41 energy diagram for sn2
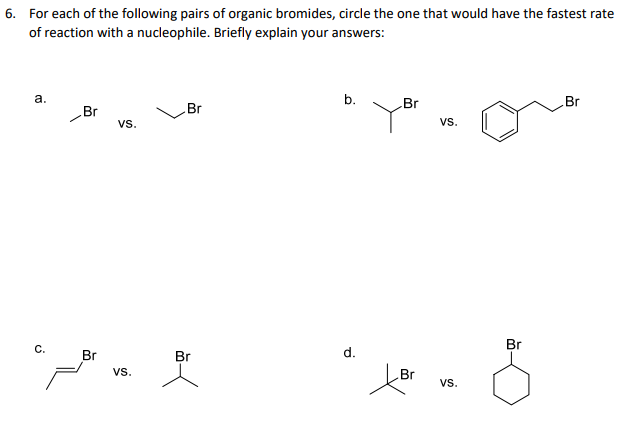
SN2 : 1o substrate in ... Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for the reaction. Label the transition state(s), intermediate(s), the energy of activation(s), and the energy of reaction. c. Draw the structure(s) of the transition state(s) using the standard conventions. We did not do d. Question 5 – The Energy Diagram of SN2 reaction: Draw an energy diagram for the following S N 2 reaction. Label the axes, the Ea, the ΔH° and the transition state of the reaction. Assume the reaction is exothermic and ΔH° = -75 kJ/mol and Ea = 50 kJ/mol. Draw the structure of reactants and products on the diagram. You can put the reactants at any energy level and then draw the rest as asked in the exercise.
7.2 SN2 Reaction Mechanism, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry. 7.3 Other Factors that Affect SN2 Reactions. 7.4 SN1 Reaction Mechanism, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry. 7.5 SN1 vs SN2. 7.6 Extra Topics on Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction. Answers to Practice Questions Chapter 7.
