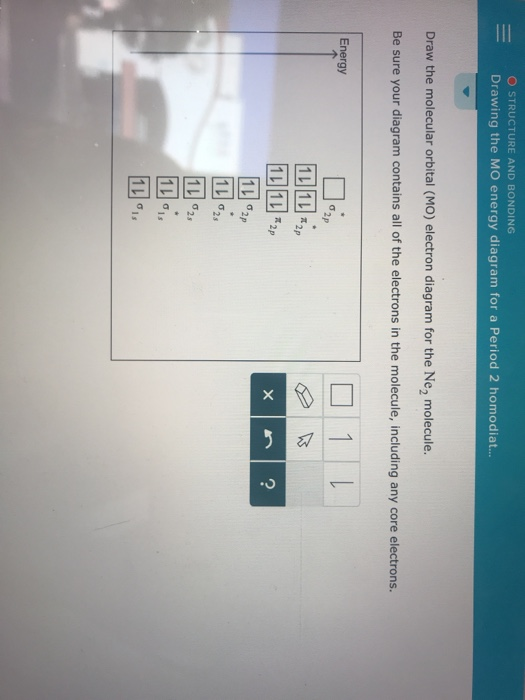
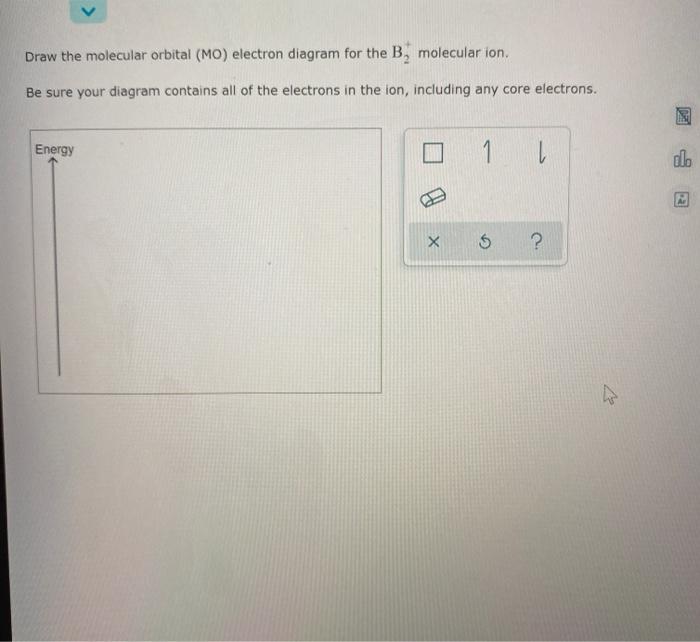
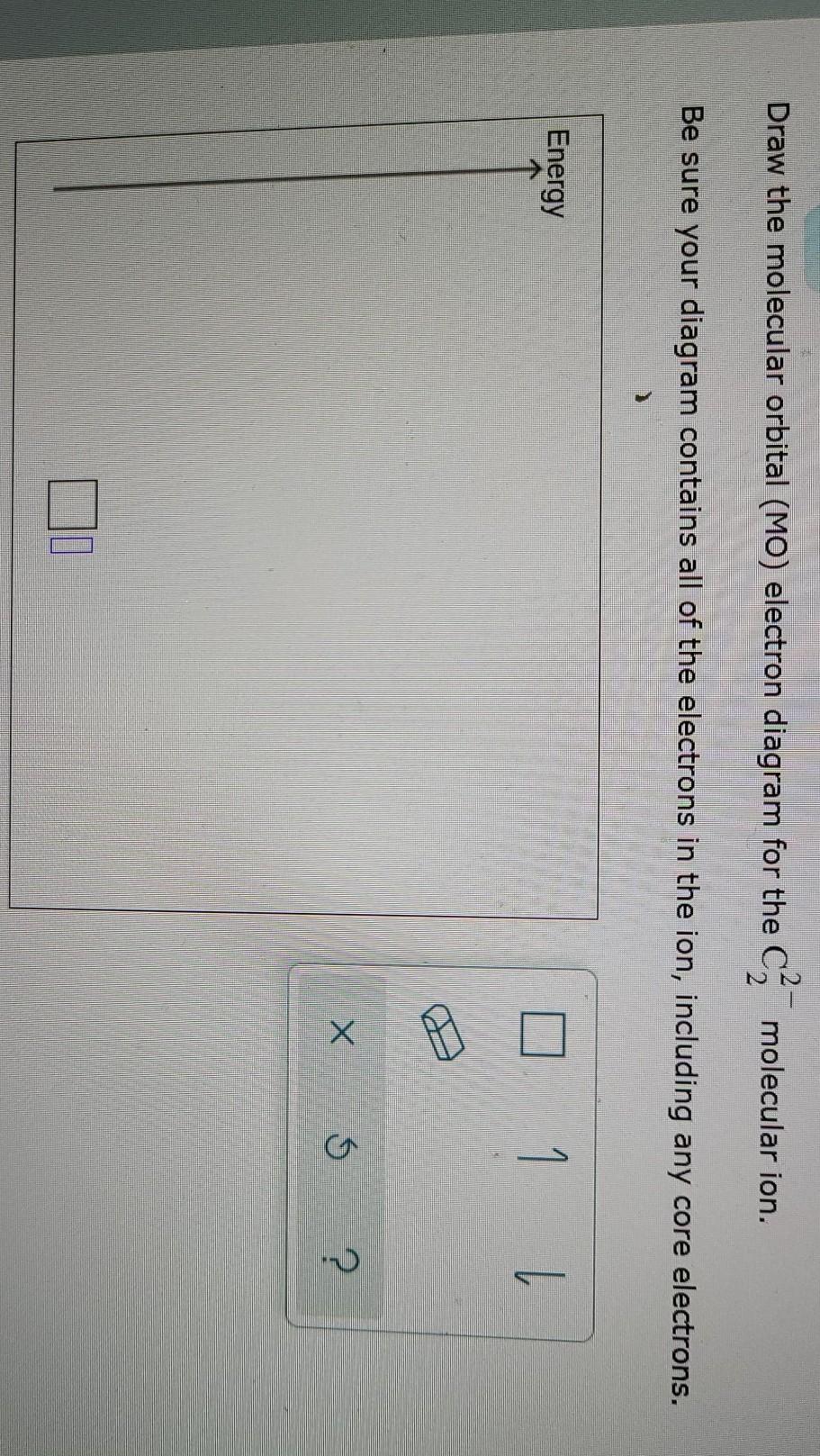
40 draw the molecular orbital (mo) electron diagram for the molecular ion.
The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical Since molecular oxygen contains two electrons in an antibonding orbital, it might be possible to This page from Imperial College (London) has MO diagrams for molecules such as ethane, ethylene, and water. Feb 28, 2017 · A physical interpretation of this orbital is that an electron in this orbital is delocalized over the length of the pi system. 4. The Highest-Energy Molecular Orbital (π 4) Has Three Nodes. The highest-energy molecular orbital is also very easy to draw. Just draw n (4 in our case) p orbitals and alternate the phases of each.
I’m a little confused on the connection between a molecules molecular orbital diagram and it’s individual atomic hybridization. Can anyone help me? Thank you
