43 the diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental dna).
The two strands of DNA form a 3-D structure called a double helix. In this diagram showing the replicationof DNA, label the following items: leading and lagging strands, Okazaki fragment, DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, helicase, primase, single-stranded binding proteins, RNA primer, replication fork, and 5' and 3' ends of the parental DNA. Shown below is a double stranded DNA molecule.Replicate this DNA and show the products formed from this replication. In your answer, indicate which strands are the new daughter strands (mark with D and in a different color) and which strands are the already existing parent strands (mark with P as shown below). Label the 5' and 3' ends of all DNA.
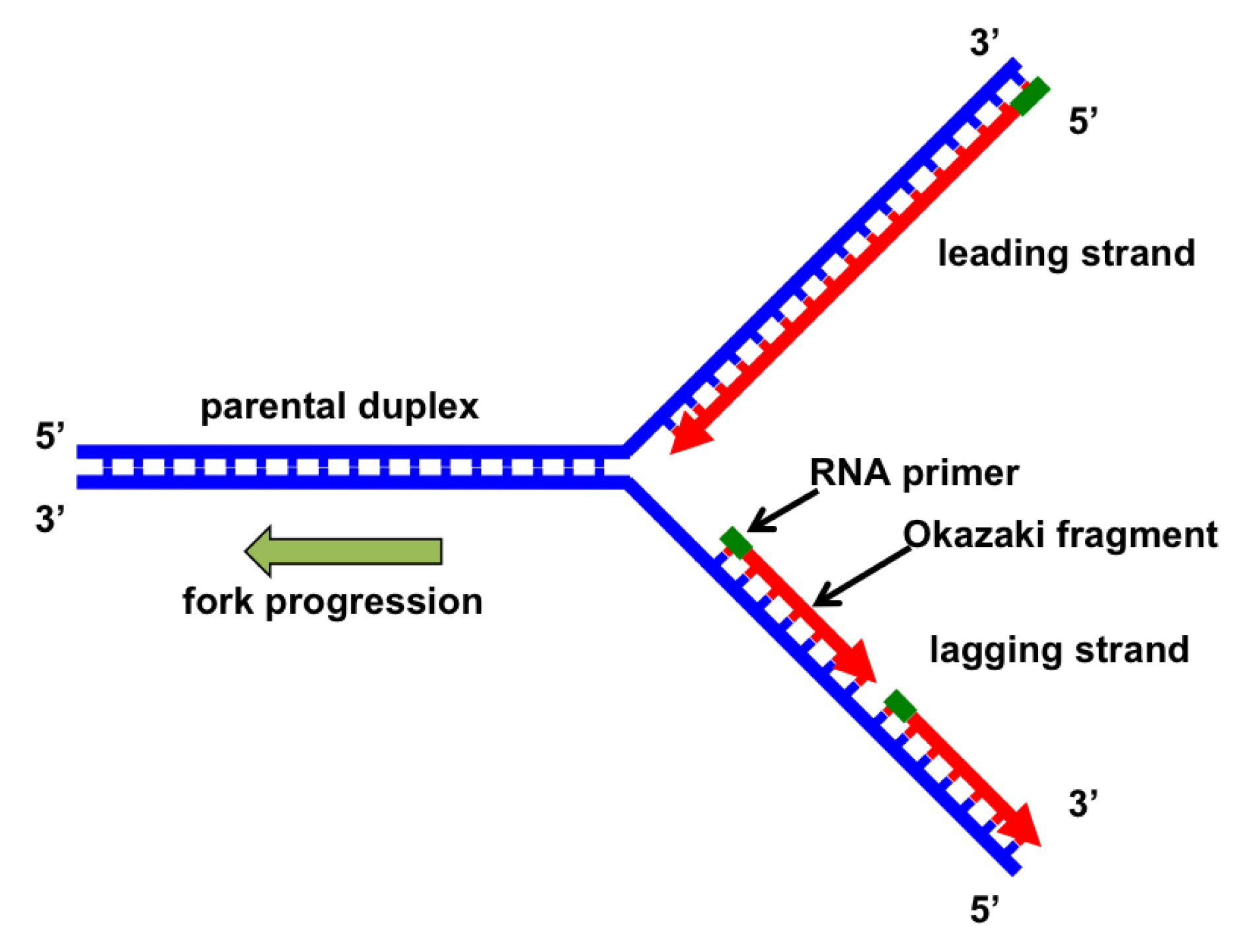
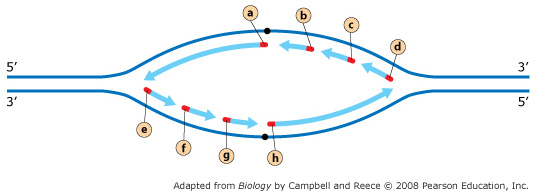
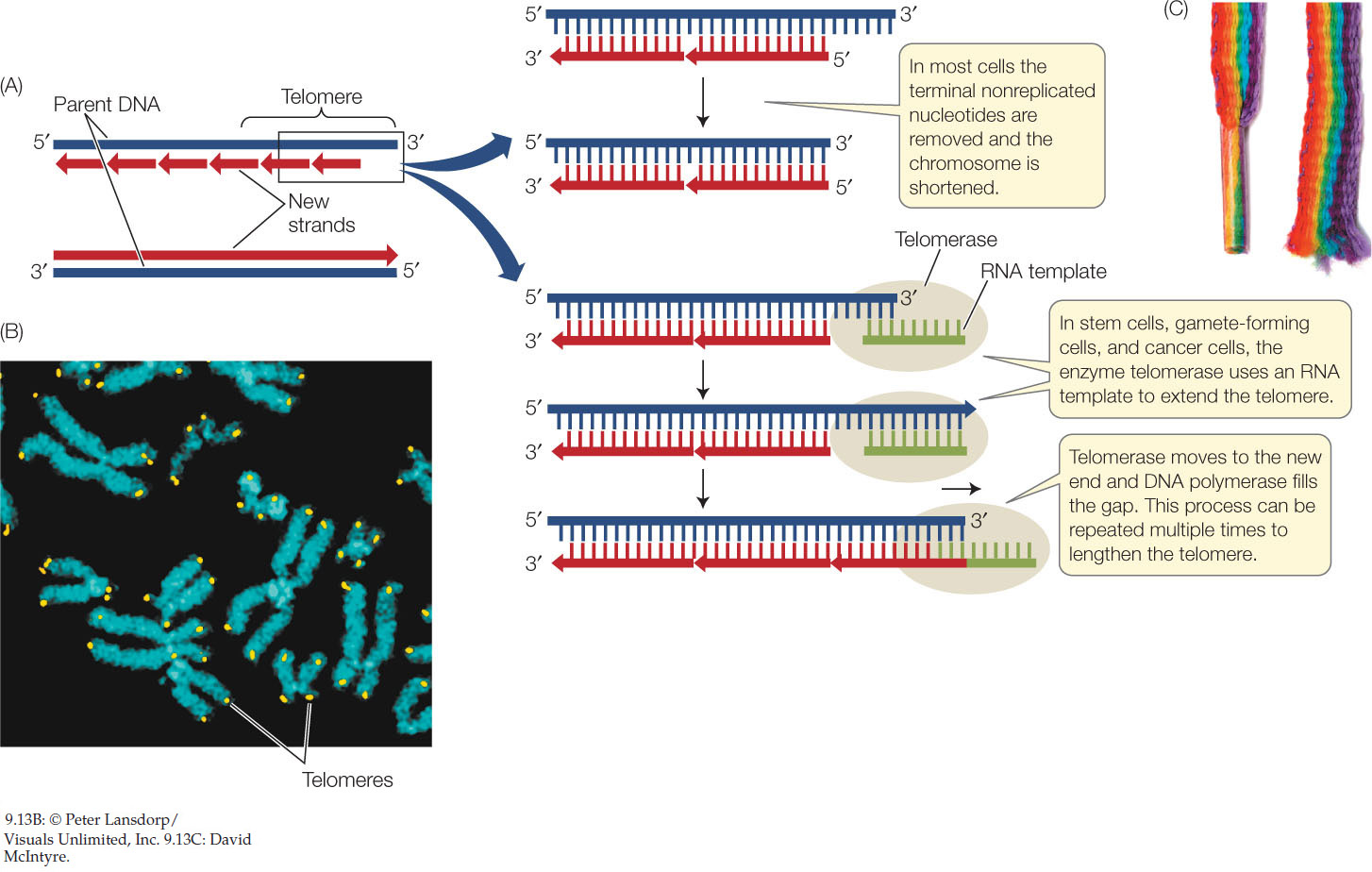
The diagram below shows a replication bubble with synthesis of the leading and lagging strands on both sides of the bubble. The parental DNA is shown in dark blue, the newly synthesized DNA is light blue, and the RNA primers associated with each strand are red. The origin of replication is indicated by the black dots on the parental strands.

The diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental dna).
