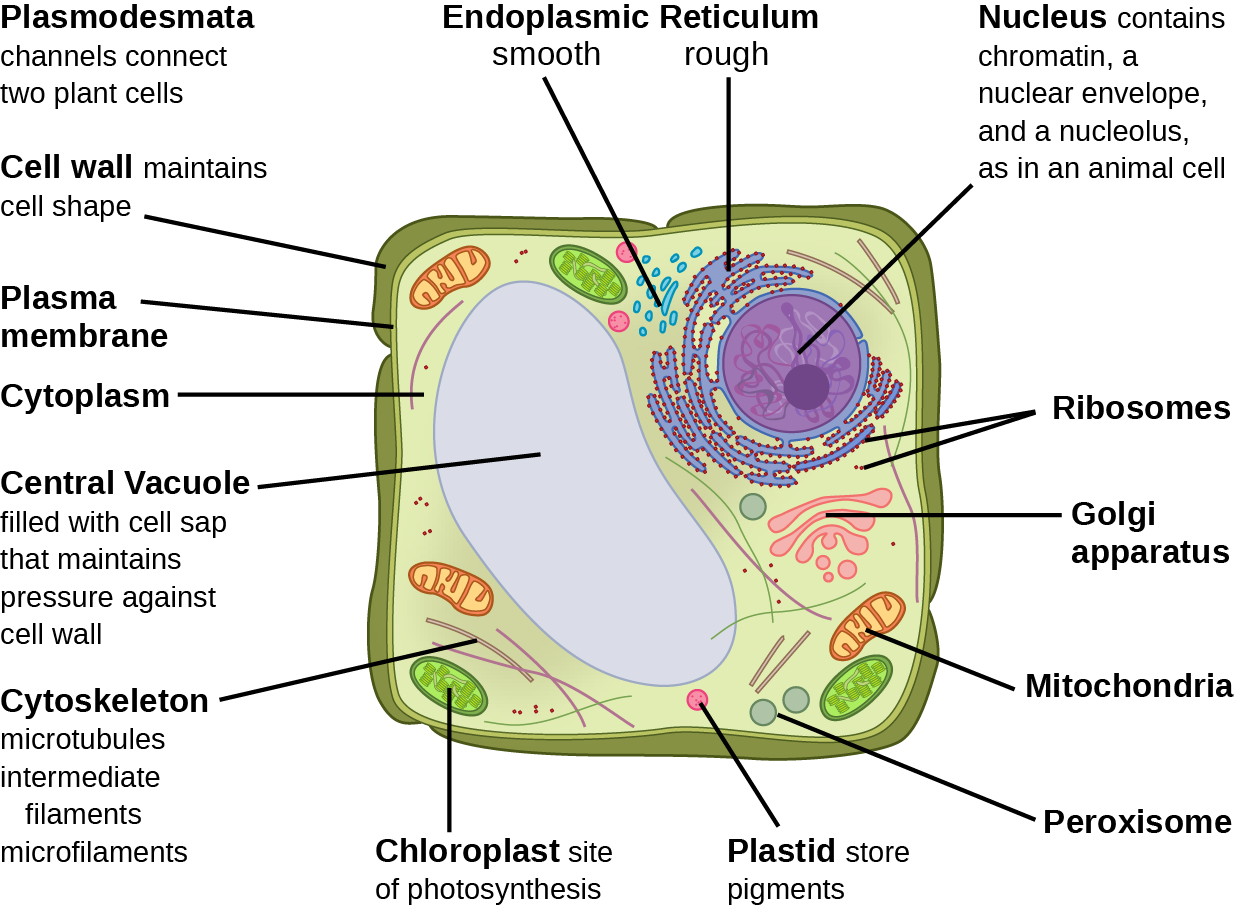
Plant cell cytoskeleton diagram
Cytoskeleton, a system of filaments or fibers that is present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton organizes other constituents of the cell, maintains the cell's shape, and is responsible for the locomotion of the cell itself and the movement of the various organelles within it.
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including bacteria and archaea.
D. In plant cells, MTs play similar role; affect cell shape indirectly by influencing cell wall formation; during interphase, most of plant cell's MTs found just Cytoskeleton MT origin in cultured animal cell is best studied by depolymerizing MTs with cold temperature or chemicals (NO, CO) & then following...
Plant cell cytoskeleton diagram.
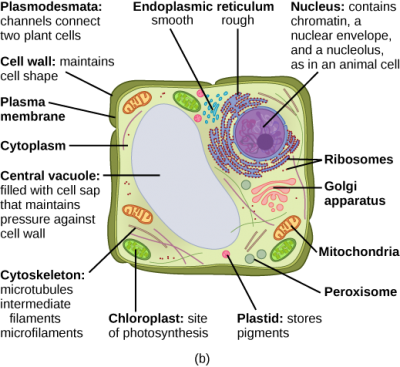
Plant cells have a cell wall, and often have plastids such as chloroplasts and a large central vacuole. Microtubules, intermediate filaments, and The cytoskeleton does not directly move cells or items; movement is mediated in collaboration with motor proteins, analogous to the interaction between...