Energy diagram for sn2
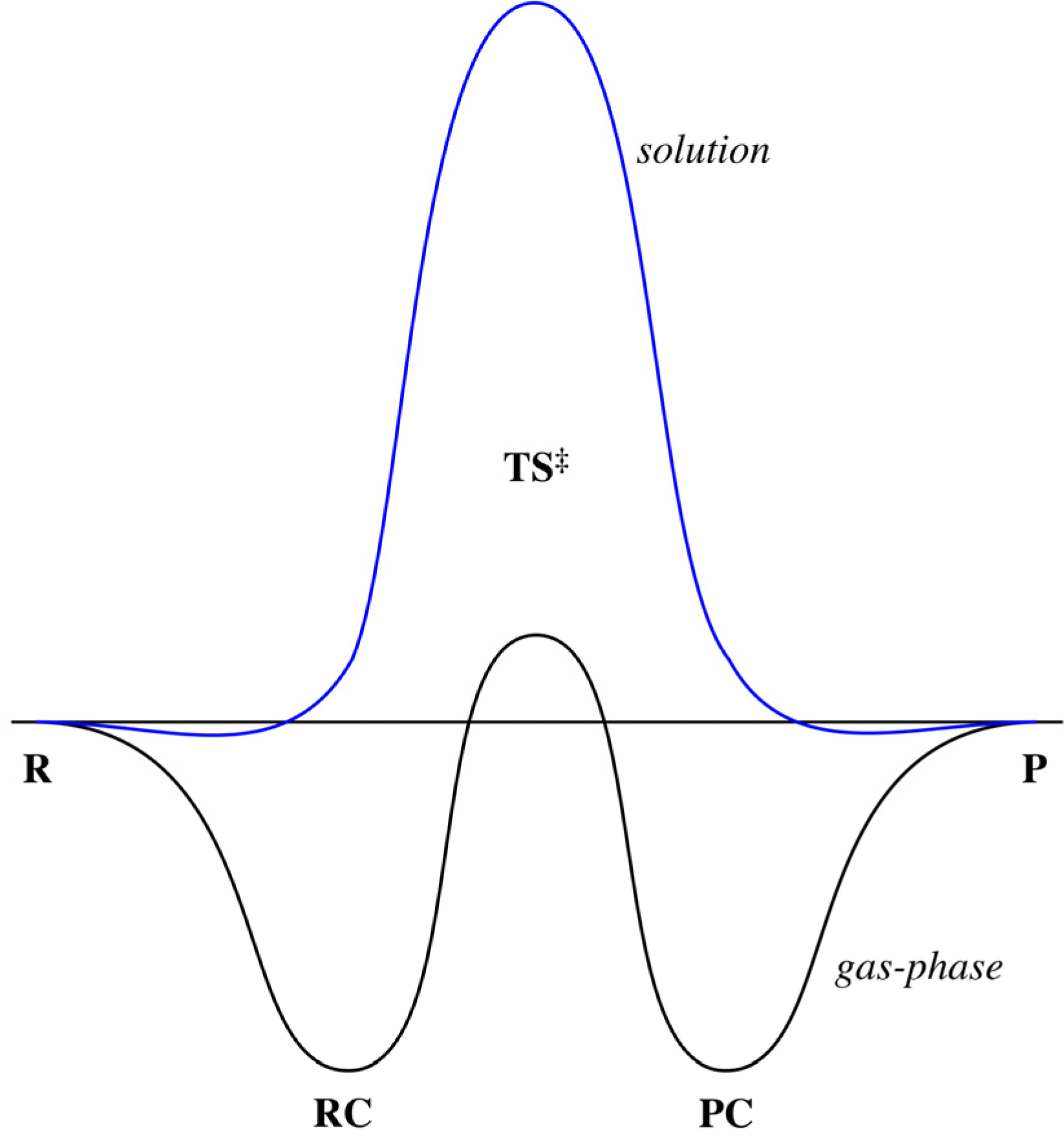
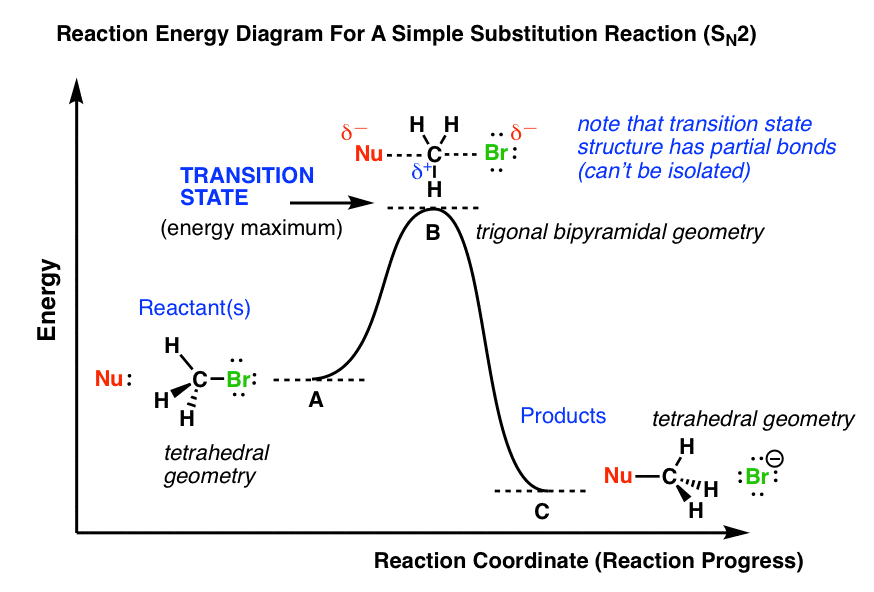
Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Considering the Sn1, SN2, E1, and E2 mechanisms, the energy diagram shown below corresponds to: energy rxn coordinate O only the Sp1 mechanism only the Sn2 mechanism both the Sn1 and E1 mechanisms O both the Sn2 and E2 mechanisms. energy diagram below. gas phase reactions polar solvent phase reactions Carbocations are more stable and have smaller energy differences in solution than the gas phase. (But methyl and primary are still too unstable to form in solution and we won't propose them in this book.) Solvent / ion interactions are the most significant SN2 - Second-order Nucleophilic Substitution; SN2 - Second-order Nucleophilic Substitution ... Transition state and energy diagram of an S N 2 reaction: Chloroform hydrolysis. Due to their extremely short lifetime, transition states cannot be measured directly. They represent an energy maximum on the reaction coordinate.