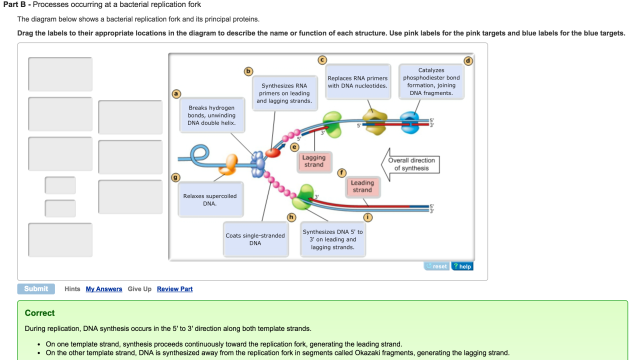
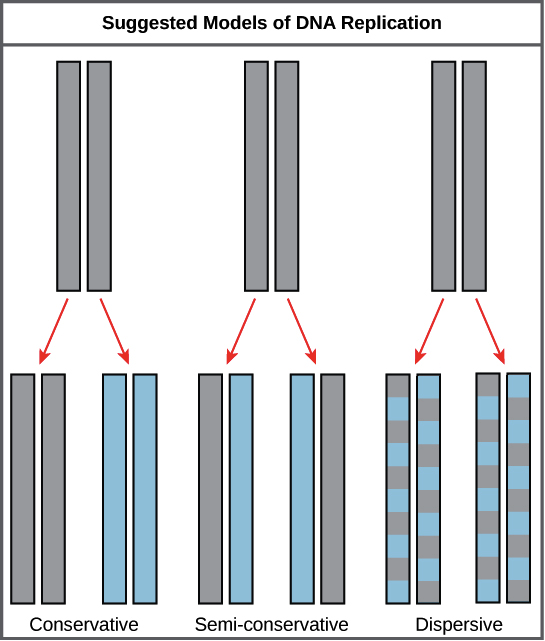
The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter DNA molecules after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red. Genetic information present in double stranded DNA molecule is transmitted from one cell to another cell at the time of mitosis and from parent to progency by faithful replication of parental DNA molecules. DNA molecule is coiled and twisted and has enormous size. This imposes several restrictions on DNA replication. The role of hydrogen bonds in DNA structure In a DNA double helix, the two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs. When two single complementary strands of DNA are near each other, hydrogen bonding between the bases usually causes the two strands to join and form a double helix.
The diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental dna).. The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter DNA molecules after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red. Initially, the simplest mechanism of DNA replication seemed to be the continuous growth of both new strands, nucleotide by nucleotide, at the replication fork as it moves from one end of a DNA molecule to the other. But because of the antiparallel orientation of the two DNA strands in the DNA double helix (see Figure 5-2), this mechanism would require one daughter strand to polymerize in the 5 ... During DNA replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or "old" strand. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. This is known as semiconservative replication. Figure 7: To better fit within the cell, long pieces of double-stranded DNA are tightly packed into structures called chromosomes. Most cells are incredibly small. For instance, one human alone ...
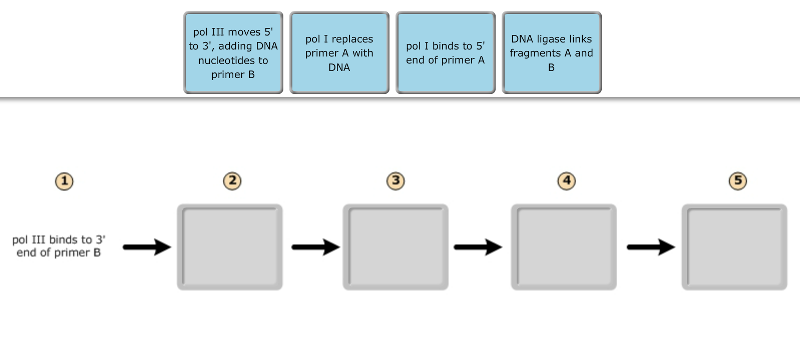
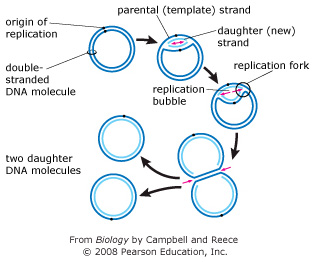
View Mastering Bio DNA.png from BIOLOGY 171L at University of Hawaii, Manoa. Part A - The mechanism of DNA replication The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the DNA helicase separates nucleotides by breaking hydrogen bonds. The double strand unwinds and unzips. The new DNA molecule has two newly-made strands. Tags: Question 13. SURVEY. 30 seconds. Q. The diagram below represents a process that occurs in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. Watson and Wilkins for the discovery of the molecular structure of DNA - the double helix. Chemical Structure of the DNA double strands DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a double-stranded molecule that is twisted into a helix like a spiral staircase. Each strand is comprised of a sugar-phosphate backbone and numerous base chemicals attached in ... Chromatin structure and DNA replication. The diagram below shows a replication fork with the two parental DNA strands labeled at their 3' and 5 4/4(5). DNA replication Stage one. transcription. After DNA replication (S phase of the cell cycle), it was observed that. Dna Transcription And Translation Worksheet Answer Key.