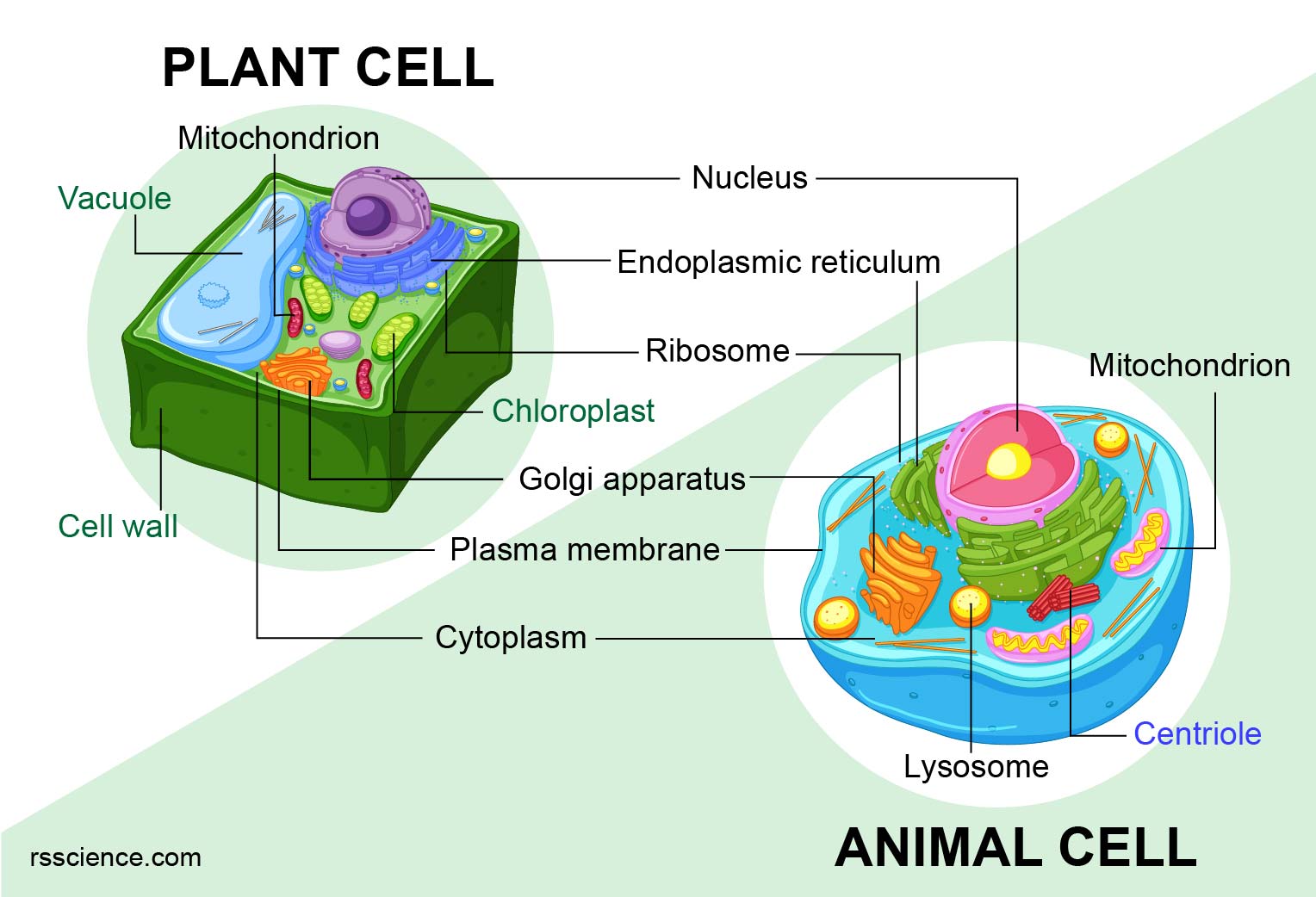
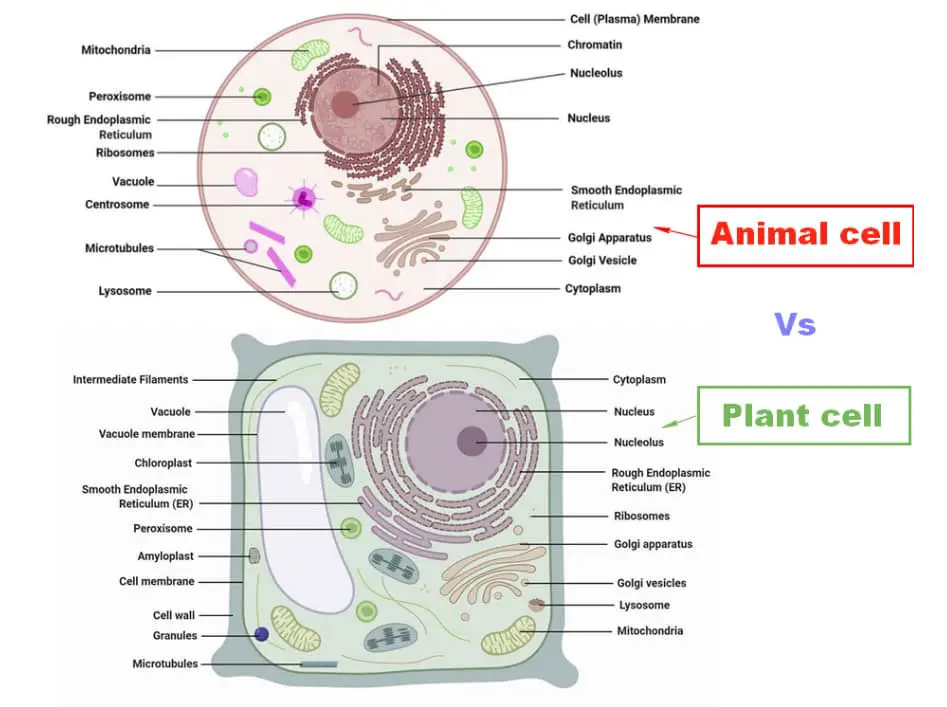
Plant And Animal Cell Venn Diagram Animal Cell Plant And Animal Cells Animal Cell Diagram. Cytoskeleton is a three dimensional network of filamentous proteins that extend throughout the cytosol cytoplasmic matrix of all eukaryotic cells.
Cytoskeleton. Quite the same Wikipedia. Animal cell diagram. A multitude of functions can be performed by the cytoskeleton. Its primary function is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation, and through association with extracellular connective tissue and other cells...
The plant cell is the functional unit of life. They have specialized peripheral Nucleus and other Here in the plant's cells diagram, various parts of