42 mo diagram khan academy
Linux (/ ˈ l i n ʊ k s / LEEN-uuks or / ˈ l ɪ n ʊ k s / LIN-uuks) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. An Ellingham diagram is a plot of ∆G versus temperature. Since ∆H and ∆S are essentially constant with temperature unless a phase change occurs, the free energy versus temperature plot can be drawn as a series of straight lines, where ∆S is the slope and ∆H is the y-intercept. The
molecular orbital diagram khan academy. molecular orbitals are usually obtained by, molecular orbitals in oxygen, molecular orbital diagram for o2, orbital molecular enlazante y antienlazante, molecular orbital diagram for f2, molecular orbital picture of pyridine, molecular orbital questions, molecular orbital examples, molecular orbital …

Mo diagram khan academy
To answer such questions different theories and concepts have been put forward from time to time. In this fourth unit of class 11 chemistry, we can answer the above questions by learning Kössel-Lewis approach, Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory, Valence Bond (VB) Theory and Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory. The electrons in an atom are arranged in shells that surround the nucleus, with each successive shell being farther from the nucleus. Electron shells consist of one or more subshells, and subshells consist of one or more atomic orbitals. Electrons in the same subshell have the same energy, while electrons in different shells or subshells have different energies. Clever is a digital learning platform for K12 schools--one friendly place for single sign-on, messaging, analytics, and more.
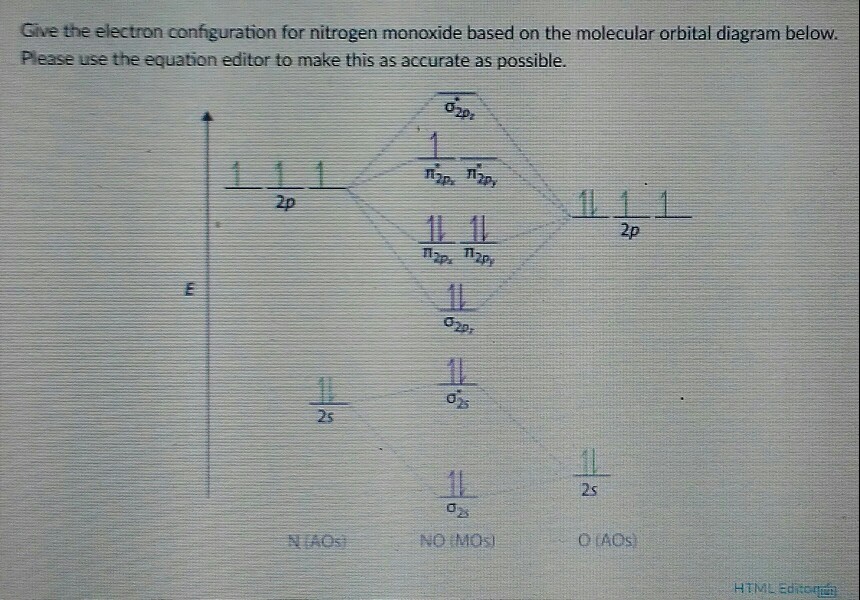