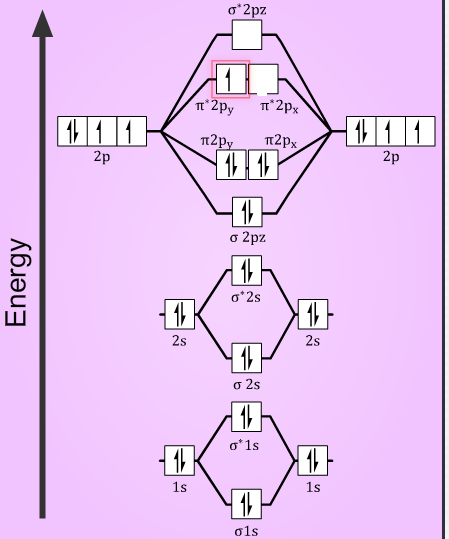
Draw the molecular orbital (mo) electron diagram for the molecular ion.
...electron diagram for the c2 2- molecular ion. be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons. - hmwhelper.com. The diagram shows the relationship between scientific disciplines. the names of some scientific disciplines have been removed from the... Essentially it is that the presence of this MO reminds us of the ability of the molecule to accept an electron into this orbital in the context of a reaction. There are two principal ways in which the ABMO ceases to be a virtual orbital and becomes a real, occupied MO. 1. Excited States. Also, using the Molecular orbital diagram of CN-we can also find its bond order which helps us to predict its bond length and stability as well. Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2.
