45 Atomic Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen
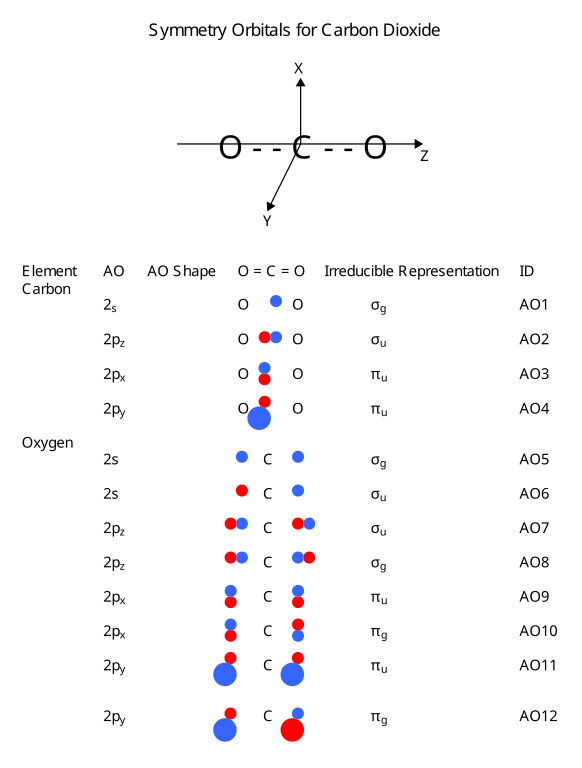
MO diagram for formation of nitrogen molecule from atoms ... Presented diagram shows how the atomic orbitals of two N atoms combine to form molecular orbitals of nitrogen molecule: each nitrogen atom has three one-occupued p-orbitals and when the atoms interact they produce three bonding molecular orbitals of nitrigen molecule - one of sigma-type(symmetry) (from atoms p z) and two pi-type (from atoms p x ... Draw the molecular orbital diagram of N2N2 + N2 Write ... Basic structure of molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen is: Electrons of nitrogen are to be filled in this diagram. Left side represents the configuration of one atom of nitrogen molecule and the right side represents the second atom of nitrogen molecule. Atomic number of nitrogen is seven. Therefore in N 2 there are a total fourteen electrons.
Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen (N) | Nitrogen Electron ... The atomic number of nitrogen is 7, the element nitrogen was discovered by a Scottish physician, Danial Rutherford. The year the element was discovered in the year 1772, through our article you will come to know about certain new things about the element Nitrogen. ... What is the Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen? When we talk about the orbital ...

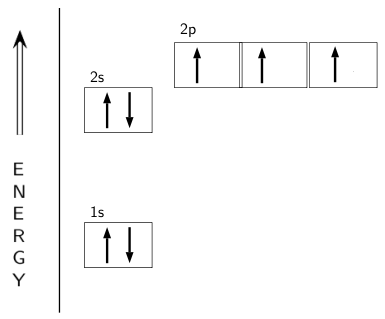
Atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen
Molecular orbital energy level diagrams -Hydrogen ... The molecular orbital energy level diagram of He 2 (hypothetical) is given in Fig. Here, N b = 2 and N a = 2. Bond order = N b -N a / 2 = 2-2 / 2 = 0. As the bond order for He 2 comes out to be zero, this molecule does not exist. 3. Nitrogen molecule (N 2). The electronic configuration of nitrogen (Z=7) in the ground state is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1x 2p ... orbitals - What is the origin of the differences between ... S-p mixing is the primary cause of the difference in the molecular orbitals of nitrogen and oxygen, which is influenced by the initial atomic orbital energies. The lighter second period elements (prior to oxygen) have a relatively small difference in energy between the 2s and 2p orbitals. 4.1 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations ... The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +1 2 m s = + 1 2 ).
Atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. Oxygen(O) electron configuration and orbital diagram The electron configuration of an element with an atomic number greater than 18 cannot be properly determined according to the Bohr atomic model. The electron configuration of all the elements can be done through orbital diagram. Electron configuration of oxygen atom through orbital. Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. How to Do Orbital Diagrams - Sciencing Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics. Electron Configuration Orbital Diagram Nitrogen - YouTube To see this video, other videos, chemistry education text, and practice problems visit my website. Website is 100% FREE to use. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram of class ... The energy level diagram of nitrogen molecule is as follows : From the diagram it is clear that there are four fully filled bonding molecular orbitals and one completely filled antibonding molecular orbital . The bond order is calculated by subtracting the number of electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals ( N b) from the number of electrons ...
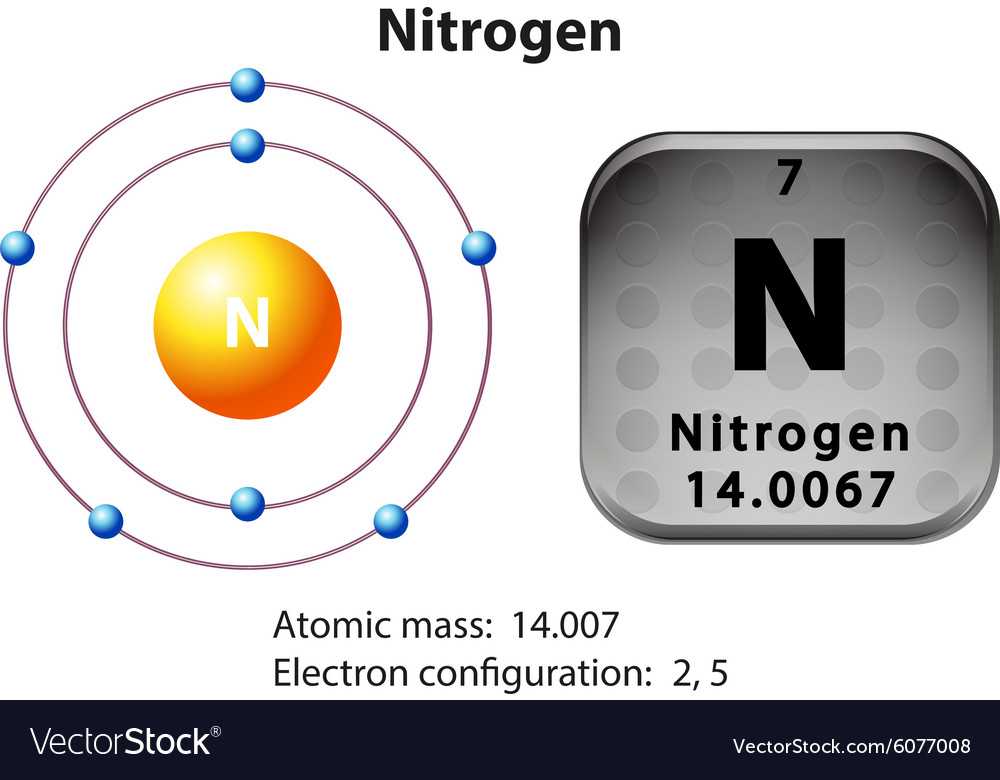
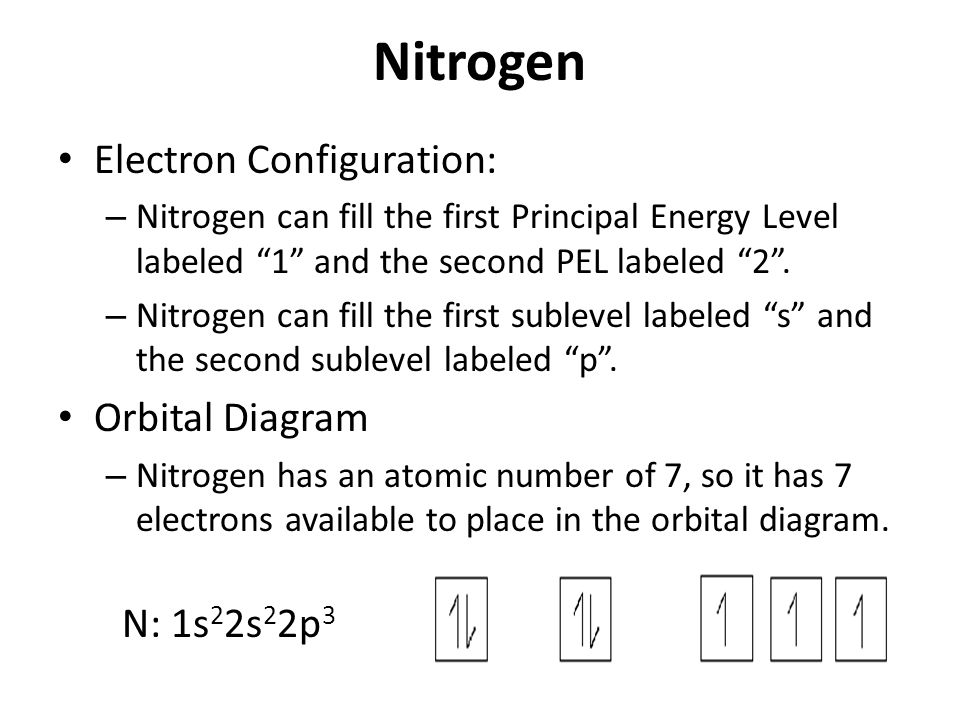
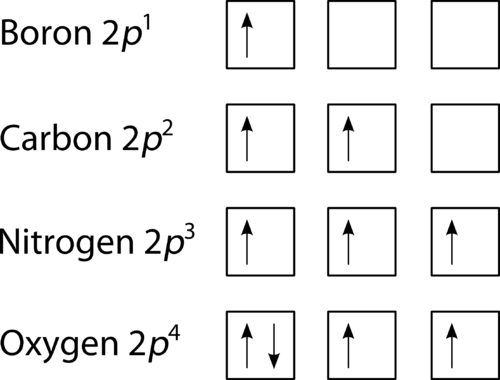