Mo diagram khan academy. 1. In molecular orbital theory, a covalent bond is formed whenever two atoms overlap all of their orbitals, regardless of whether they are valence orbitals or not, to create bonding and antibonding orbitals. 2. Yes, this is found in p subshells when forming homonuclear molecules with some atoms. For atoms like nitrogen, the lack of electron ... Permalink. I would also greatly appreciate a series on this topic. (Lewis,) VSEPR, Valence Orbitals and MO. In MO theory explaining bonding, anti bonding, and non bonding orbitals in general and how to fill the electrons in the orbitals. Between molecules like N2, O2 and others like HF. I only did Khan Academy and some Kaplan prep books. I noticed an improvement on my practice LSAT tests after doing Khan. Watch all of the video lessons. Take a practice test. Note where you did poorly, then go back and read through their lessons in that section. Rewatch the necessary videos and follow along closely. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular…
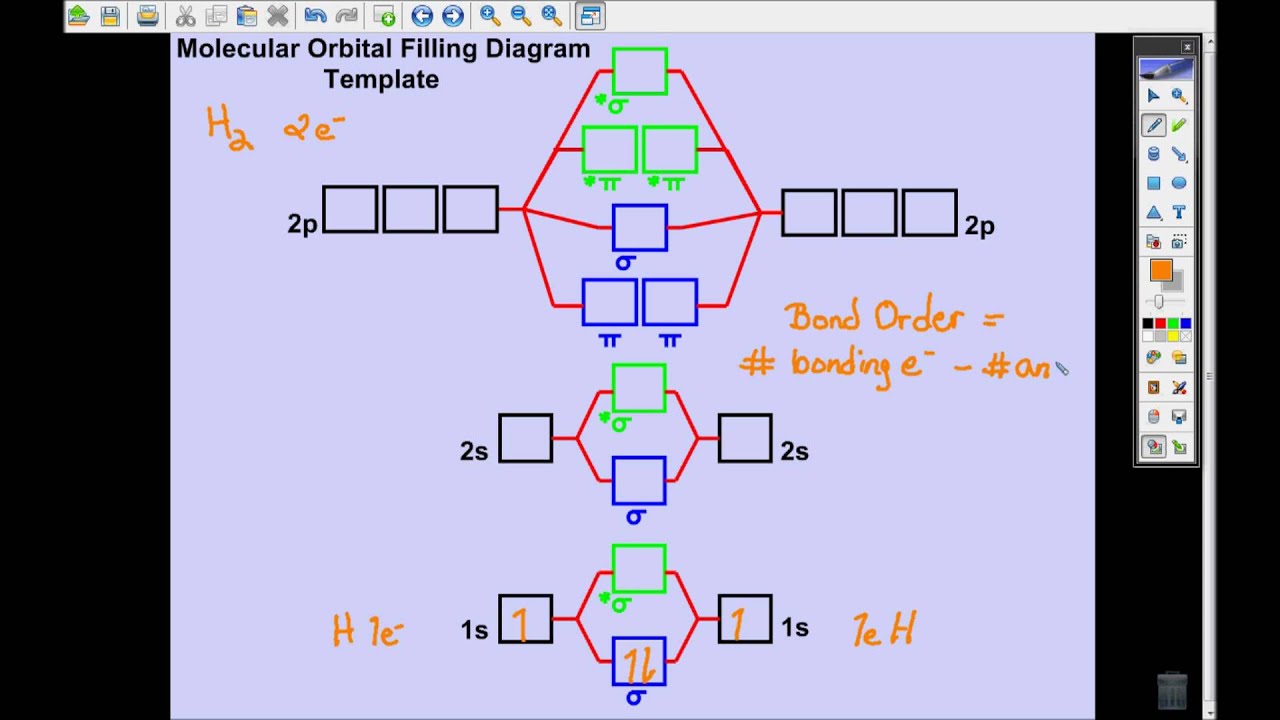
Molecular orbital. source : chemed.chem.purdue.edu. Relationship between Electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour : 1) Bond order : It is defined as the number of covalent bonds between the two combining atoms of a molecule. From the team: We love it when teams challenge the expected way of building progression frameworks. The 8th Light team and Claudia have devised a new way of looking at the problem, placing technical ability and organisational impact on different axes, reflecting the diversity of interest between ‘born ICs’ and people more interested in moving into leadership or management roles, amongst ... This is a very basic introduction to molecular orbital theory. It covers the basics of how to solve for bond order. The intuition of bond order, orbital conf... Lewis dot structure of cn- CN- Lewis Structure: How to Draw the Dot Structure for the CN- CN is known as cyanide which exists as a pseudohalide anion. That belongs come the cyano group and also consists the carbon and also a nitrogen atom having actually a triple bond.