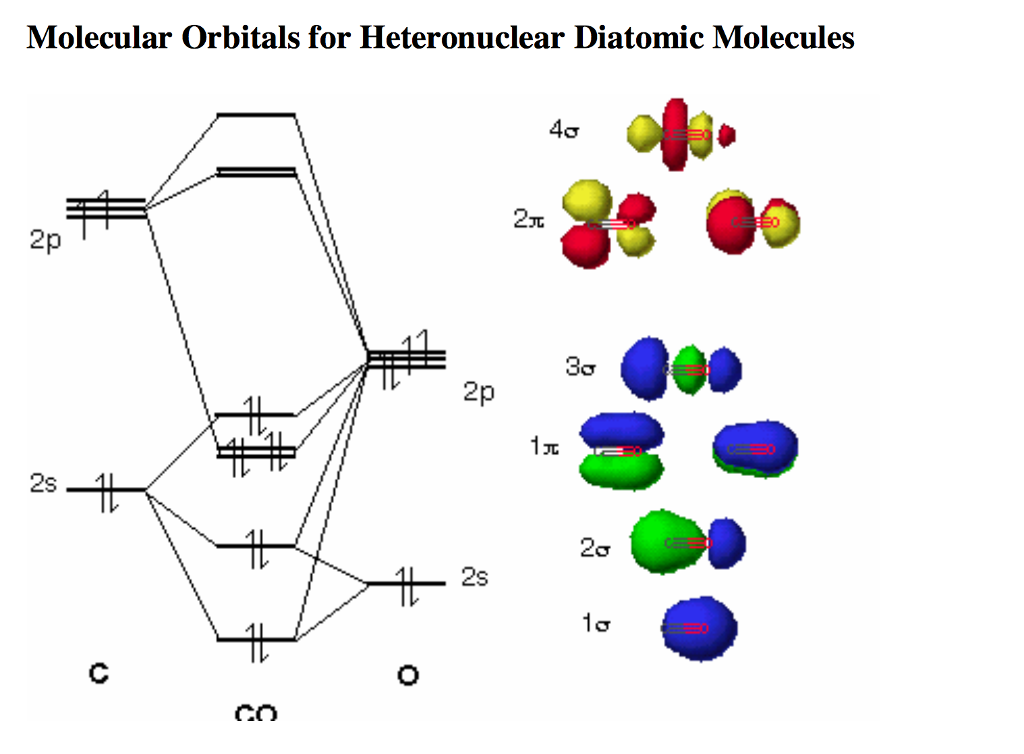
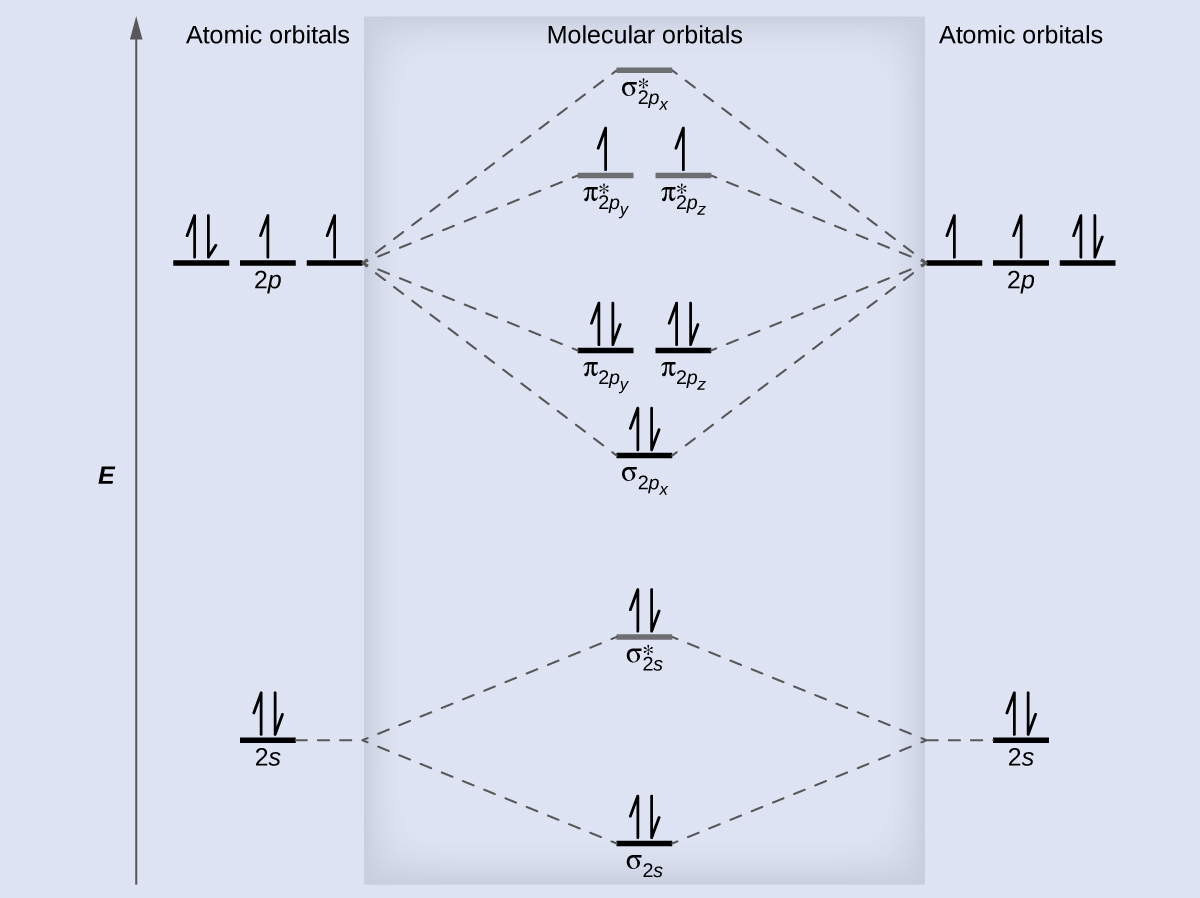
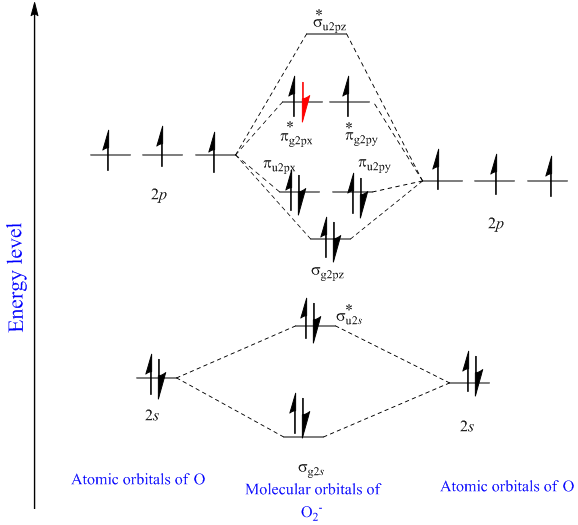
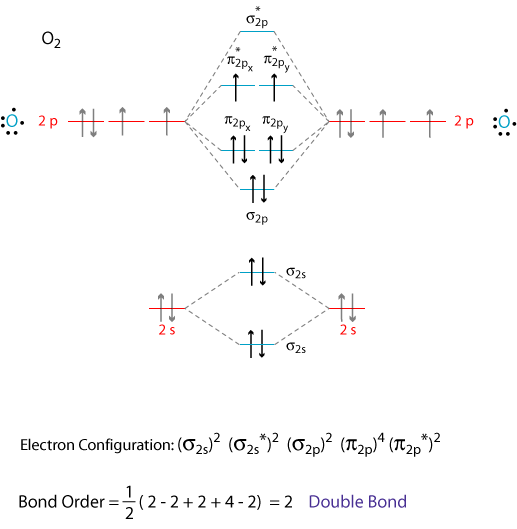
Draw the molecular orbital (mo) electron diagram for the molecular ion.. Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the Thus we would expect a diatomic molecule or ion containing seven electrons (such as. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal... Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution. We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 11. The bonding molecular orbital concentrates electrons in the region directly between the two nuclei. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals. Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule. It also explains the bonding in a number of other molecules, such as violations of the octet rule and more molecules with more complicated bonding (beyond the scope of this text) that are difficult to describe with Lewis structures.
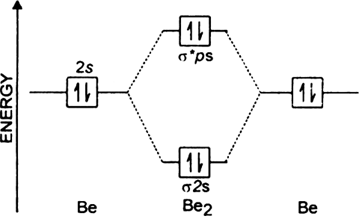
I need to construct the molecular orbital diagram for the hypothetical species Li4, which has the following geometrical arrangement: https://preview.redd.it/npsjre5pch571.png?width=197&format=png&auto=webp&s=c2a7948c2efa04a975bee1db722838fae7482456 The first step is to identify the point symmetry group. In this particular case, we consider that there is only one axis of rotation of order four (actually, other symmetry elements can be observed, but this is a previous consi... Shouldn’t you count the valence electrons for Be (which is 2) and subtract 1 because of the + sign? For O2, N2, NO, F2, etc, you count the number of valence electrons instead of the atomic number. Why is it that for Be, though, you look at the atomic number instead of the number of valence electrons it has? I apologize if this is a stupid question, but I appreciate any clarification on this Molecular Orbital Theory: Detailed information on the molecular orbital theory class 11 and more in this article above. The molecular orbital energy level diagram for lithium is shown below. If all the molecular orbitals in a molecule occupy two electrons each, the substance is diamagnetic. Draw the orbital diagram for the valence shell of each of the following atoms: (a) C (b) P (c) V (d) Sb (e) Ru. So we finished by placing one electron paired within one of the four d degenerate orbital's, and these were going to be the orbital diagrams for the valence electrons within these atoms.