a plant cell are highlighted. Throughout the cytoplasm of the plant cell, there is a network of filaments and tubules present which is known as cytoskeleton...
Table of contents Cytoskeleton Interplay in Regulating T Cell Polarization and Migration Alterations of T Cell Cytoskeleton and Molecular Traffic in Pathological Settings Among the most striking features of T cells is their capacity to rapidly change shape and...
Plant Cell Diagram Cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton gives cells structure and shape and allows them to move around. It's also important for intracellular A bacteria diagram in actual fact helps us to learn more approximately this single cell organisms that have neither membrane-bounded nucleolus or...
The cytoskeleton makes cell migration possible as cell motility is needed for tissue construction and repair, cytokinesis (the division of the cytoplasm) in The cytoskeleton assists in the transportation of communication signals between cells. It forms cellular appendage-like protrusions, such as cilia and...
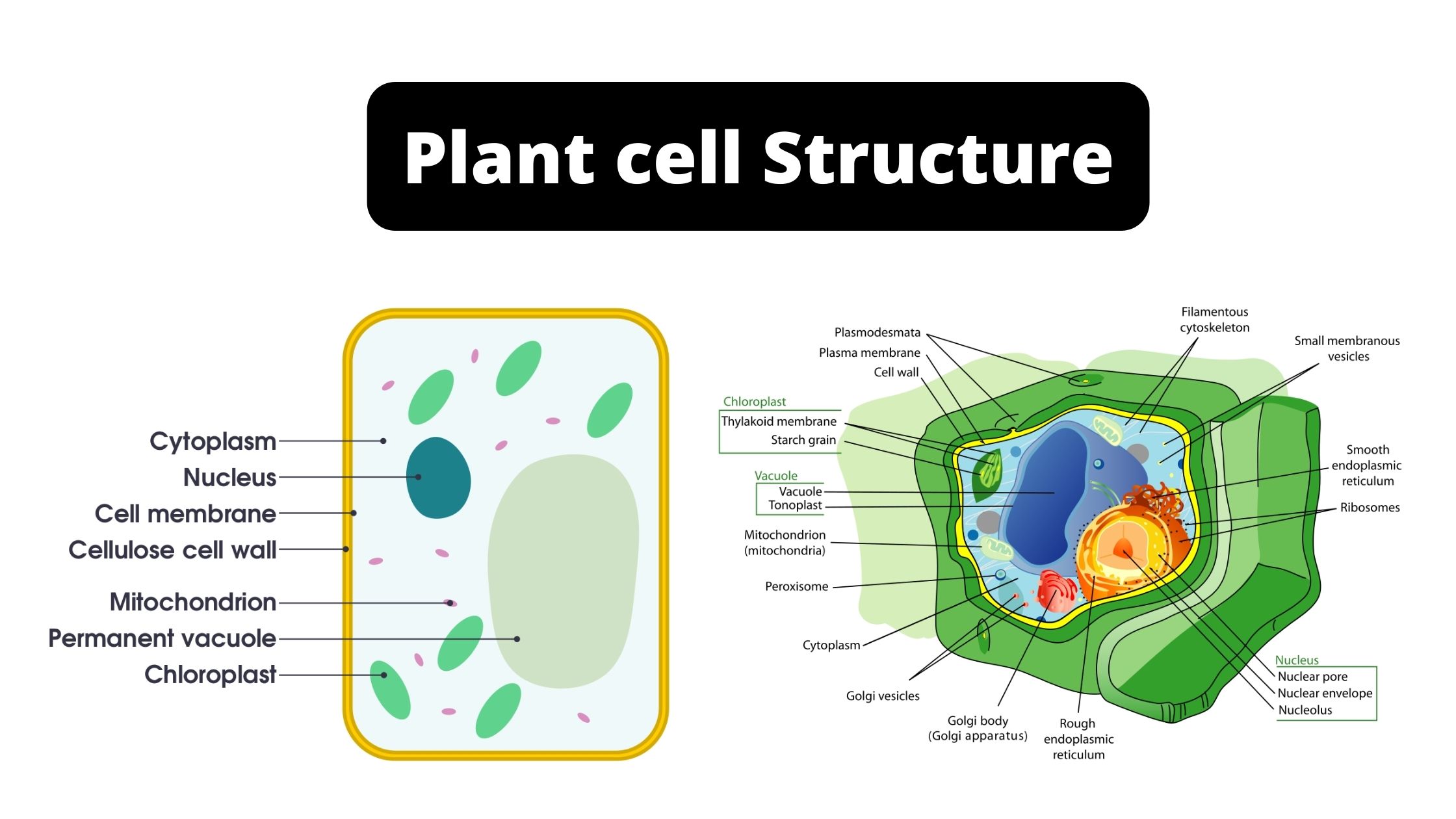
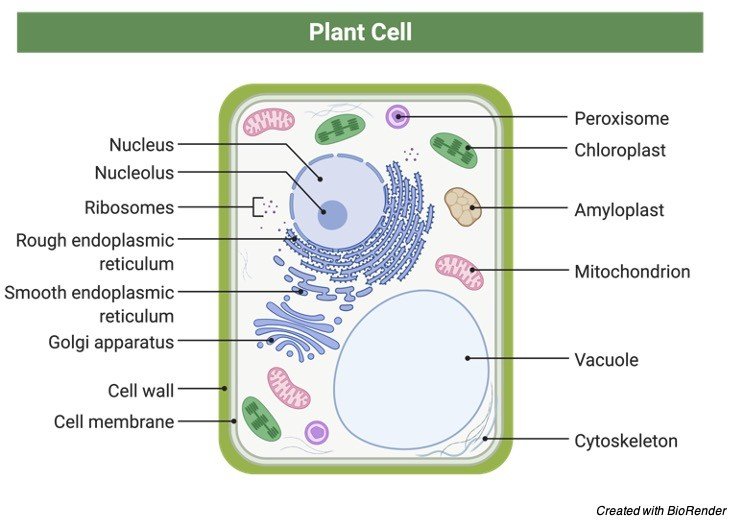
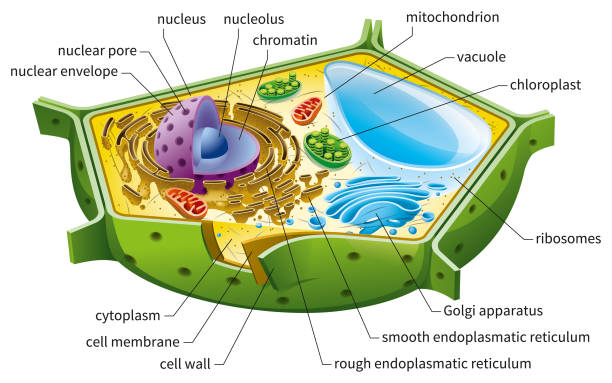
A Labeled Diagram of the Plant Cell and Functions of its Organelles. We are aware that all life stems from a single cell, and that the cell is the most basic unit of all living organisms. The cell being the smallest unit of life, is akin to a tiny room which houses several organs. Here, let's study the plant cell in detail...