Search the world's information, including webpages, images, videos and more. Google has many special features to help you find exactly what you're looking for. Hope the updated tutorial about how to download mod apks from sbenny.com was easy to understand. If not, feel free to comment below and I'll answer all your ... This photo about: Molecular orbital Diagram Khan Academy, entitled as Why Is The Bond Order In The So₃ Molecule 1 33 And Not 2 Molecular Orbital Diagram Khan Academy - also describes Why is the bond order in the SO₃ molecule 1 33 and not 2 and labeled as: ], with resolution 1980px x 1287px Dec 09, 2021 · Bond order is defined as the number of covalent bonds between two atoms in a molecule. It is equal to one half of the difference between the number of electrons in the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. B o n d o r d e r = N b - N a 2 = 1 2 ( N b - N a) Here N b is the number of electrons in the bonding molecular ...
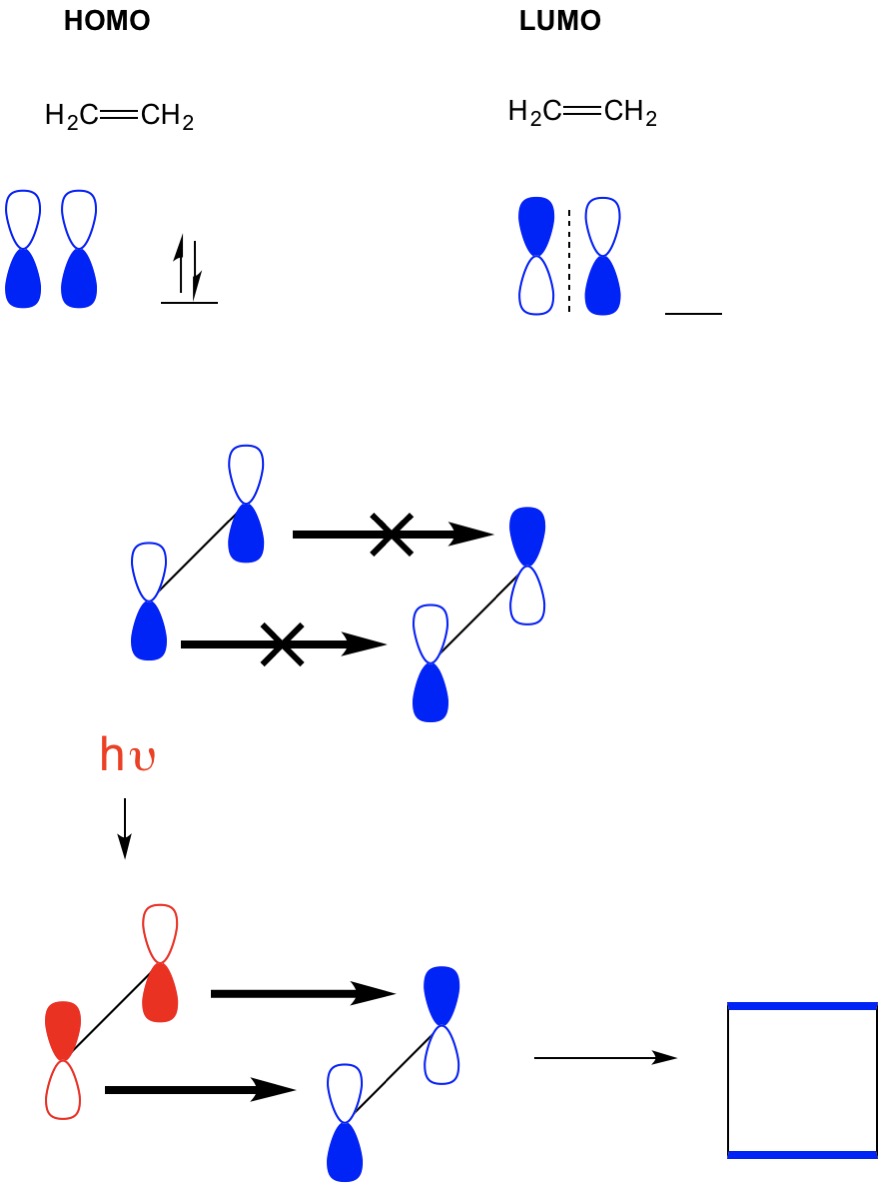
For chem videos, quizzes and more download Chemistry X for free on the App Store! Correlation Diagrams - by considering the positions and energies of electr...
