42 Cardiac Cycle Diagram Labeled
The Anatomy of the Heart, Its Structures, and Functions The heart is the organ that helps supply blood and oxygen to all parts of the body. It is divided by a partition (or septum) into two halves. The halves are, in turn, divided into four chambers. The heart is situated within the chest cavity and surrounded by a fluid-filled sac called the pericardium. This amazing muscle produces electrical ... Unlabeled Wiggers Diagram - schematron.org English: A Wiggers diagram, showing the cardiac cycle events occuring in the left ventricle. In the atrial pressure plot: wave "a" corresponds to atrial contraction. Please use the Wiggers diagrams below showing systemic arterial, left ventricular, and left atrial . The diagram below contains five sets of tracings, labeled "A".
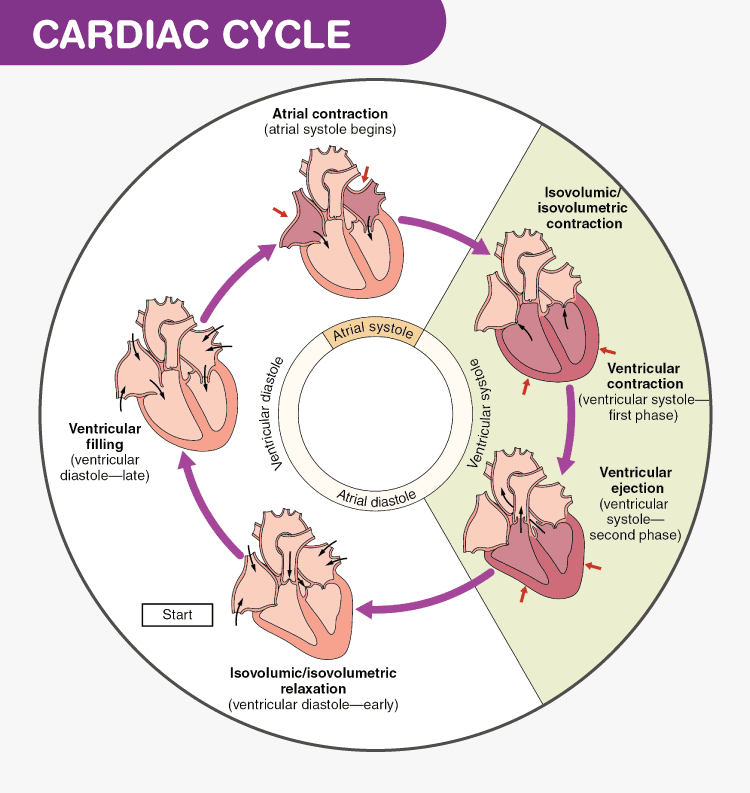
Cardiac Cycle- Physiology, Diagram, Phases of the Cardiac ... Cardiac Cycle Diagram The diagram below represents the different phases of the cardiac cycle. The atrial systole, ventricular diastole, ventricular systole and ventricular diastole are clearly mentioned in the cardiac cycle diagram given below. Cardiac Cycle Physiology The human heart consists of four chambers, comprising left and right halves.