Energy diagram for sn2. Construct the gas phase Reaction Coordinate Diagram for the Cl + CH3Cl SN2 reaction by plotting the relative energy in kJmol 1 versus Cl + C | {z} Distance H3 Cl. Place the Reaction Coordinate Diagram on the graph provided below and plot the energies on a relative energy scale. Label the various species along the reaction pathway. 0 5 10 15 20 ... 19/12/2012 · The Quick N’ Dirty Guide To Determining SN1/SN2/E1/E2, Part 4 : The Role of Temperature. In previous installations of the Quick N’ Dirty Guide, we’ve examined the substrate, the base/nucleophile, and the solvent.Today, we’ll address the final variable to consider: the temperature. If you’ve been following so far, you may have noticed that by this point we should … Oct 24, 2018 · Question 5 – The Energy Diagram of SN2 reaction: Draw an energy diagram for the following S N 2 reaction. Label the axes, the Ea, the ΔH° and the transition state of the reaction. Assume the reaction is exothermic and ΔH° = kJ/mol and Ea = 50 kJ/mol. Draw the structure of reactants and products on the diagram. You can put the. SN2 reaction coordinate diagram. In this diagram, there are really only three parts: the reagents, the transition state, and the products. Answer: SN2 rxn. is a one step, concerted; rxn is simply where nucleophile attack the saturated carbon centre / atom (bearing a suitable leaving group) from back side / 180° away from the leaving group (-L) . So, it's energy profile is simple . Draw it by using Gibbs free energy term, not enthalp...
The reaction energy diagram for an SN2 reaction, showing the backside attack and transition state with 5 groups attached to carbon.MOC members get access to ... No base = SN1/SN2, but we already knew that. 3) Leaving group: Cl is a decent leaving group. Decent LG = SN2. 4) Solvent: acetone is a polar aprotic solvent = SN2. 5) Substrate: It's secondary at the leaving group = SN1 OR SN2. Almost all of the factors point to an SN2 reaction, with the notable exception of the type of substrate. 1. What does SN2 stand for? Ans: SN2 stands for Nucleophilic Substitution, Second Order (organic chemistry). 