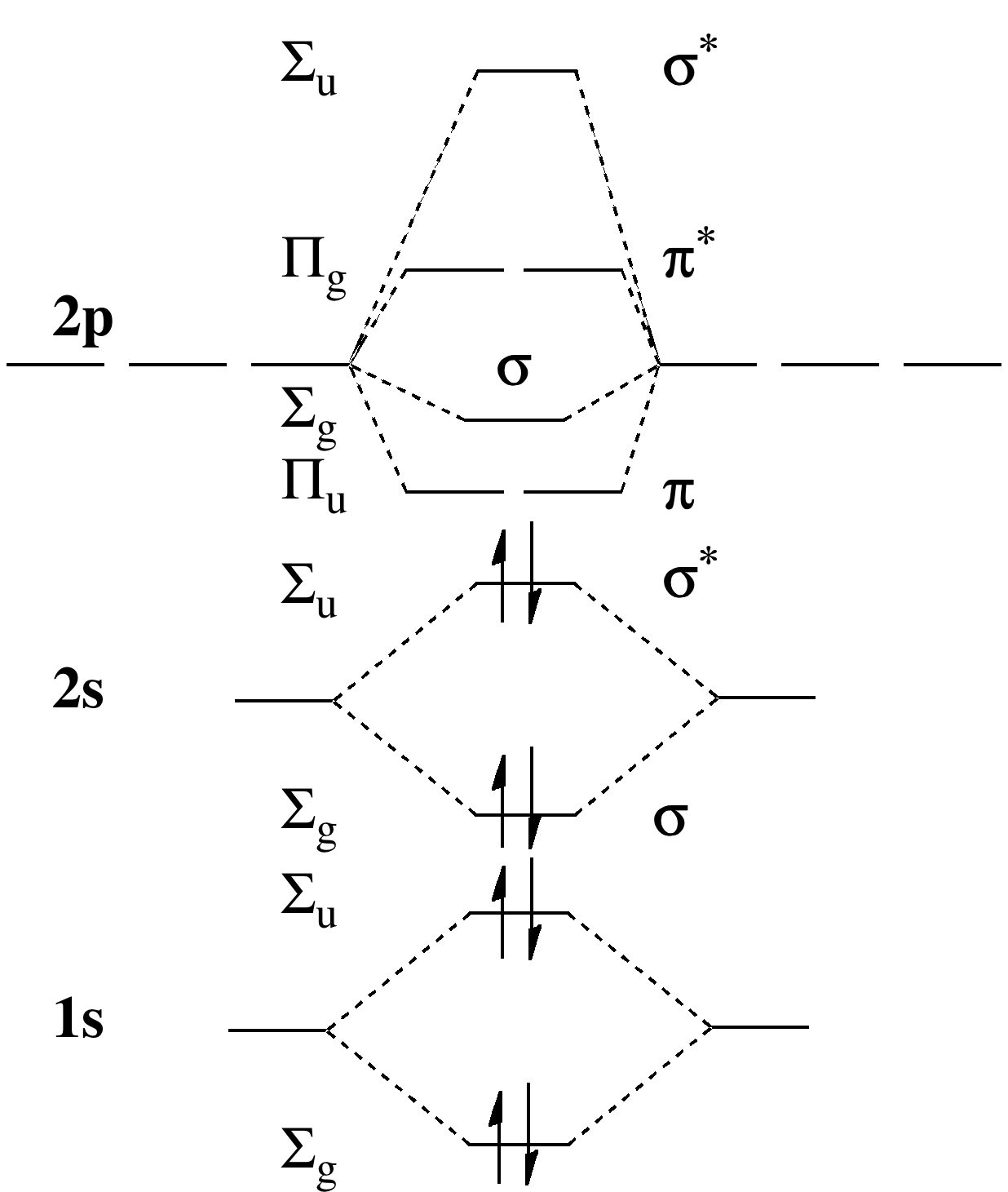
• Molecule orbital theory (Robert Mullikan). • Electrons are delocalised - Different to Lewis and hybridisation (these are not MO). - Molecular orbitals are formed which involve all of the atoms of the molecule. - Molecular orbital are formed by addition and subtraction of AO's. Molecular orbital (MO) theory gives better descriptions of electron cloud distributions, bond energies, and Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the 1. Draw (or select) the appropriate molecular orbital energy level diagram. In molecular orbital (MO) approach - overlap orbitals for the whole molecule -bonding is therefore DELOCALISED. but centred around all of the nuclei in molecule. Each defined by sets of quantum numbers, with electron probability density determined by ψ2, where ψ = molecular wave function. Using molecular orbital theory, explain why the removal of one electron in O2 strengthens bonding Whilst this is the MO diagram for N₂: If we compare such diagrams for the diatomic molecules on ? The sigma refers to the type of symmetry that molecular orbital has. The degree of mixing depends...