Cardiac cycle diagram labeled
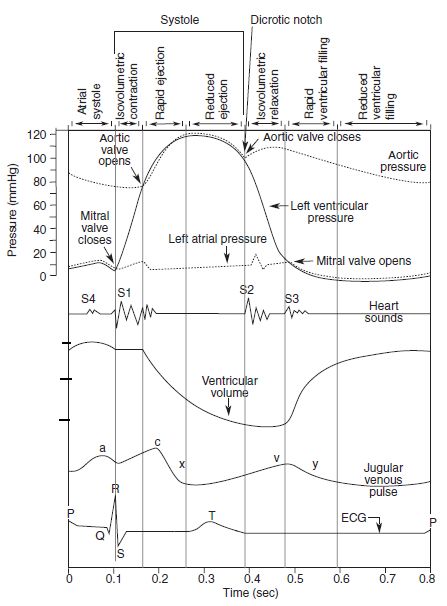
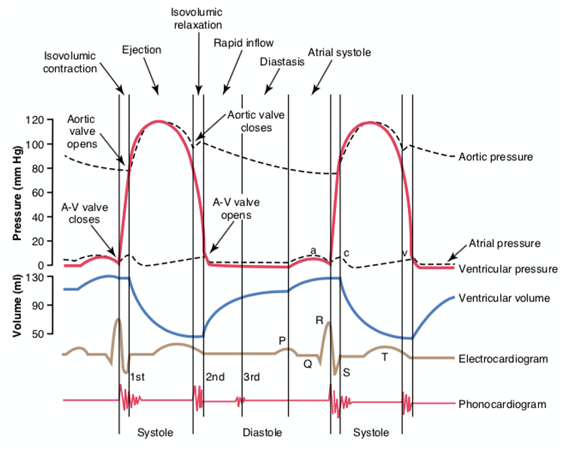
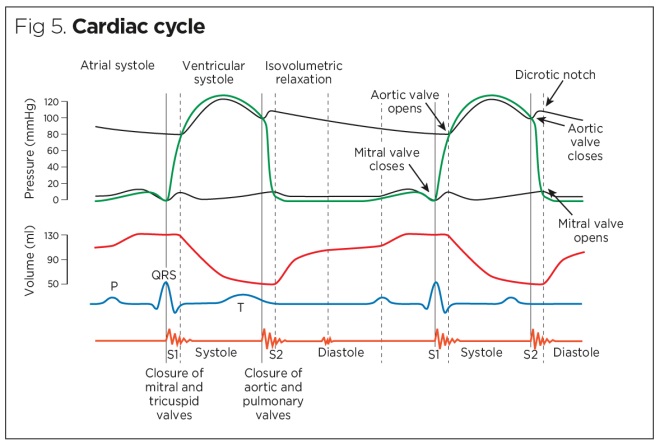
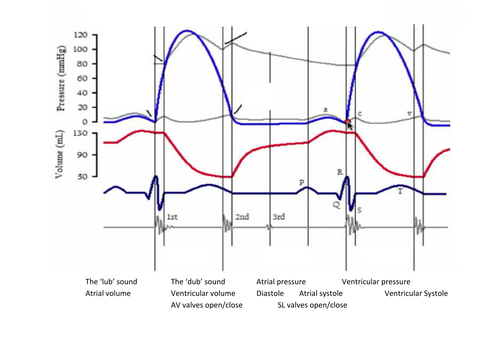
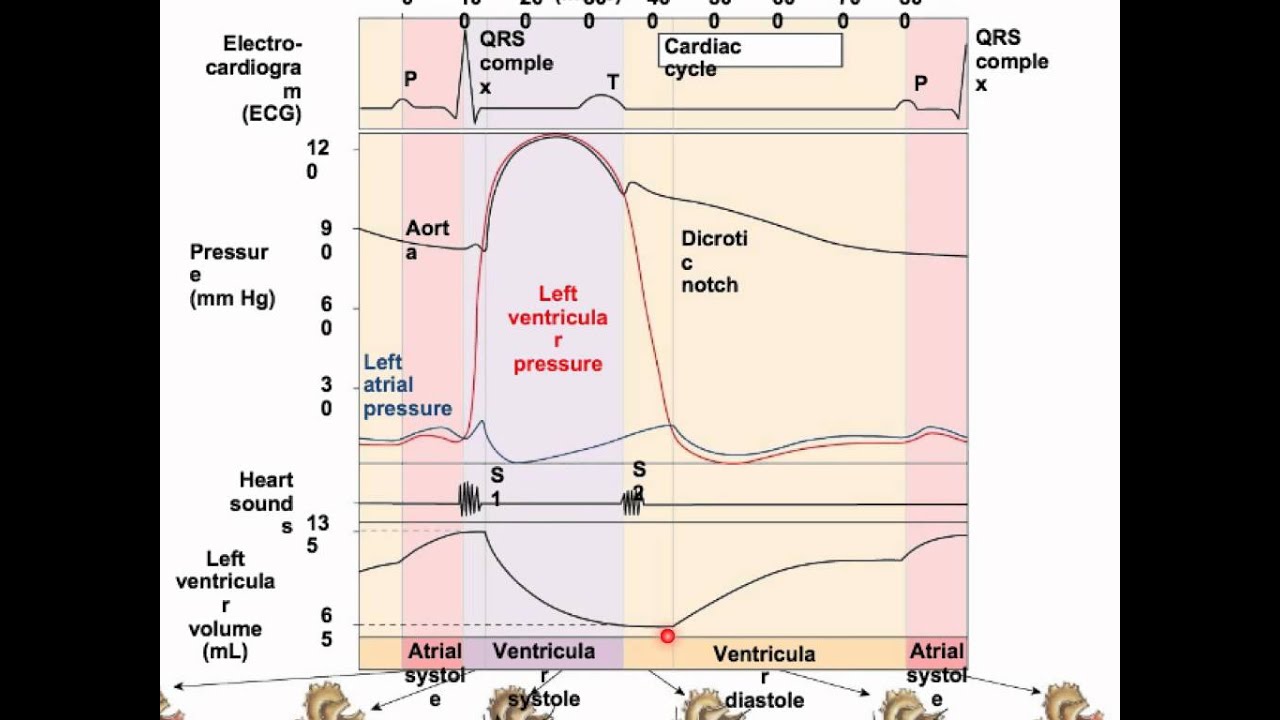
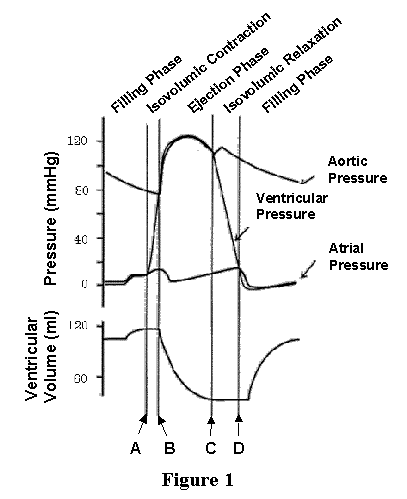
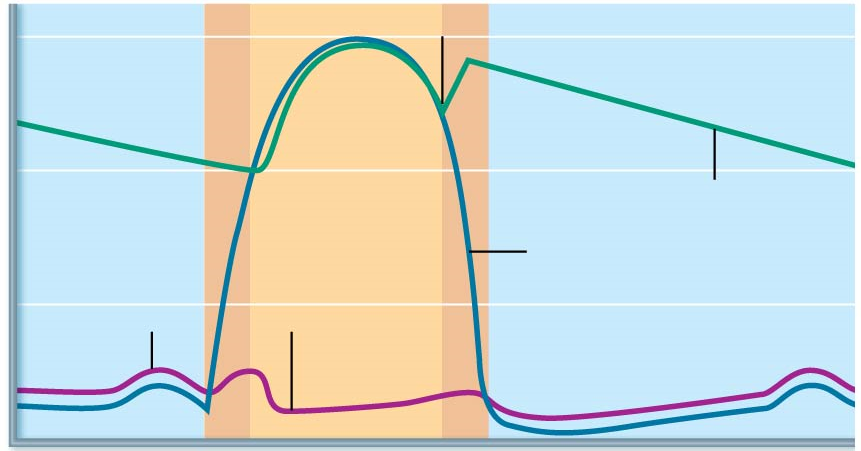
The Wright table of the cardiac cycle: a stand-alone ... This diagram remains the most commonly used model to teach the cardiac cycle today. A typical Wiggers diagram is shown in Fig. 1. Fig. 1. The Wiggers diagram. From top to bottom, the lines show: 1) aortic pressure, 2) ventricular pressure, 3) atrial pressure, 4) electrocardiogram, 5) mitral and aortic valve opening and closing, and 6) heart sounds. 1.6 Anatomical Terminology - Anatomy and Physiology - OpenStax Body Planes. A section is a two-dimensional surface of a three-dimensional structure that has been cut. Modern medical imaging devices enable clinicians to obtain “virtual sections” of living bodies. We call these scans. Body sections and scans can be correctly interpreted, however, only if the viewer understands the plane along which the section was made. The cardiac cycle and Wiggers diagram The cycle diagram depicts one heartbeat of the continuously repeating cardiac cycle, namely: ventricular diastole followed by ventricular systole, etc.—while coordinating with atrial systole followed by atrial diastole, etc.The cycle also correlates to key electrocardiogram tracings: the T wave (which indicates ventricular diastole); the P wave (atrial systole); and the QRS 'spikes' complex ...