⚗️Which orbital diagram represents nitrogen (atomic number ... The choice A accurately specifies and illustrates the orbital diagram of a Nitrogen atom with 7 electrons. Based on the number of electrons in a Nitrogen atom, there are two energy levels, the s and p sub-levels: Nitrogen = 2, 5 The first energy level, S will take up two electrons with opposite spin. Nitrogen Bohr Model - How to draw Bohr diagram for ... Nitrogen is neutral and its atomic number is 7, hence, the number of protons and electrons available for its Bohr diagram is also 7. The number of neutrons for the Bohr diagram of Nitrogen can be found by subtracting the number of protons from the atomic mass (rounded to the nearest whole). The Electron Configurations of Atoms - Chemistry at Illinois Boron (atomic number 5) has five electrons. Four electrons fill both the 1s and 2s orbitals. The fifth electron is added to a 2p orbital, the sublevel next higher in energy (Figure 5.9). The electron configuration of boron is: B: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1. Table 5.2 shows the electron configurations of the elements with atomic numbers 1 through 18. The ... What is the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen? What is the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen? The remaining three electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Therefore the N electron configuration will be 1s22s22p3. The configuration notation for Nitrogen (N) provides an easy way for scientists to write and communicate how electrons are arranged around the nucleus of the Nitrogen atom.