2. What is the difference between sn1 and sn2? Ans: The phase deciding the rate is unimolecular for SN1 reactions, whereas it is bimolecular for an SN2 reaction. SN1 is a two-stage system, while SN2 is a one-stage process. Energy Diagram for an SN2 Reaction. 7.6 Other Nucleophiles 7-32 ROH and RO- as Nucleophiles(7.6A) 7-32 ROH Nucleophiles. RO- Nucleophiles (Williamson Ether Synthesis). Limitations of the Williamson Ether Synthesis. Alkoxide Ion Formation. Formation of Cyclic Ethers (Epoxides). R2NH and R2N- as Nucleophiles(7.6B) 7-35
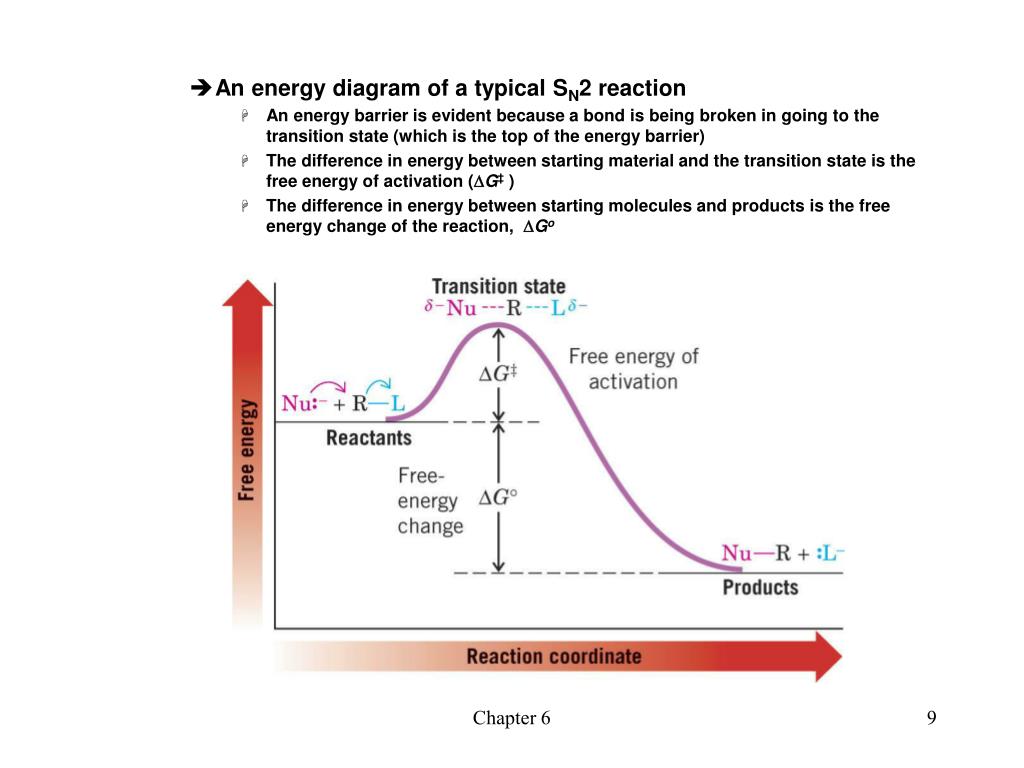
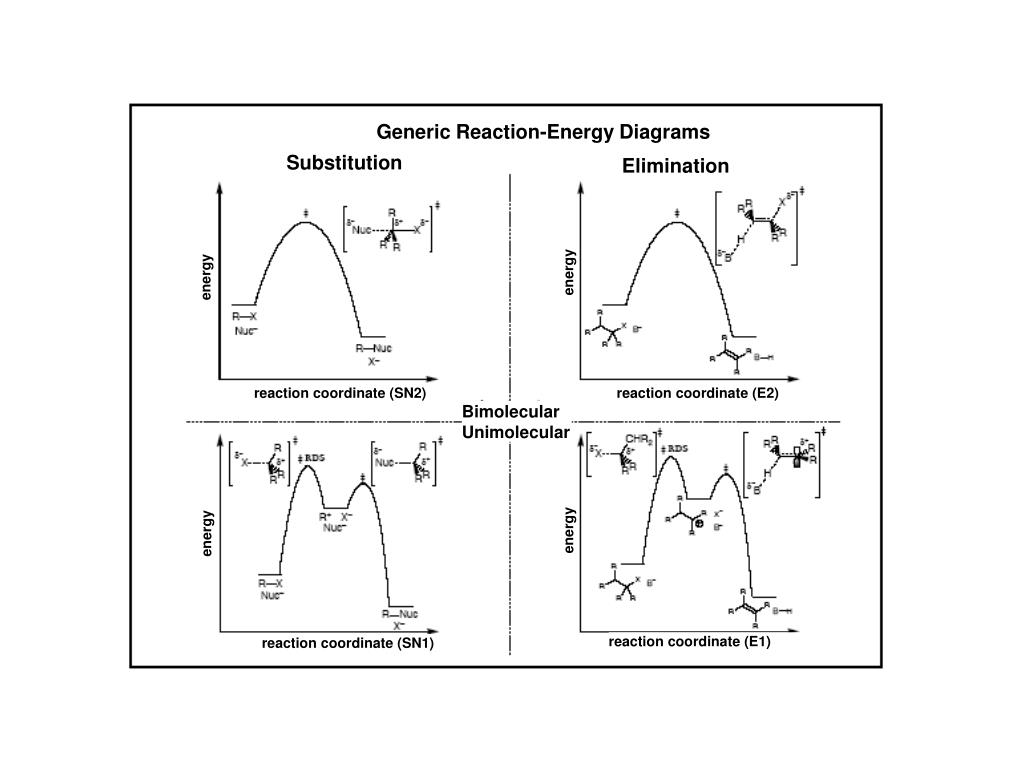
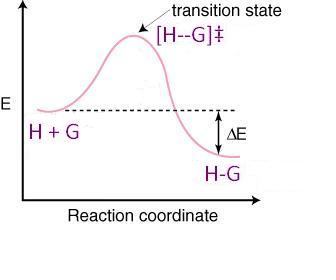
Gravitational potential energy; spring potential energy. Total mechanical energy. Net W nc = ΔE. Conservation of energy problems. A problem in which mechanical energy is not conserved. video. Work and energy. document. Physics: “ Conservation of energy & momentum problem”. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Energy diagram of SN1 and SN2 reactions. The order of hydrolysis of RX by SN1 is 3^o>2^o 1^o RX and by SN^2 path is 1^o>2^o>3^o RX .Which of the following statements are correct for the above energy diagras of SN1 and SN2 reactions? The S N 1 reaction energy diagram illustrates the dominant part of the substrate with respect to the reaction rate. The rate-determining step is the formation of the . Substitution Reactions (SN2 versus SN1) SN1. Elimination Reactions: E2 versus E1. Substrate: Alkene Stability Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams. An energy level diagram is a diagram that shows the energies of the reactants, the transition state(s) and the products of the reaction with time The transition state is a stage during the reaction at which chemical bonds are partially broken and formed
Energy diagrams SN1 and SN2. Jessica L. Santos. 699 followers. Organic Chemistry Reactions. Chemistry Help. Ap Chem. School Hacks. School Tips. Study Hard. Study Materials ... Sn1, Sn2, E1, E2 Orgo Reactions Handy Chart. Abigail Ameri. General Chemistry and Organic Chemistry. Organic Chemistry Reactions. Chemistry Help.