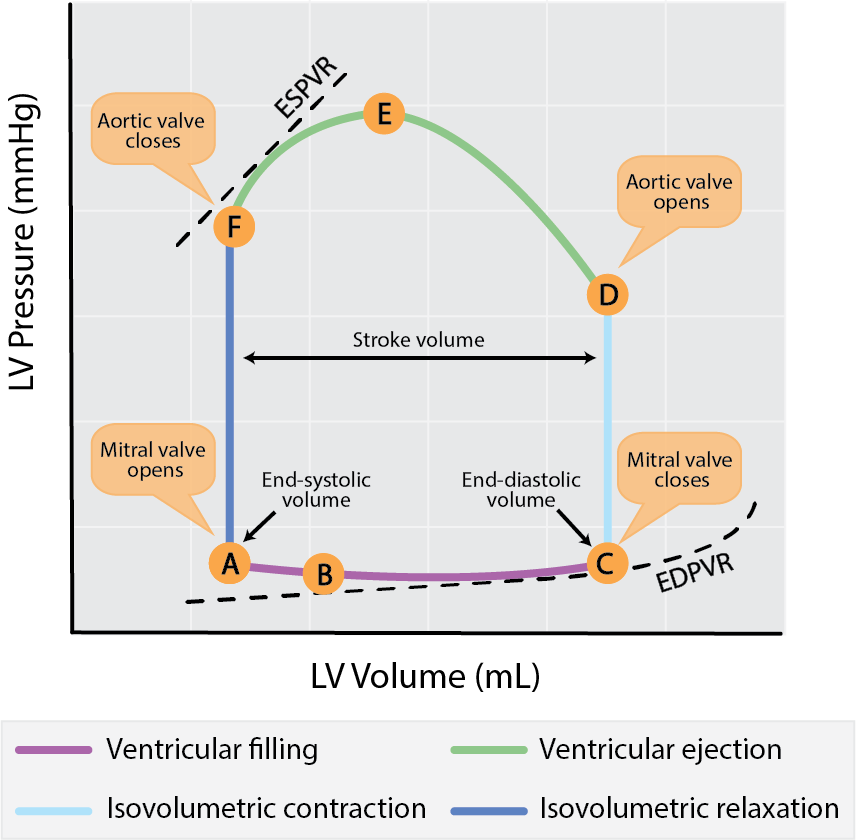
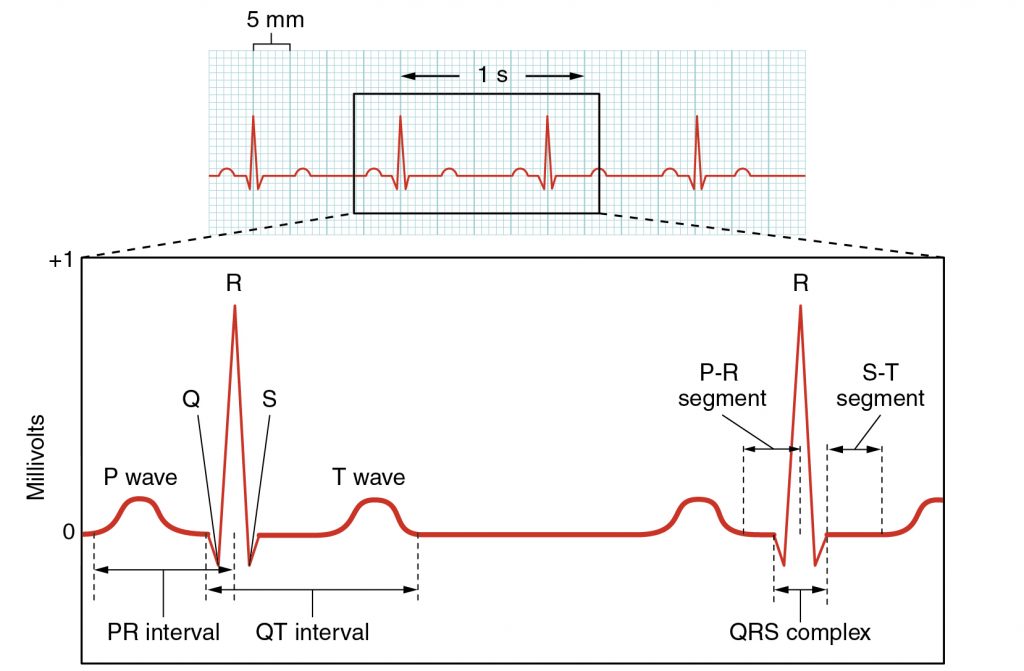
Cardiac cycle diagram labeled. EKG or ECG Waveform Parts Easily Explained and Labeled - EZmed EKG or ECG waveform parts are explained clearly to make EKG interpretation easy. Learn the meaning of each component of an EKG wave with this step-by-step labeled diagram of the conduction system of the heart. Provides information on atrial depolarization and the P wave, ventricular depolarization a DOC Cardiac Cycle - Parker University For each phase of the cardiac cycle: (1) Draw in arrows to indicate direction blood flow (2) Draw in the heart valves to indicate whether they are open or closed. (3) Color in the relative amounts of blood within each chamber or arterial trunk. Diastole Isovolumic Relaxation Rapid Inflow Atrial Systole Systole Isovolumic Contraction Ejection The Cardiac Cycle V: The Wiggers Diagram - Anatomy ... The Cardiac Cycle III: Volumes in the Left Ventricle: 6 mins: 0 completed: Learn. The Cardiac Cycle IV: Heart Sounds: 7 mins: 0 completed: Learn. The Cardiac Cycle V: The Wiggers Diagram: 10 mins: 0 completed: Learn. The Cardiac Cycle VI: The Ventricular Pressure-Volume Loop: 9 mins: 0 completed: Learn. Cardiac Output I: Definitions: 5 mins: 0 ... PDF The Cardiac Cycle THE CARDIAC CYCLE Objectives: Identifying Factors which affect heart rate Describe Cardiac Functional Anatomy (including a review of blood flow and valves) Understand the Wiggers Diagram of Cardiac Cycle Differentiate between Wiggers Diagram and the Pressure Volume Curve Review the electrical basis of excitable cardiac tissue