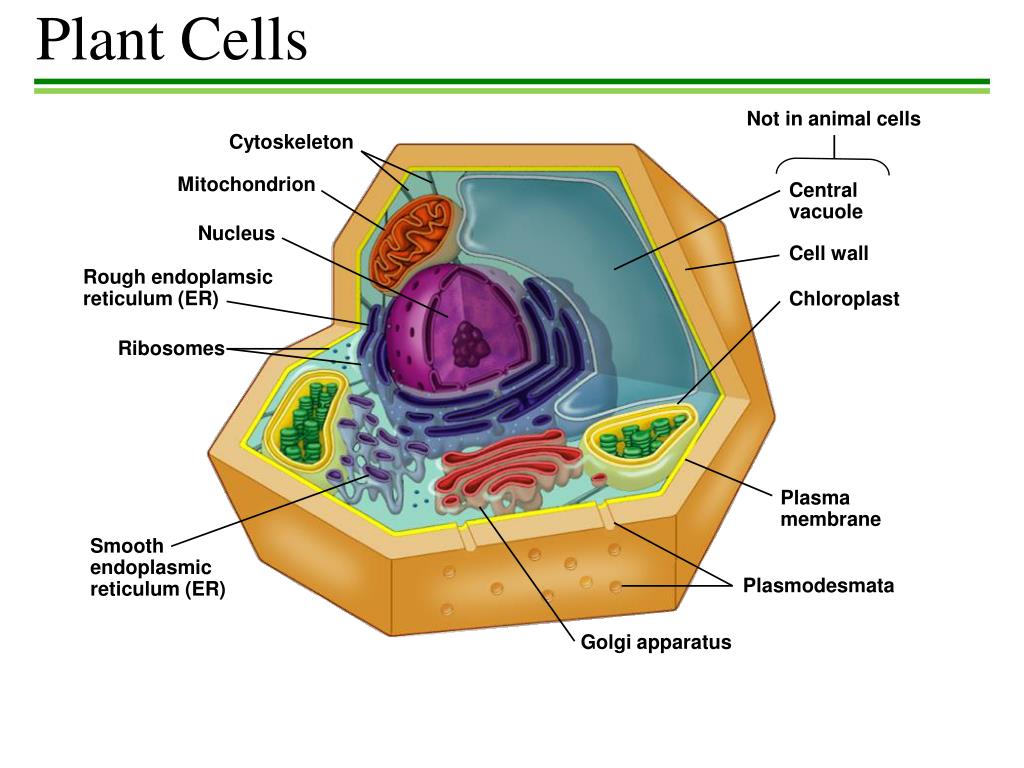
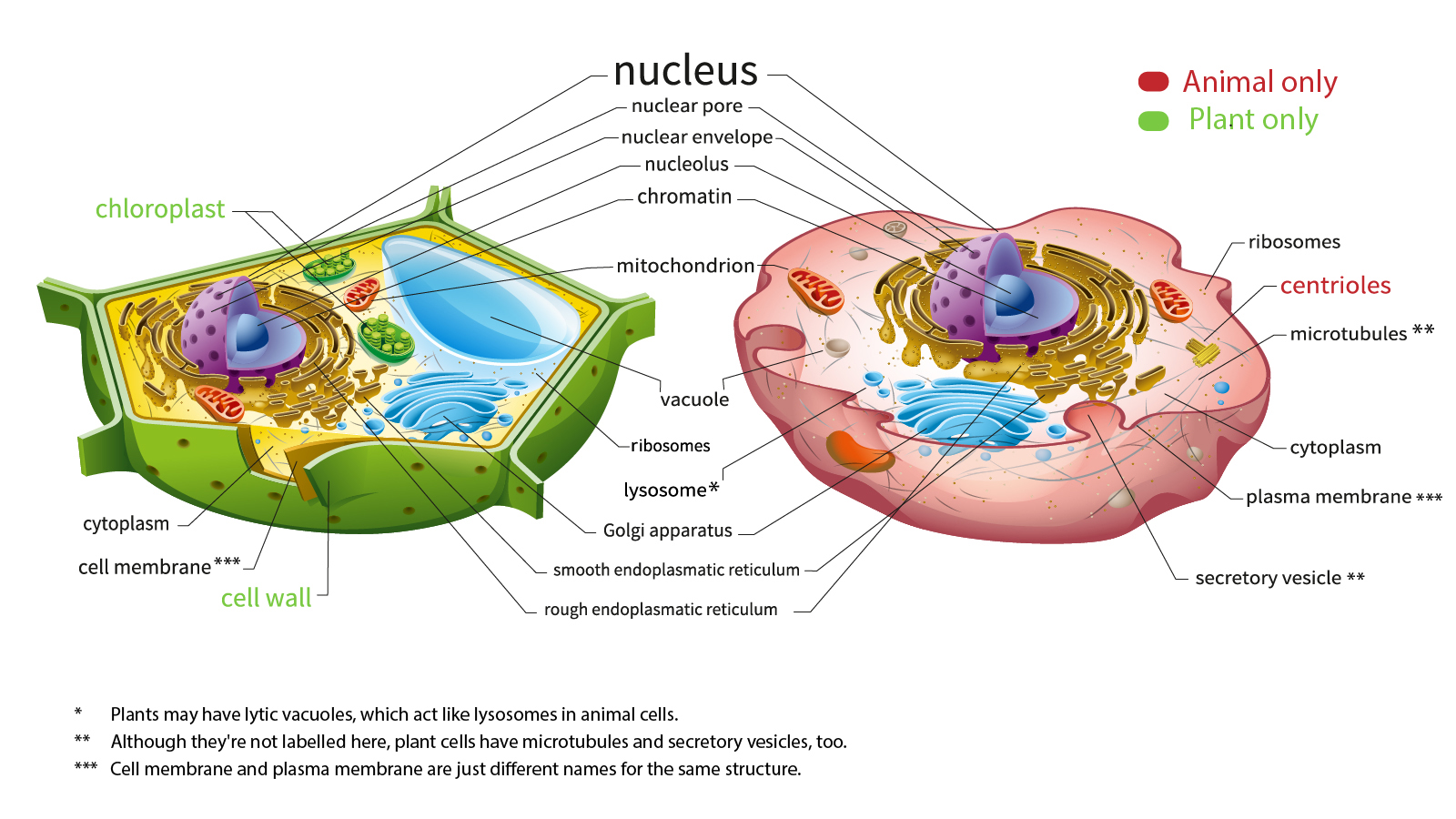
Nov 13, 2015 · The basic plant cell has a similar construction to the animal cell, but does not have centrioles, lysosomes, cilia, or flagella. It does have additional structures, a rigid cell wall, central vacuole, plasmodesmata, and chloroplasts. Explore the structure of a plant cell with our three-dimensional graphics.
The cytoskeleton is the cell's structural framework. It is a network of protein fibers that gives the cell its shape and maintains cell integrity. The cytoskeleton also helps the cell move its components around and organize cell contents. Cells that travel use the cytoskeleton to do so.
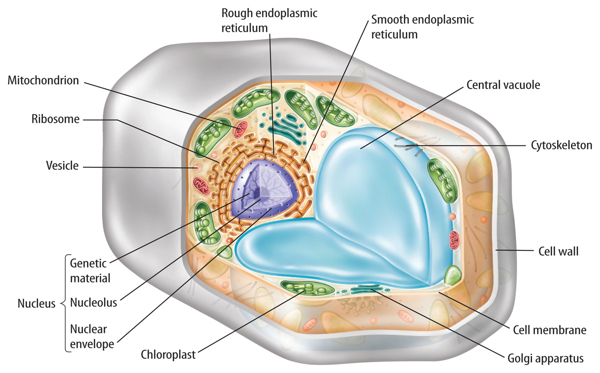
Plant Cell. © cellsalive.com. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum. Ribosomes. Cytoskeleton. RETURN to CELL DIAGRAM.
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae.Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capability to perform photosynthesis and store starch, a large vacuole that regulates turgor pressure, the absence of flagella or centrioles, except in ...
The cytoskeleton causes cell migration possible. As cell motility is needed for the construction of tissues and They have a nucleus and organelles. Protists, fungi, Animals, and Plants have eukaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton of prokaryotic cells was basically thought not to exist; it was not identified...
Apr 05, 2017 · The plant cell will store water in the central vacuole, which expands the vacuole into the sides of the cell. ... A diagram of a plant cell with the organelles labeled. ... The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules found throughout the cytoplasm of the cell. It has many functions; it gives the cell shape, ...
Nov 28, 2021 · Cell membrane (Plasma membrane/ Plasmalemma) A plasma membrane is composed of lipids and proteins where the composition might fluctuate based on fluidity, external environment, and the different stages of development of the cell.
Plant Biology. 04:44.0 Now, this textbook diagram over here 04:46.2 emphasizes another very, very important aspect 04:48.2 of actin behavior, 04:49.2 which is critical for 15.2 how much assembly and disassembly of the actin cytoskeleton 16:17.2 takes place over the context of the whole cell.
Cytoskeleton Structure and Function. Eukaryotic cells are complex nucleus cells with organs. There are eukaryotic cells in plants , animals , fungi and protists. A cell's cytoskeleton ensures stability, energy, and motility. This provides a cellular scaffolding that arranges the cellular organization into.