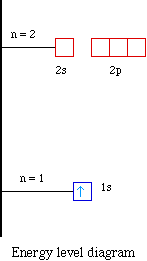
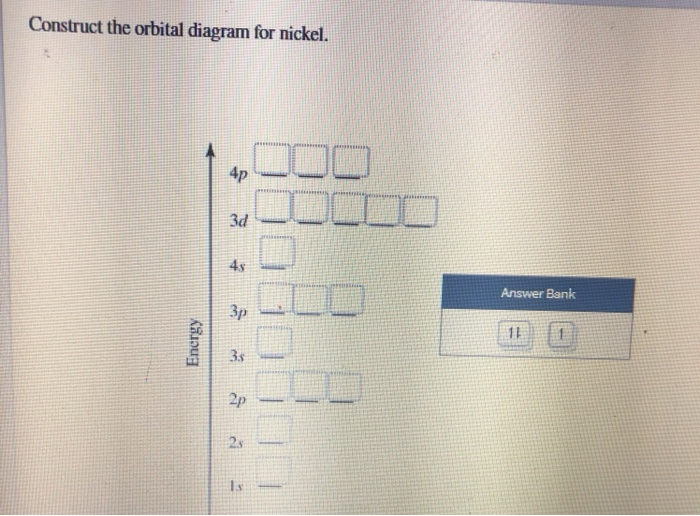
Nitrogen Orbital Filling Diagram - schemacheck.com Jan 13, 2022 · As 1s can only hold 2 electrons and the other next two electrons for Nitrogen (N) go in the 2s orbital. The three electrons that are remained will go in . Bromine Orbital Diagram. Answer to Write the electron configuration and give the orbital diagram of a bromine (Br) atom (Z = 35). the σ bonds. I've drawn the overlaps below in the MO diagrams. Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram of N2 - YouTube Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (N2)Use aufbau and Hund to fill with 10 valence electronsYou get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2).Bond Or... What is the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen? | Study.com Atomic Orbital Diagrams: These are also known as electron-in-a-box diagrams. This is a simplified diagram of how the electrons are arranged within the orbitals for a particular atomic species. Solved Fill in the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen ... Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (17 ratings) Transcribed image text: Fill in the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. Answer Bank Energy Construct the orbital diagram for nickel. 1000 Answer Bank Energy 2 _ _ _.
Molecular Nitrogen and Related Diatomic Molecules Here is the full molecular orbital diagram for N2. Now we add the 10 electrons, 5 from each nitrogen atom. Note that the bottom sigma symmetry orbital is strongly bonding, the top one is strongly antibonding, and the 2 in the middle are only weakly bonding and antibonding, respectively.
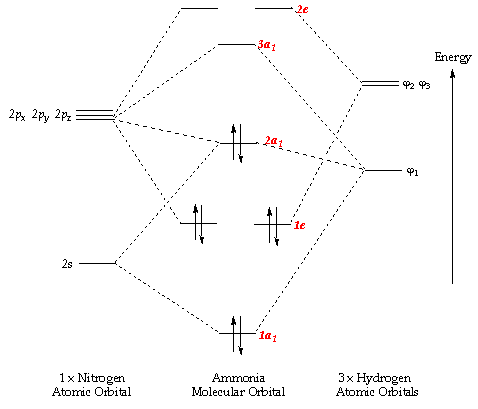
Molecular Orbital Theory – Chemistry The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one orbital that can hold two electrons. The molecular orbitals formed by the combination of the …
Molecular orbital - Wikipedia In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule.This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms atomic orbital and molecular orbital were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean one …
atomic and ionic radius - chemguide The left hand diagram shows bonded atoms. The atoms are pulled closely together and so the measured radius is less than if they are just touching. This is what you would get if you had metal atoms in a metallic structure, or atoms covalently bonded to each other. The type of atomic radius being measured here is called the metallic radius or the covalent radius depending on the …
Molecular Orbital Theory | Boundless Chemistry An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron in any specific region around an atom’s nucleus. An orbital may also refer to the physical region where the electron can be calculated to exist, as defined by the orbital’s ...