Cardiac Cycle and Heart Anatomy | Human Anatomy - Quizizz The left ventricle must force blood into all the capillaries of the lungs. the left ventricle doesn't skip leg day. This is false, the walls of the right ventricle are thicker. Blood from the left ventricle is pumped throught the entire body. The left ventricle must force blood into all the capillaries of the lungs. Transcription of DNA - Stages - TeachMePhysiology 20.9.2021 · DNA transcription is the process by which the genetic information contained within DNA is re-written into messenger RNA (mRNA) by RNA polymerase. This mRNA then exits the nucleus, where it acts as the basis for the translation of DNA. By controlling the production of mRNA within the nucleus, the cell regulates the rate of gene expression.In this article we will … Diagram of the phases of cardiac cycle with main parts ... Download Diagram of the phases of cardiac cycle with main parts labeled. Circulation of blood through the heart. Vector illustration in flat style over white background. Stock Vector and explore similar vectors at Adobe Stock. PDF The Cardiac Cycle the cardiac cycle. Quiz Questions #3a, 4a, 5a, 6a: Cardiac Cycle Phase • These question asks you to view a diagram of the heart and predict what stage of the cell cycle it's in. You may take notes on the diagrams below. The dye-labeled blood has been colored light here to make it more visible. Quiz Question #3b, 4b, 5b, 6b: Cardiac Cycle Graphs
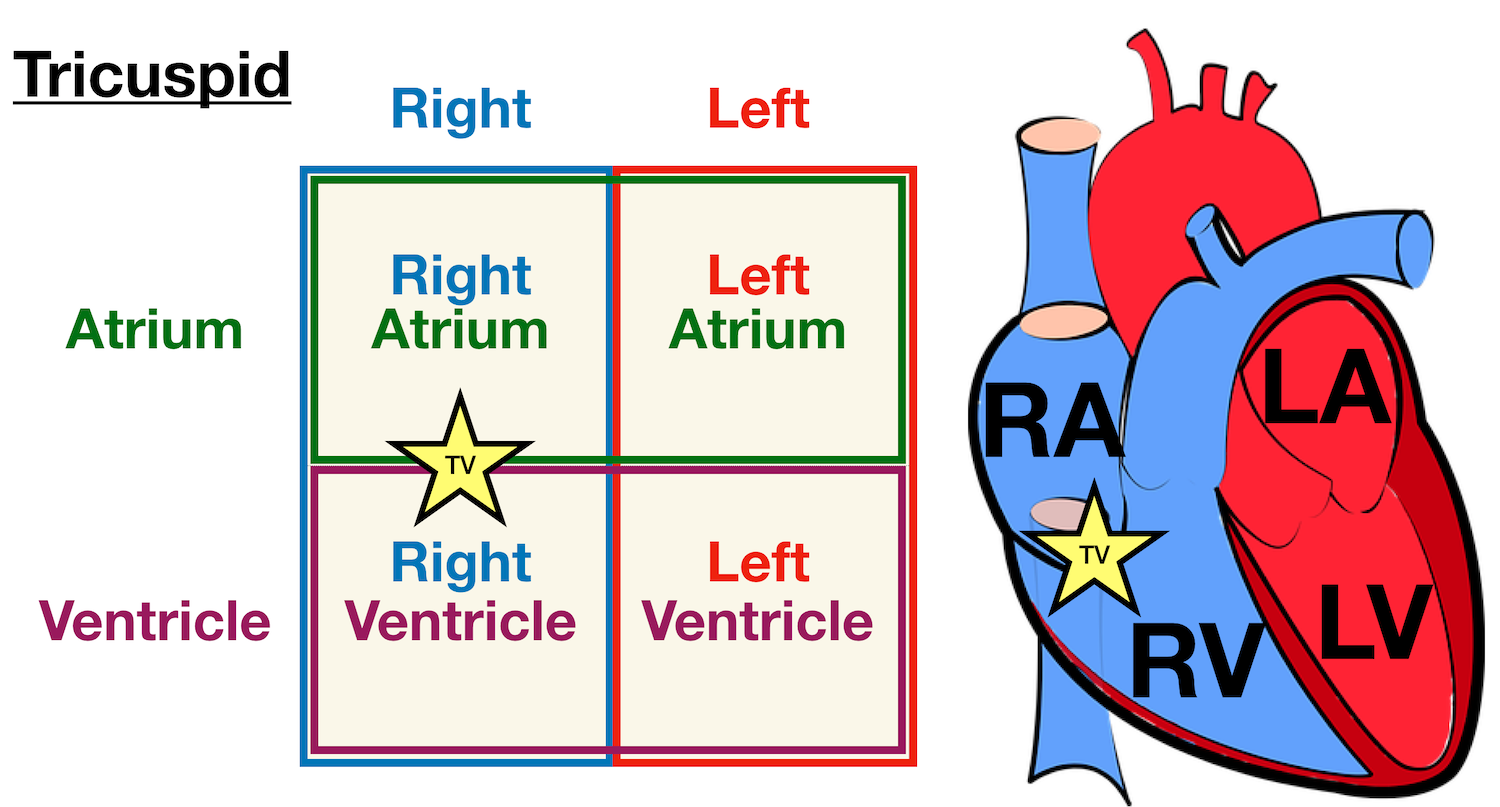