Jun 25, 2015 — In the term S N2, the S stands for substitution, the N stands for nucleophilic, and the number two stands for bimolecular, meaning there are two ...
Substitution Reactions (SN2 versus SN1). Substrate: ... SN2. SN1. Elimination Reactions: E2 versus E1. Substrate: ... Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams.2 pages
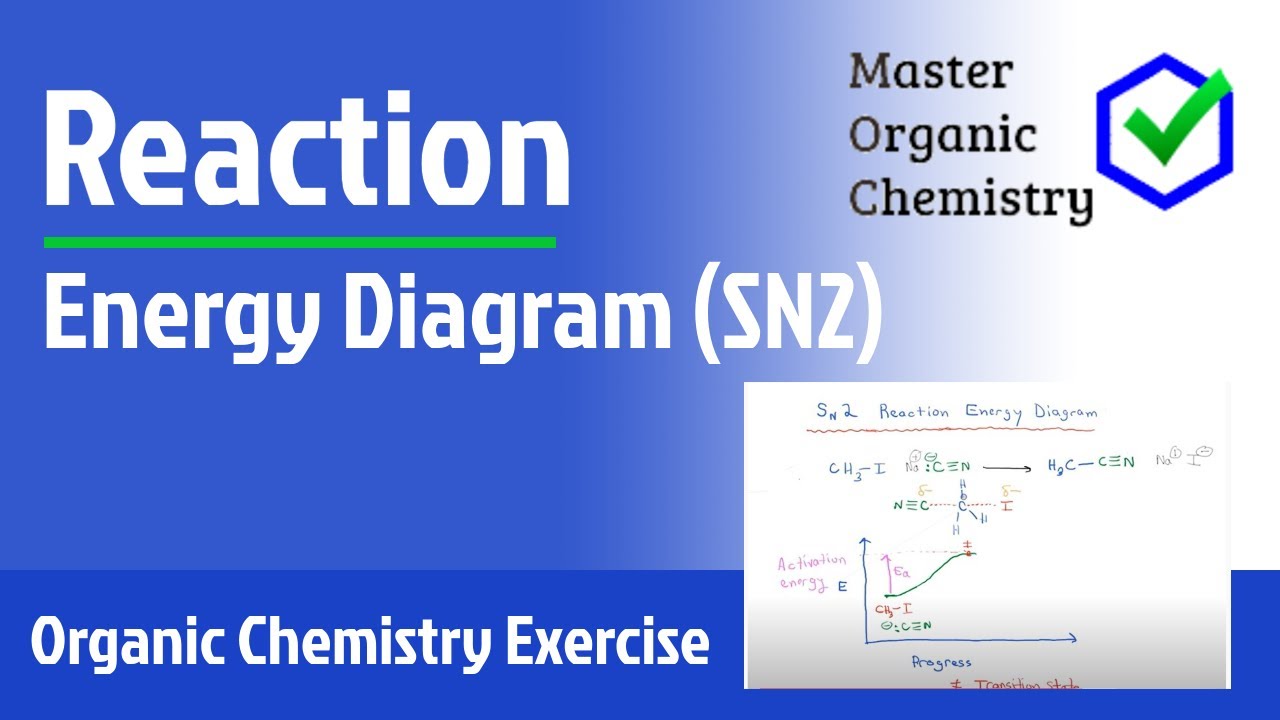
The change in energy for the above reaction is represented in the energy level diagram given below. SN2 is a single-step reaction, so the diagram only shows one curve. The lower energy of the products CH 3 OH and Br - compared to the reactants CH 3 Br and OH - suggests that the reaction is exothermic and that the products are more stable.