Ab initio MO calculations with the 6-31+G* basis sets are carried out on the identity exchanges X(-) + RX reversible arrow XR + X(-) with X = F and Cl, and geometries and the HF (Delta E(HF ...
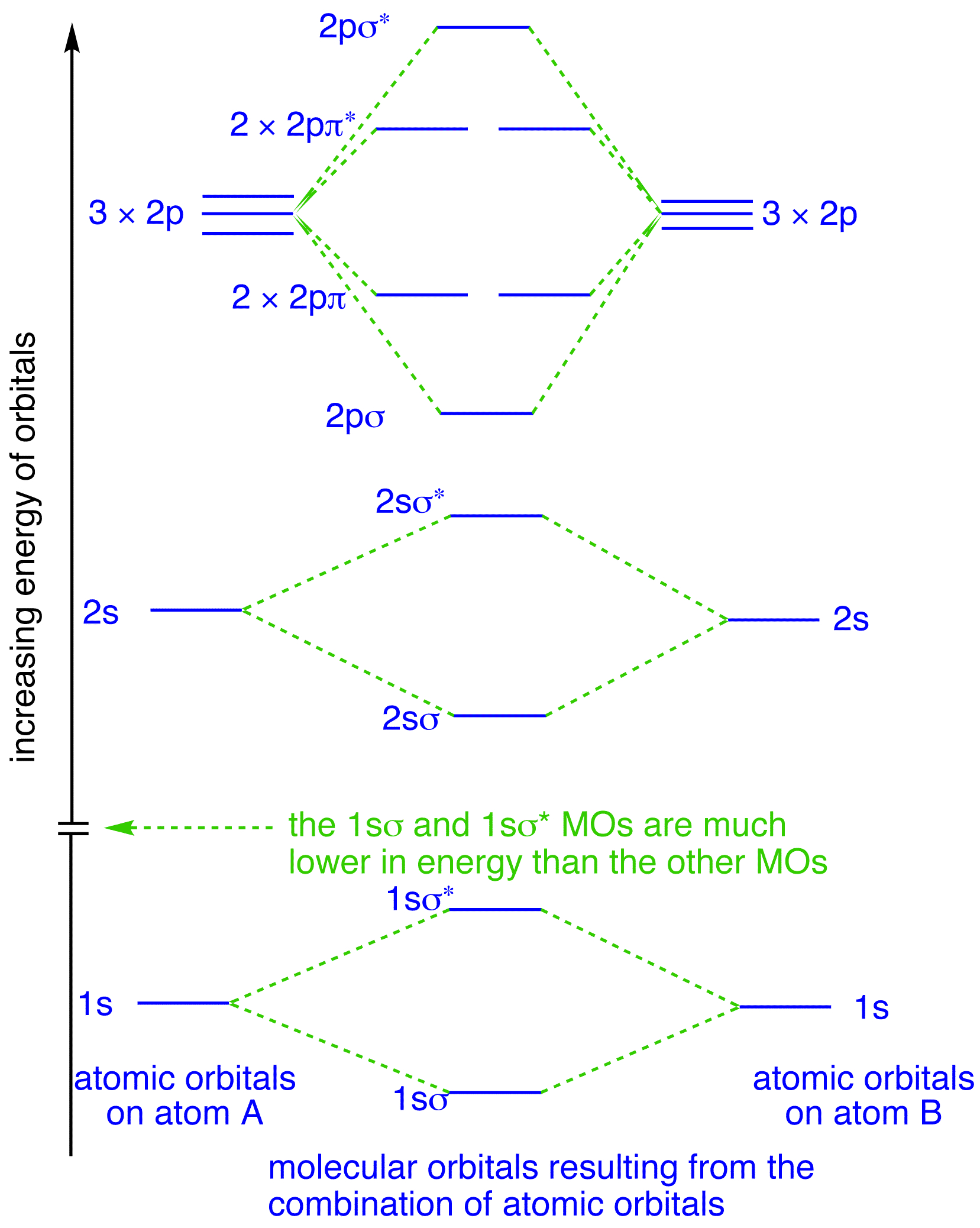
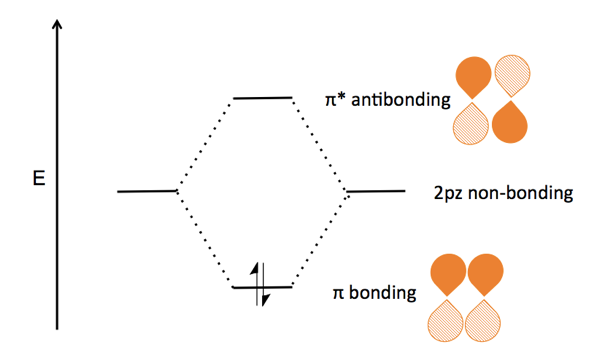
This is called the "Bonding molecular orbital" This is called the "Anti-bonding molecular orbital" 0 x V r -d d EB EA ECE 407 - Spring 2009 - Farhan Rana - Cornell University 0 x V r 1s atomic energy level 0 x V r -d d 2Vss Energy levels of the molecule LCAO: Energy Level Splitting and the Energy Matrix Element Bonding
Lecture43 bining Localized electron and molecular orbital model molecular orbital theory - khan academy help center molecular orbital theory follow sanjay d souza and i think that a step by step overview by khan academy would really make a difference 1 Molecular Orbitals of Ethene
Valence Bond Model vs. Molecular Orbital Theory . Because arguments based on atomic orbitals focus on the bonds formed between valence electrons on an atom, they are often said to involve a