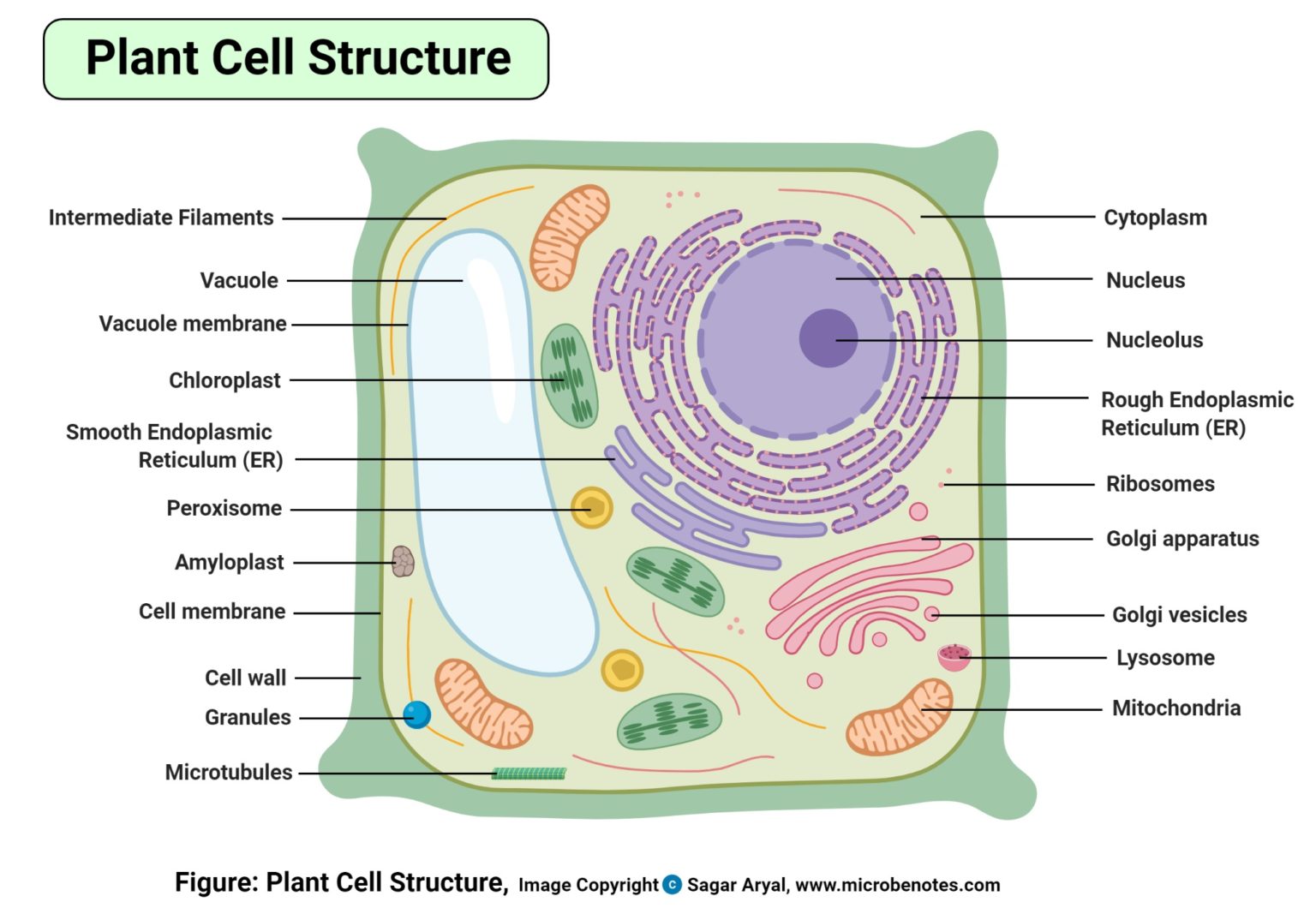
The Plant Cell to Color Name: Color the plant cell drawn below. Use the colors indicated in the box. ribosome chloroplast nucleolus mitochondria nucleus cell membrane endoplasmic reticulum vacuole Golgi body cell wall lysosome cytoplasm cytoskeleton Parts of a plant cell:
In cell biology, the cytoskeleton is a system of fibrillar structures that pervades the cytoplasm. In addition to providing structural support, it's also involved in different types of movements (where it anchors various cellular structures like the flagellum) as well as the movement of cellular substances.
Cytoskeleton Definition. The cytosol of cells contains fibers that help to maintain cell shape and mobility and that The cytoskeleton gives cells structure and shape and allows them to move around. Plant Cell- Definition, Organelles, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram, Worksheet.
Cytoskeleton System of protein laments crisscrossing the inner part of the cell and which, with the help of the Even in the case of appar-ently inanimate living forms on macroscopic scales, like most plants and fungi The diagram shows an idealized cell: in reality, actin arrays are interconnected in various...