21/11/2012 · Deciding SN1/SN2/E1/E2: The Key Role Of The Alkyl Halide (“Substrate”) Having gone through the SN1, the SN2, the E1, and the E2 reactions in turn, we can now say the following: Both substitution reactions and elimination reactions occur with alkyl halides (and related species).
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (15 ratings) Transcribed image text: 4. Draw the potential energy diagram for the following SN2 reaction. Cl +NaSH SH NaCI I. IV.
Proticii. Aproticiii. Solvent Polarity1. Dielectric constant2. Non-polar solvent (nps)3. Polar solvent (ps)4. Border line solventCurrent LectureI. SN2 examplesa. Example:b. Example:c. Example:II. Energy Diagrams: show change in energy during a reaction. When bonds break, there is an increase in energy. When bonds form, there is a decrease in ...
Sn2 Energy Diagram. Fig Transition state and energy diagram of an S N 2 reaction: Chloroform hydrolysis. They represent an energy maximum on the reaction coordinate. SN2 Reaction follows second order rate kinetics. It forms a product via one transition state. Transition state is the state at which it posses. It starts with the kinetics of SN2 reaction and covers the energy diagrams including questions on activation energy, enthalpy, the order of reaction and curved.
The energy changes for the above reaction can be represented in the energy diagram shown in Fig. 7.1. S N 2 is a single-step reaction, so the diagram has only one curve. The products CH 3 OH and Br - are in lower energy than the reactants CH 3 Br and OH -, indicates that the overall reaction is exothermic and the products are more stable.
The following figures illustrate the energy profile diagram of S N 1 and S N 2 reactions. Difference Between S N 1 and S N 2 Reactions Rate Law. S N 1 Reaction: S N 1 Reaction is unimolecular and a first order reaction. So substrate affects the reaction rate. S N 2 Reaction: S N 2 Reaction is bimolecular or a second order reaction. So, both ...
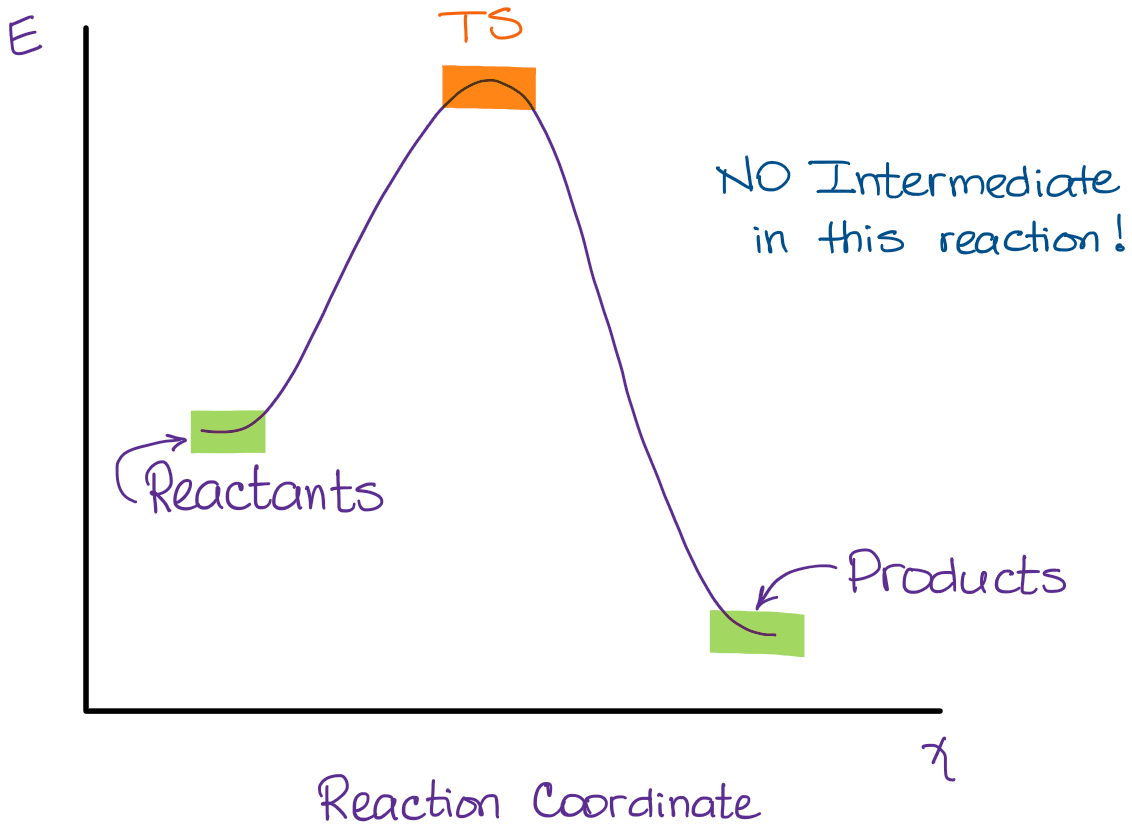