Cardiac Cycle - Summary and Wigger's Diagram | Epomedicine The duration of 1 cardiac cycle is 0.8 seconds. The cycles are different in the atria and the ventricles. Atrial systole makes up only 0.1 second and is responsible for active ventricular filling. The remaining 0.7 seconds, the atria relaxes and receives venous return from the venacavae. Electrocardiography - Clinical Methods - NCBI Bookshelf The electrocardiogram (ECG) records from the body surface and registers the differences in electrical potential generated by the heart. The signal recorded is determined by action potentials generated by millions of individual cells and their sequence of activation. A multitude of factors, both cardiac and extracardiac, alter the final electrical signal. Heart Anatomy: Labeled Diagram, Structures, Blood Flow ... Image: Cardiac anatomy diagram showing the right and left side of the heart. The right side includes chambers 1 and 2. The left side includes chambers 3 and 4. Top vs Bottom of the Heart Next, we can divide the top 2 chambers of the heart from the bottom 2 chambers. The 2 chambers on top are known as the atria, and they include boxes 1 and 3. PDF Cardiovascular Physiology lab - University of Hawaiʻi You should be able to label a figure like this and relate it to the conducEon aspects of the cardiac cycle. Describe what is occurring in each panel of this diagram. Be able to label all the parts of the heart and associated blood vessels. ObjecEve 2 BP & Pulse: Indicate the normal length of the cardiac cycle, the relave