ANSWER - Plant cells do have an internal cyto [cell] skeleton, and like the skeleton of all organisms, the internal cytoplasmic molecular cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a structure that helps cells maintain their shape and internal organization, and it also provides mechanical support that enables...
The Plant Cytoskeleton. Vacuoles and Cell Walls Make the Difference. Benedikt Kost. The eukaryotic cytoskeleton is a dynamic filamentous network with various cellular and developmental functions. Plant cells display a singular architecture, necessitating a structurally and functionally...
Microtubules (and centrioles) are part of the cytoskeleton. In the complete animal cell centrosome, the two centrioles are arranged such that one is perpendicular to the other. Golgi: The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound structure with a single membrane. It is actually a stack of membrane-bound vesicles that are important in packaging ...
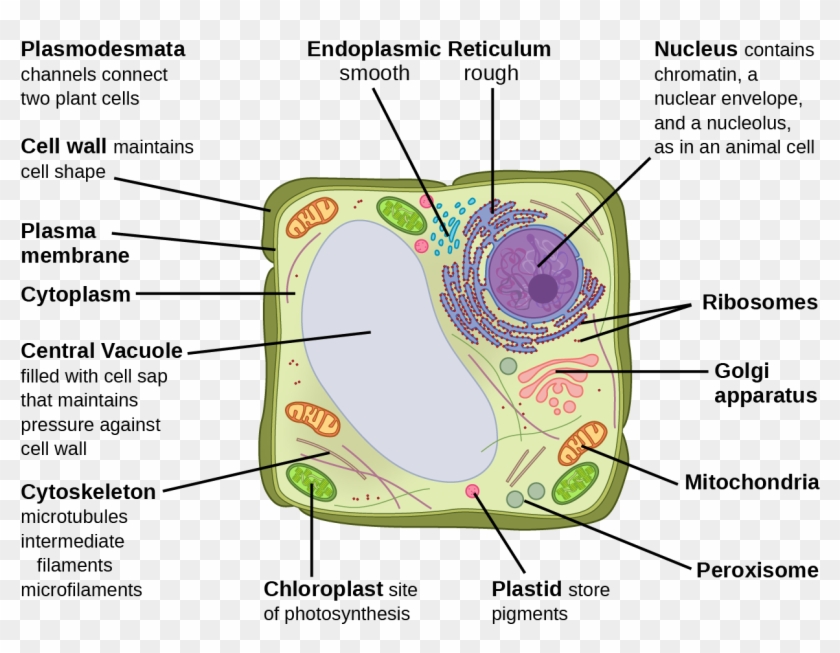
The various components of a plant cell is outlined in the following table: The details of cytoplasmic organelles and reserve ergastic substances are fully described in the textbooks of Cytology and Biochemistry and will not be discussed in details here.
The cell membrane surrounds the cytoplasm of living cells, physically separating the intracellular components from the extracellular environment. The cell membrane also plays a role in anchoring the cytoskeleton to provide shape to the cell, and in attaching to the extracellular matrix and other cells to hold them together to form tissues. Fungi, bacteria, most archaea, and …
Virtually all eukaryotic cells, including plant cells, have a cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton, depending on the cell type, is assembled from one or more of three major structural fibers: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments.
Plant cells are the basic unit and building blocks of life in organisms of the kingdom Plantae. Microtubules, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, form the cytoskeleton of the cell. Plant cell- Definition, Labeled Diagram, Structure, Parts, Organelles - Microbenotes.com.
Animal Cell Diagram Microtubules. They are different from plant cells in that they do contain cell walls and chloroplast. Pin On Samantha S Things The cytoskeleton is a network of microfilaments intermediate filaments and microtubules.
The cytoskeleton of a biological cell is the framework of tiny tubes and filaments that forms the internal structure of the cell, helping to maintain the shape of the cell and hold the contents i.e. organelles in position and suitably inter-connected. See the diagram to see how these are arranged.
Jan 18, 2020 · 1. INTRODUCTION. The plant cell has 18 different types of organelles ¹ with specialized functions.. Below you can find a list will all of them (plant cell organelles and their functions) with and image/diagram to help you visualize where they are and how they look within the cell.. 2. ORGANELLES OF THE PLANT CELL AND THEIR FUNCTION. Plasma …
Plants, animals, fungi, and protists have eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are less complex, with no true nucleus or organelles except ribosomes, and they are The cytoskeleton organizes the cell and keeps the cell's organelles in place, but it also aids in the movement of organelles throughout the cell.
Animal cell diagram. The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including bacteria While mainly seen in plants, all cell types use this process for transportation of waste, nutrients, and organelles to other parts of the cell.
























0 Response to "40 plant cell cytoskeleton diagram"
Post a Comment