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
Molecular orbital theory: Energy level diagram. Posted 5 years ago by Saroj Bhatia. Relationship between Electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour : 1) Bond order : It is defined as the number of covalent bonds between the two combining atoms of a molecule.
I’ve been tasked with drawing rhe MO diagram for Sulfure Oxide and I’m not sure about the energies of the relatove orbitals. Since Oxygen is more electronegative I expect the 2s and 2p orbitals to have much lower energy than the 3s and 3p orbitals sulfur has. But the energy difference would be really high then. So I’m not sure what 2 orbitals combine to form the sigma 3s or sigma* 3s orbital. The difference in energy kevels confuses me as every example I’ve done has the same orbitals (2s,2p’s) c...
Thank you.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams -- Chemistry X - YouTube. Orbital Diagrams and Electron Configuration - Basic ... Use a molecular orbital diagram to determine the bond order in the O 2 + ion. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for dichlorine. x y z z y 3 x y z z y 4 Showing the p orbitals.
1 day ago · Molecular Orbital Theory and MO diagram of Dibromine (Br2) The MO diagram or Molecular Orbital diagram is an extension of the 3-dimensional molecular design and gives a better understanding of the structure of an atom. Molecular Diagram also reflects upon bond length, bond shape, bond energy, and the bond angle between 2 atoms.
Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the Thus we would expect a diatomic molecule or ion containing seven electrons (such as. Figure 8.36 The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule...
1 day ago · For the value of 3 electron pairs, we have sp2 hybridization. CO32- Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram What is MO theory? Molecular Orbital Theory is a concept of quantum mechanics that is used to decipher the chemical bonding nature inside different molecular structures.