Oct 19, 2018 · SN2 Reaction follows second order rate kinetics. It forms a product via one transition state. Transition state is the state at which it posses. You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram. The point of maximum energy in the reaction coordinate diagram in Figure is the transition state.
2.4 IUPAC Naming of Organic Compounds with Functional Groups With the ability to identify functional groups, next we will learn how to give IUPAC names to compounds containing a few functional groups, by following a set of rules.
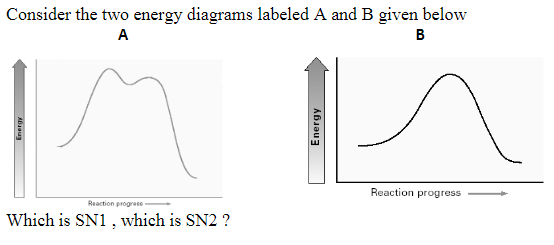
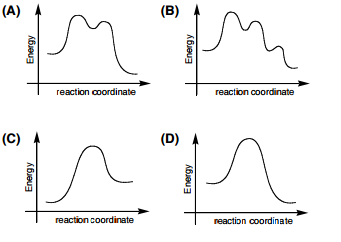
Transcribed Image Text. Identify the energy diagram which represents exothermic SN2 reaction. B Cheistry s Reaction coordinate D Chemist Select one: О а. С O b.
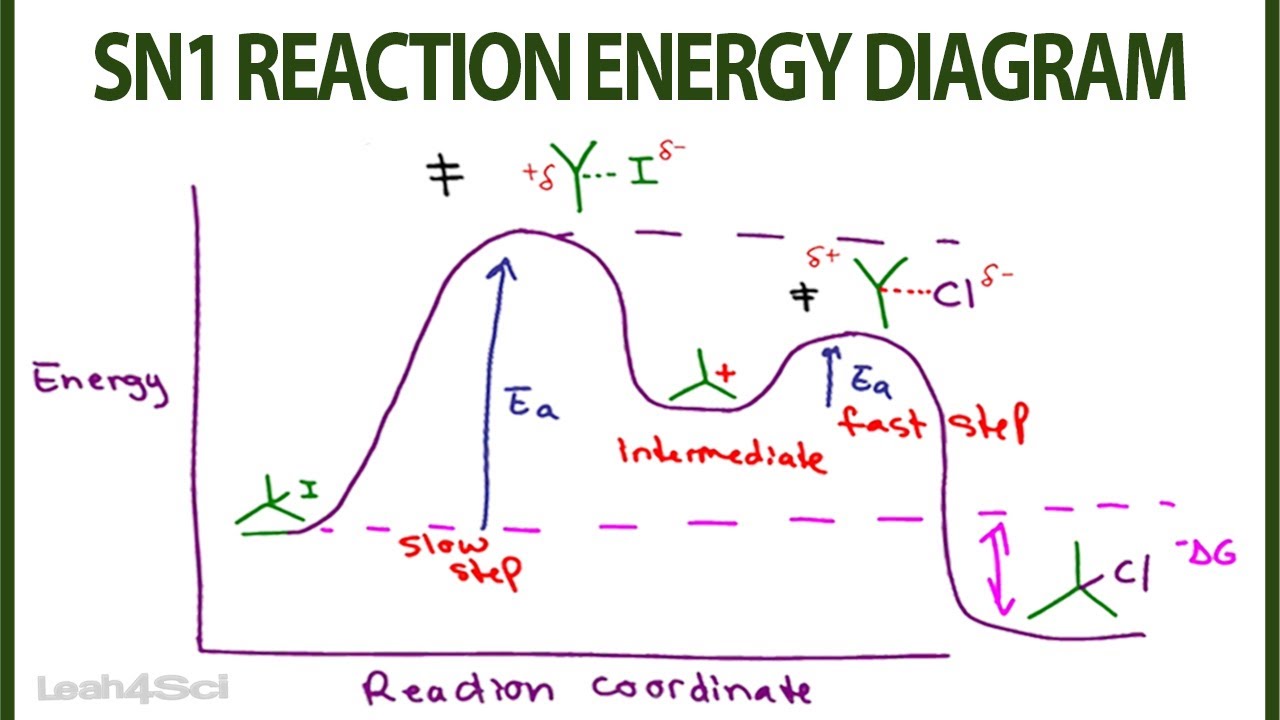
A potential energy diagram for an S N 1 reaction shows that the carbocation intermediate can be visualized as a kind of valley in the path of the reaction, higher in energy than both the reactant and product but lower in energy than the two transition states.
http://Leah4sci.com/substitution-elimination presents: SN2 Energy Diagram Need help with Orgo? Download my free guide '10 Secrets to Acing Organic Chemistry'...
Considering the SN1, SN2, E1 and E2 mechanisms, the energy diagram shown below corresponds toa) only the SN1 mechanism.b) only the SN2 mechanismc) both the SN1 and E1 mechanismd) both the SN2 and E2 mechanism
A potential energy diagram for an S N 1 reaction shows that the carbocation intermediate can be visualized as a kind of "mountain valley" in the path of the reaction, higher in energy than both the reactant and product but lower in energy than the two transition states.
7.4 SN1 Reaction Mechanism, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry. The reaction between tert -butylbromide and water proceeds via the SN1 mechanism. Unlike S N 2 that is a single-step reaction, S N 1 reaction involves multiple steps. Reaction: (CH 3) 3 CBr + H 2 O → (CH 3) 3 COH + HBr. In step 1, C—Br bond breaks and Br departs with the ...