valence-bond theory.. The valence-bond model can't adequately explain the fact that some molecules contains two equivalent bonds with a bond order between that of a single bond and a double bond.
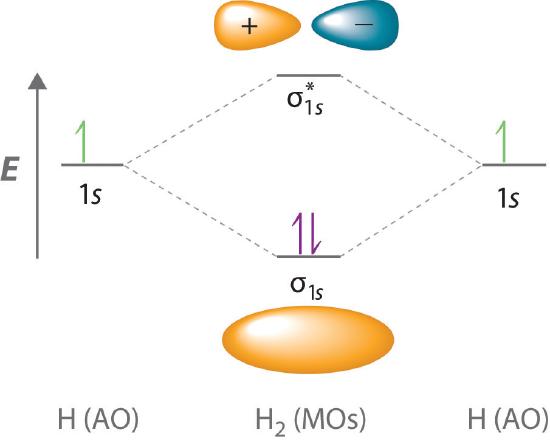
The energy levels in a hydrogen molecule can be represented in a diagram - showing how the two 1s atomic orbitals combine to form two molecular orbitals, one bonding (s) and one antibonding (s *). This is shown below - by clicking upon either the s or s * molecular orbital in the diagram - it will show graphically in a window to the right: 3.
Take A Sneak Peak At The Movies Coming Out This Week (8/12) Why Your New Year’s Resolution Should Be To Go To The Movies More; Minneapolis-St. Paul Movie Theaters: A Complete Guide
I actually consider myself good at math. I genuinely like this subject. But seriously how am I supposed to understand. " Definition 1.5.1 If A is an m × n matrix then by the transpose of A we mean the n × m matrix AT whose (i, j)th element is the (j, i)th element of A. If A = [aij ]m×n, then AT= [aji]n×m."