Cardiac cycle phases: Definition, systole and diastole ... The cardiac cycle is defined as a sequence of alternating contraction and relaxation of the atria and ventricles in order to pump blood throughout the body. It starts at the beginning of one heartbeat and ends at the beginning of another. The process begins as early as the 4th gestational week when the heart first begins contracting.. Each cardiac cycle has a diastolic phase (also called ...
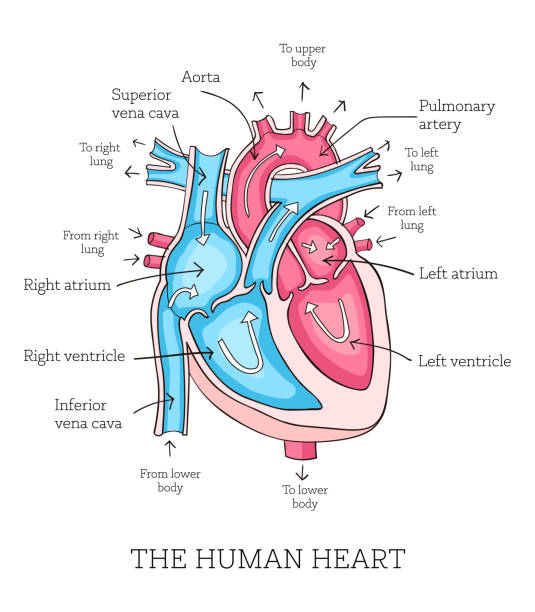
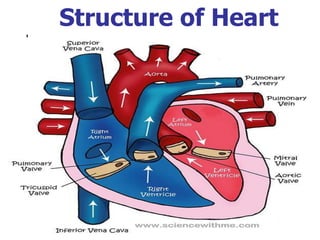
Heart Blood Flow | Simple Anatomy Diagram, Cardiac ... Diagram: Blood flow through the heart, cardiac circulation pathway steps, and cardiac anatomy and structures. Blue arrows (deoxygenated blood); Red arrows (oxygenated blood). Now that we have a good understanding of the blood flow through the heart using the cartoon diagrams, we can apply it to a more realistic image of the heart.
Wiggers Diagram - Human Physiology A Wiggers diagram shows the changes in ventricular pressure and volume during the cardiac cycle. Often these diagrams also include changes in aortic and atrial pressures, the EKG, and heart sounds. Diastole starts with the closing of the aortic valve (the second heart sound).
19.3 Cardiac Cycle - Anatomy & Physiology The period of timethat begins with contraction of the atria and ends with ventricular relaxation is known as the cardiac cycle (Figure 19.3.1).The period of contraction that the heart undergoes while it pumps blood into circulation is called systole.The period of relaxation that occurs as the chambers fill with blood is called diastole.Both the atria and ventricles undergo systole and diastole ...