The region enclosed by the box includes the two parental DNA strands (dark blue) and the two newly synthesized strands (light blue). synthesizing a new, complementary strand. The diagram below shows a replication fork with the two parental DNA strands labeled at their 3' and 5 4/4 (5). A DNA Molecule Consists of Two Complementary Chains of Nucleotides. A DNA molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotide subunits. Each of these chains is known as a DNA chain, or a DNA strand.Hydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together ().As we saw in Chapter 2 (Panel 2-6, pp. 120-121), nucleotides are ... The diagram below shows a replication bubble with synthesis of the leading and lagging strands on both sides of the bubble. The parental DNA is shown in dark blue, the newly synthesized DNA is light blue, and the RNA primers associated with each strand are red. The origin of replication is indicated by the black dots on the parental strands. Part A - The mechanism of DNA replication The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter DNA molecules after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red.
The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental duplex). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red.
The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental duplex). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter duplexes after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red. Best Answer
This structure is described as a double-helix, as illustrated in the figure above. It is a nucleic acid, and all nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides. The DNA molecule is composed of units called nucleotides, and each nucleotide is composed of three different components, such as sugar, phosphate groups and nitrogen bases.
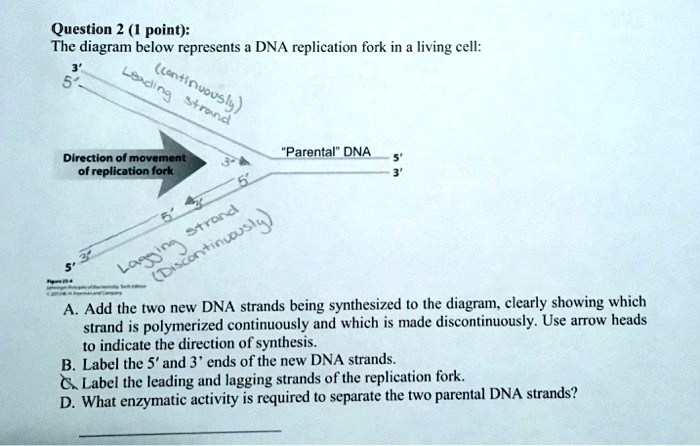
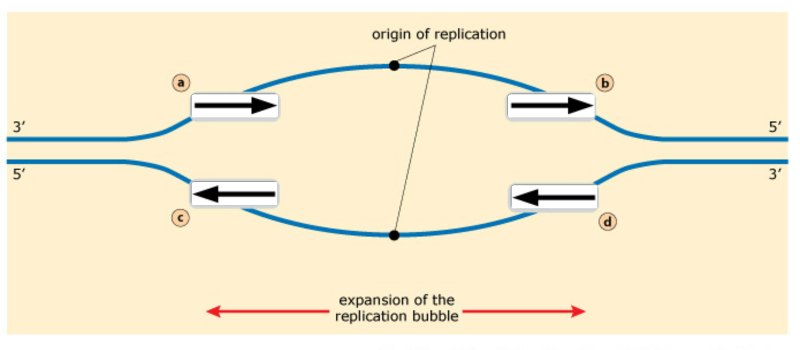
1. Below is a replication fork (one side of an origin): a double-stranded DNA partially opened up to provide single-stranded regions where replication can occur. Draw and label the following: RNA primers (label 3′ and 5′ ends), leading-strand DNA polymerase and new DNA (label 3′ and 5′ ends and show direction of synthesis
The role of hydrogen bonds in DNA structure In a DNA double helix, the two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs. When two single complementary strands of DNA are near each other, hydrogen bonding between the bases usually causes the two strands to join and form a double helix.
Genetic information present in double stranded DNA molecule is transmitted from one cell to another cell at the time of mitosis and from parent to progency by faithful replication of parental DNA molecules. DNA molecule is coiled and twisted and has enormous size. This imposes several restrictions on DNA replication.
The diagram below shows a double-stranded DNA molecule (parental DNA). Drag the correct labels to the appropriate locations in the diagram to show the composition of the daughter DNA molecules after one and two cycles of DNA replication. In the labels, the original parental DNA is blue and the DNA synthesized during replication is red.


















0 Response to "43 the diagram below shows a double-stranded dna molecule (parental dna)."
Post a Comment