Clever is a digital learning platform for K12 schools--one friendly place for single sign-on, messaging, analytics, and more.
The electrons in an atom are arranged in shells that surround the nucleus, with each successive shell being farther from the nucleus. Electron shells consist of one or more subshells, and subshells consist of one or more atomic orbitals. Electrons in the same subshell have the same energy, while electrons in different shells or subshells have different energies.
To answer such questions different theories and concepts have been put forward from time to time. In this fourth unit of class 11 chemistry, we can answer the above questions by learning Kössel-Lewis approach, Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory, Valence Bond (VB) Theory and Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory.






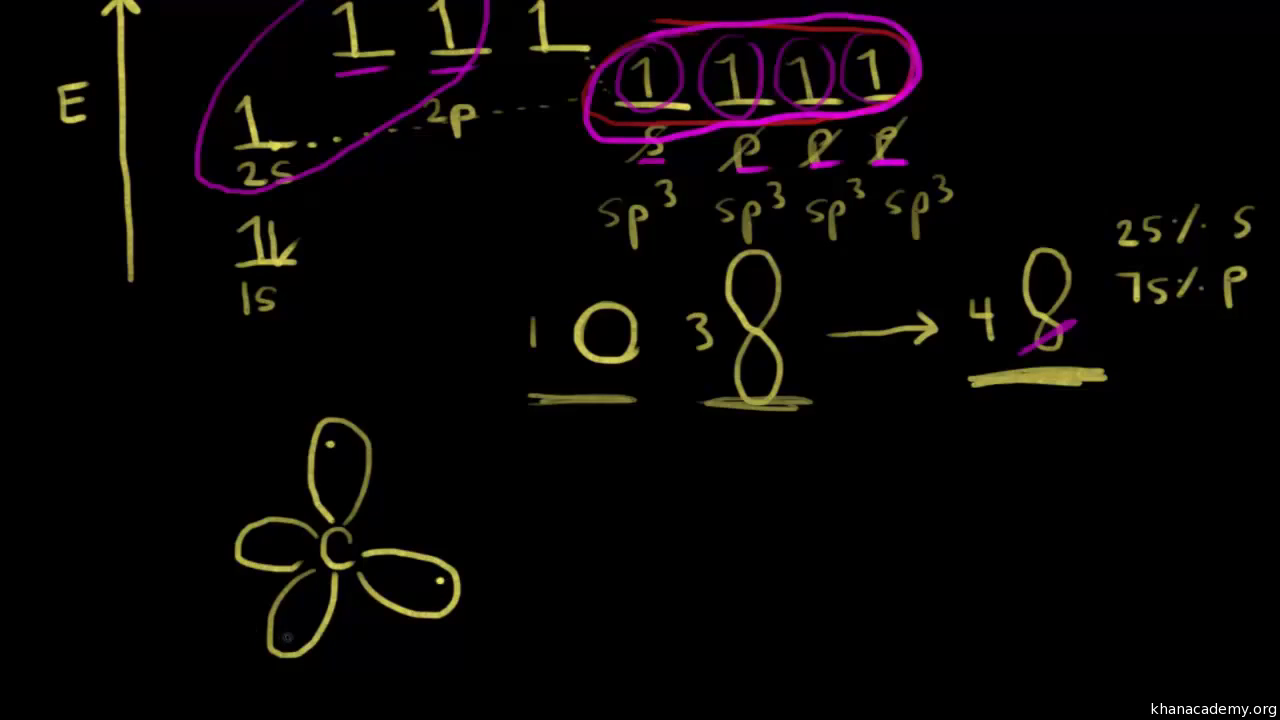






![Crystal Field Theory Valence Bond Theory [cof6] 3 Plex Ion ...](https://www.untpikapps.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/crystal-field-theory-valence-bond-theory-cof6-3-plex-ion-molecular-orbital-diagram-khan-academy.jpg)











0 Response to "42 mo diagram khan academy"
Post a Comment