PDF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM - BiologyMad THE CARDIAC CYCLE 1. The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in one heartbeat. In its simplest form, the cardiac cycle is the simultaneous contraction of both atria, followed a fraction of a second later by the simultaneous contraction of both ventricles. 2. The heart consists of cardiac muscle cells that connect with each other - they are branched - and
Cardiac Cycle with Heart Diastole and Systole Process ... Cardiac cycle with heart diastole and systole process labeled outline diagram. Illustration about circulation, medicine, artery, care, cardiac, pumping, medical, system - 221540249
Cardiac Cycle Phases & Diagram | What is the Cardiac Cycle ... The cardiac cycle has alternating phases of contraction, called systole, and relaxation or diastole. Based on a heart rate of 75 beats per minute, one cycle lasts about 800 milliseconds.
PDF LC: Label the heart and describe the cardiac cycle LC: Label the heart and describe the cardiac cycle Starter: 1. Which side of the heart contains oxygenated blood? 2. Which side of the heart has is larger 3. Can you explain why it is larger? 4. What is the purpose of valves?
Cardiac Cycle Phases and Blood Flow: Step-By-Step Heart ... The cardiac cycle has 2 main phases, systole and diastole, defined by whether the heart is depolarized and contracting vs repolarized and relaxed. This post will walk you through one cycle of the heart using a step-by-step diagram that will provide you with easy notes and a simple explanation of cardiac physiology.
Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity | Anatomy and ... Identify blocks that can interrupt the cardiac cycle Recall that cardiac muscle shares a few characteristics with both skeletal muscle and smooth muscle, but it has some unique properties of its own. Not the least of these exceptional properties is its ability to initiate an electrical potential at a fixed rate that spreads rapidly from cell to cell to trigger the contractile mechanism.
PDF Cardiovascular System Components of the Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System Components of the Cardiovascular System • consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels • transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs) & systemic (the rest of the body) • responsible for the flow of blood, nutrients, oxygen and other gases, and hormones to and from cells • about 2,000 gallons (7,572 liters) of blood ...
PDF Colour Heart Diagram Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart Page 10 Developed by Tony Curran (Clinical Nurse Educator) and Gill Sheppard (Clinical Nurse Specialist) Cardiology (October 2011) The four heart valves open and close in response to pressure changes that occur in the ventricles during each cardiac cycle.
The Cardiac Cycle Diagram Flashcards - Quizlet Start studying The Cardiac Cycle Diagram. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Cardiac Cycle - CV Physiology The cardiac cycle diagram shown to the right depicts changes in aortic pressure (AP), left ventricular pressure (LVP), left atrial pressure (LAP), left ventricular volume (LV Vol), and heart sounds during a single cycle of cardiac contraction and relaxation. These changes are related in time to the electrocardiogram.
PDF The Cardiovascular System - Pearson (mi″o-kar′de-um) consists of thick bundles of cardiac muscle twisted and whorled into ringlike arrange-ments (see Figure 6.2b, p. 184). It is the layer that actually contracts. Myocardial cells are linked together by intercalated discs, which contain both desmo-somes and gap junctions. The gap junctions at the
The cardiac cycle and Wiggers diagram The cycle diagram depicts one heartbeat of the continuously repeating cardiac cycle, namely: ventricular diastole followed by ventricular systole, etc.—while coordinating with atrial systole followed by atrial diastole, etc.The cycle also correlates to key electrocardiogram tracings: the T wave (which indicates ventricular diastole); the P wave (atrial systole); and the QRS 'spikes' complex ...
1.6 Anatomical Terminology - Anatomy and Physiology - OpenStax Body Planes. A section is a two-dimensional surface of a three-dimensional structure that has been cut. Modern medical imaging devices enable clinicians to obtain “virtual sections” of living bodies. We call these scans. Body sections and scans can be correctly interpreted, however, only if the viewer understands the plane along which the section was made.
The Wright table of the cardiac cycle: a stand-alone ... This diagram remains the most commonly used model to teach the cardiac cycle today. A typical Wiggers diagram is shown in Fig. 1. Fig. 1. The Wiggers diagram. From top to bottom, the lines show: 1) aortic pressure, 2) ventricular pressure, 3) atrial pressure, 4) electrocardiogram, 5) mitral and aortic valve opening and closing, and 6) heart sounds.











.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/diastole-597a49286f53ba00110ad63f.jpg)








0 Response to "42 Cardiac Cycle Diagram Labeled"
Post a Comment