SN2 reaction coordinate diagram In this diagram, there are really only three parts: the reagents, the transition state, and the products. The transition state is the point in the reaction with the highest energy level, and the difference in energy between the reagents and transition state is called the activation energy (often abbreviated as Ea).
The energy diagram of the E1 mechanism demonstrates the loss of the leaving group as the slow step with the higher activation energy barrier: The dotted lines in the transition state indicate a partially broken C-Br bond. The Br being the more electronegative element is partially negatively charged and the carbon is partially positively charged ...
Energy profile diagram of SN 1 reaction: Stereochemistry of SN 1 reaction: In SN 1 reaction, carbocations are formed as the intermediate which are trigonal and planar. Carbocation has a flat structure so that nucleophile can attack it from either side (i.e. front or back) resulting in the formation of two products, one with retention of ...
SN2 - Second-order Nucleophilic Substitution; SN2 - Second-order Nucleophilic Substitution ... Transition state and energy diagram of an S N 2 reaction: Chloroform hydrolysis. Due to their extremely short lifetime, transition states cannot be measured directly. They represent an energy maximum on the reaction coordinate.
energy diagram below. gas phase reactions polar solvent phase reactions Carbocations are more stable and have smaller energy differences in solution than the gas phase. (But methyl and primary are still too unstable to form in solution and we won't propose them in this book.) Solvent / ion interactions are the most significant
Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Considering the Sn1, SN2, E1, and E2 mechanisms, the energy diagram shown below corresponds to: energy rxn coordinate O only the Sp1 mechanism only the Sn2 mechanism both the Sn1 and E1 mechanisms O both the Sn2 and E2 mechanisms.





















0 Response to "41 energy diagram for sn2"
Post a Comment