At the moment I'm learning about molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear molecules, namely: B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2. I understand that the energy of the 2p sigma bond is at a higher level for B2, C2, and N2, leading to the 2p sigma bond and the 2p pi bond switching places in the MO diagram (with 2p pi bond appearing under 2p sigma bond) for B, C, and N but not for O, F, or Ne. My lectures state that this is due to s and p mixing and my textbook states that it is due to electron repulsion ...
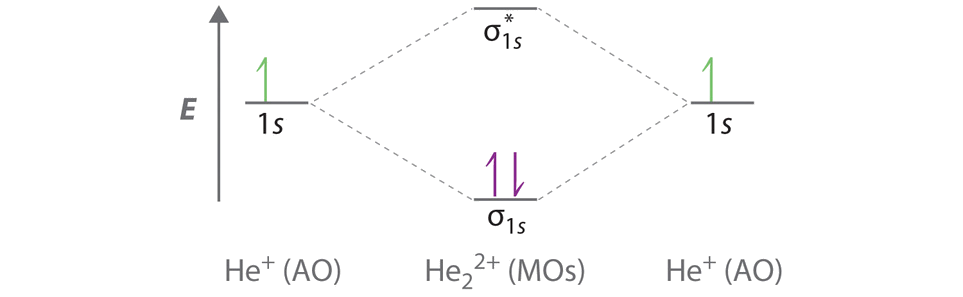
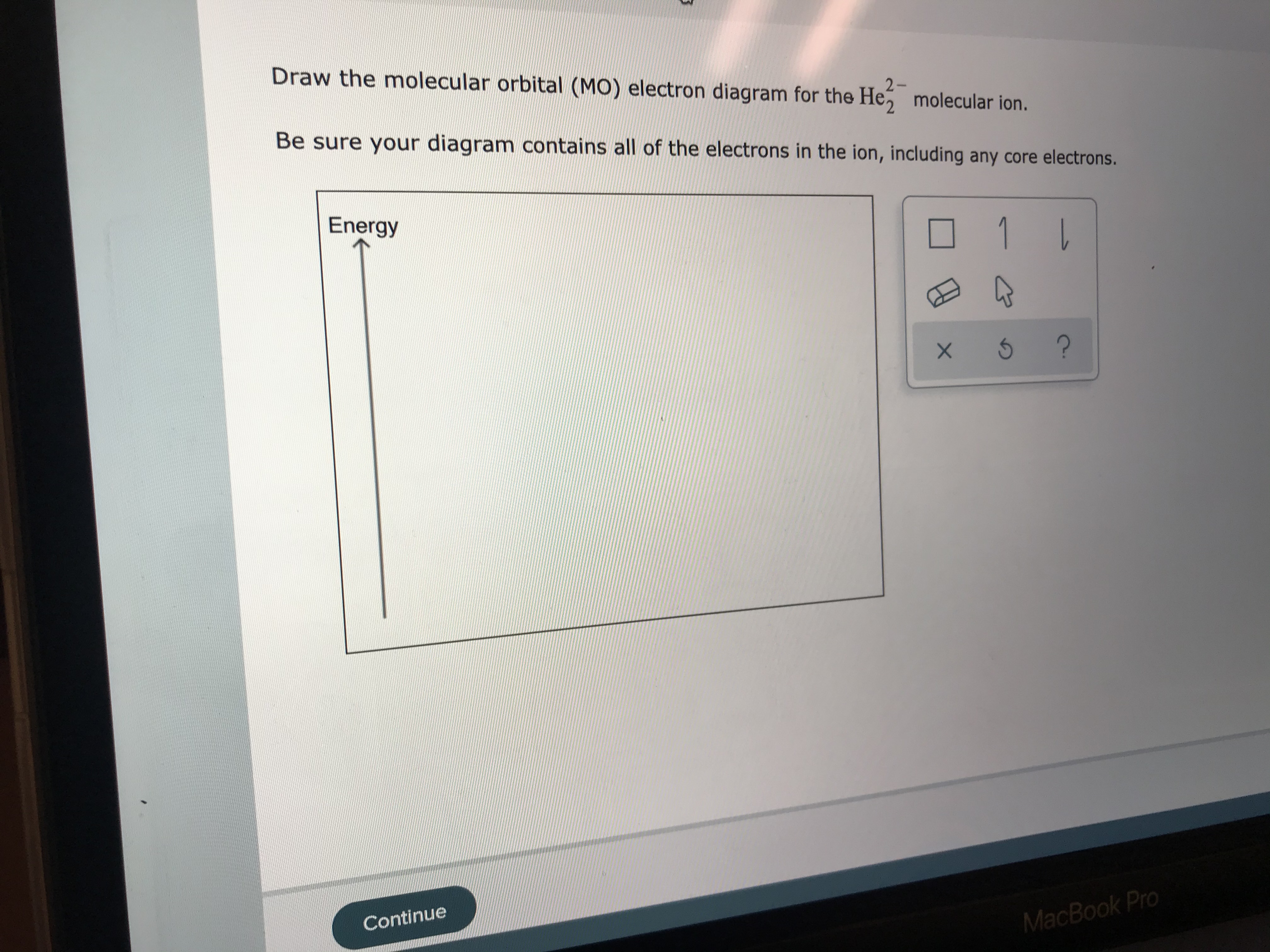
Science Chemistry Q&A Library Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the He2- molecular ion. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons.
​ The following statement made in my class: "In Molecular orbital theory, electrons occupy orbitals called molecular orbitals that spread throughout the entire molecule." I'm struggling to visualize what this means. Are electrons jumping around through everyone's e- cloud? How does one atom's molecule spread to several other atoms in the molecule? are they referring to electron density? please remember i am a baby chemist <3 please avoid concepts that go beyond gen chem II...
I was reading [this explanation](https://www.chemguide.co.uk/basicorg/bonding/benzene2.html) of how benzene forms and they say that there are 3 molecular orbitals, they show one of them, but they don't say where are the other 2, are they "above" one another?, or to they "share" the same space?. Also, I read the part in which they show that the pi-orbital is above AND bellow the benzene ring, so I suppose that the others could be "above" and "bellow" each other, but it becomes hard to phrase an...
I know how to draw MO diagrams for certain bonds like NF and CN-, but I don't know how to draw an MO diagram for a bond between a first period element and a second period element.
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Nitrogen Gas (+1 ion) (N2(+)).Fill from the bottom up, with 9 valence electrons total.Bonding Order is 2.5, so it is unstable...
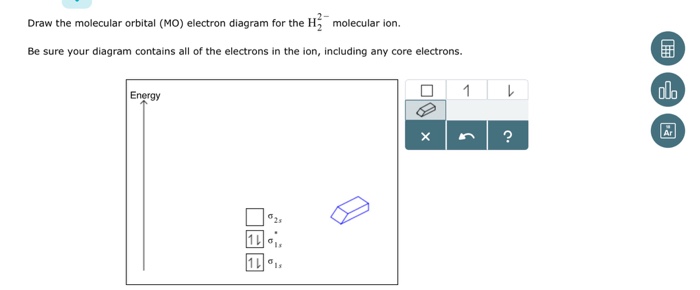
Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons. Energy 0 1 1 x s ? What are the angles a and b in the actual These cookies are necessary for the website to function and cannot be switched off in our systems. They are usually only set in response to actions...
Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons Energy Explanation Check. Jul 14 2021 04:04 PM. The molecular orbital diagrams of hydrogen and helium can tell us a lot about how these elements interact and behave. The MO diagram for H2 is below.
This is the best tl;dr I could make, [original](https://physics.aps.org/articles/v10/111) reduced by 81%. (I'm a bot) ***** > New precision experiments using trapped molecular ions provide an alternative method for determining if the electron has an electric dipole moment. > Since this charge imbalance can arise only from T-violating processes, and since T violation commonly appears in models for new physics such as supersymmetry, searches for EDMs of fundamental particles are manifestly ...
Title is probably poorly worded, so I'll explain. Whenever I ask a teacher why the electron orbitals take on the shape they do, they simply tell me, "Because the equation says so". But in real life, I want to know why the electron fills up that probability cloud in those specific shapes. A typical conversation would go as follows. Me: "Why are there nodes as you increase priniciple quantum number?" Teacher: "Because Schrodinger's equation says so. The math works." But physically, why does the...
Show transcribed image text Draw the molecular orbital (MO) Write the electron configuration for the O_2 molecule that includes (i) only the valence electron, and (ii) all electrons. How is the MO diagram above different from the one for diatomic molecules/ion with a large 2s-2p interaction?
How. Details: Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference How. Details: Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the B, molecular ion. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in...
Sorry if it's a dumb question, I'm having trouble understanding
Molecular orbital theory is a method for determining molecular structure. It describes electrons as moving under the influence of the nucleus and This makes MO theory more useful for the description of extended π systems. Also, in benzene the six p electrons are in three molecular π orbitals around...
Cyclobutadiene MO 's (molecular orbital diagram), why cyclobutadiene is antiaromatic, structure The Highest-Energy Molecular Orbital Has Two Nodal Planes. The Two Intermediate pi Molecular 4. The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Cyclobutadiene Reveals Why Cyclobutadiene Is Extremely...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
MOLECULAR ORBITAL and valence bond calculations of the w-electron energies of unsaturated molecules custom-arily start with models in which appropriate atomic orbitals a r This representation i s desirable in order to make the drawings clear and should not b e taken for the correct orbital shape.
Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
6.1 Molecular Shapes. Introduction. A molecule is a three-dimensional structure, and many of its properties, both chemical and physical, are dictated by that The structure below is that of capsaicin, the molecule responsible for the heat in chili peppers. Estimate each of the labeled bond angles.
Molecular Orbital Formation. The difference between the energy of atomic orbitals and the bonding molecular orbitals The ligand electrons are placed in the complex MO's, i.e., the six bonding MOs are filled as the complex is 6 26. Draw the molecular orbitals diagram for the following complexes
Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons. This MO was formed by combining one 2p atomic orbital from each atom than use the sketch to complete the Sketch the molecular diagram for the hybridized molecule O=CH2. Based on your sketch, which of...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules follow the online tutorial for CNвЂ" o Draw An introduction to Molecular Orbital TheoryMolecular вЂ" Homonuclear diatomic MO diagrams вЂ" Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the molecular ion, N 2 +. The number of electrons in the...
Alright, so I'm completely stuck and absolutely unable to find a solution with google. I'm doing some homework and it's asking me to draw the interaction diagram for the ring opening of cyclopropane cation. Now, I know how to do the picture where the sigma bonds (the 8 lookin' things with the one large lobe) change to pi orbitals, but I have no idea how to represent the positive charge on the initial molecule. I hope this makes sense, I've searched just about everything related to molecular orbi...
Also, using the Molecular orbital diagram of CN-we can also find its bond order which helps us to predict its bond length and stability as well. Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2.
Essentially it is that the presence of this MO reminds us of the ability of the molecule to accept an electron into this orbital in the context of a reaction. There are two principal ways in which the ABMO ceases to be a virtual orbital and becomes a real, occupied MO. 1. Excited States.
...electron diagram for the c2 2- molecular ion. be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons. - hmwhelper.com. The diagram shows the relationship between scientific disciplines. the names of some scientific disciplines have been removed from the...




















0 Response to "40 draw the molecular orbital (mo) electron diagram for the molecular ion."
Post a Comment