Nitrogen Electron Configuration (N) with Orbital Diagram Jan 21, 2021 — The electron configuration of nitrogen is 1s2 2s2 2p3. You can see the image below.
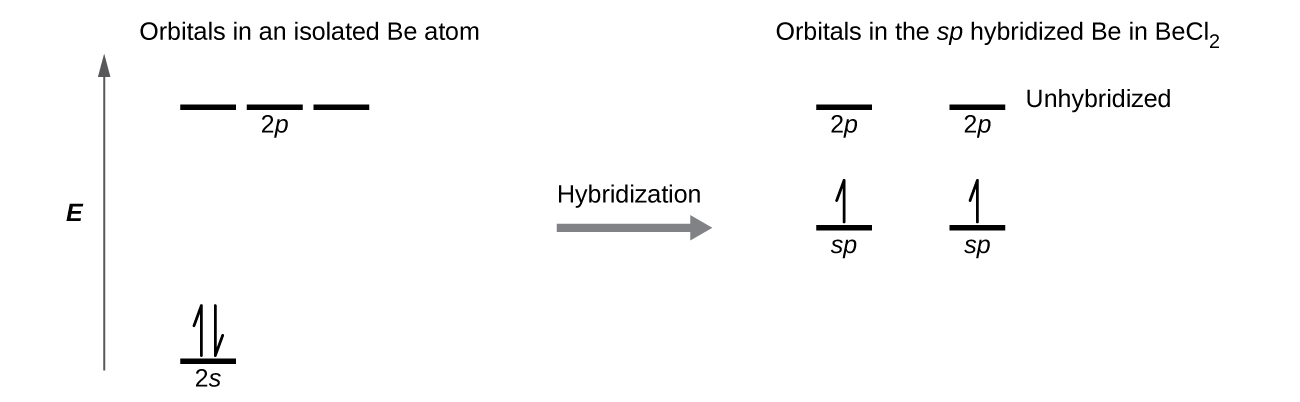
Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals - University of Illinois ... Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals . We can use Lewis dot structures to determine bonding patterns in molecules. We can then use VSEPR to predict molecular shapes, based on the valence electron pairs of the Lewis structures. Once we know a molecular shape, we can start to look at the physical properties of compounds. For example, we should now be able to predict which molecules will be polar.
Nitrogen(N) electron configuration and orbital diagram Nitrogen(N) is the 7th element in the periodic table and its symbol is ‘N’. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of nitrogen and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of nitrogen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles.Hopefully, after reading this article you will know in detail about this.
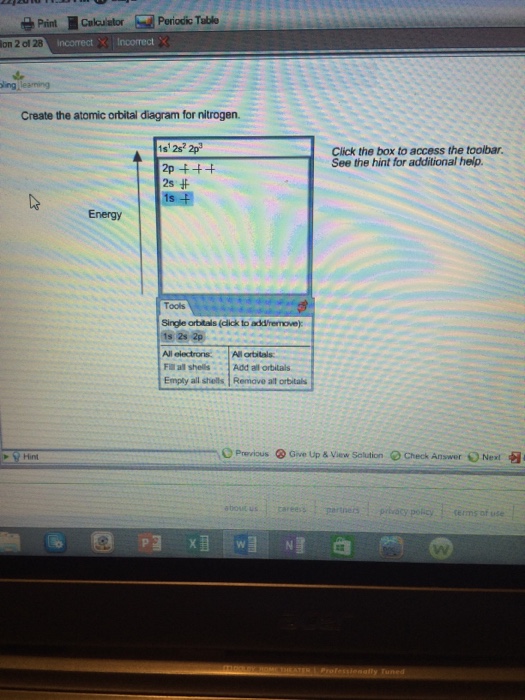
Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. - Clutch Prep Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. Learn this topic by watching The Electron Configuration Concept Videos All Chemistry Practice Problems The Electron Configuration Practice Problems Q. Construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion.TiTi2+Ti4+ Q. Write the corresponding electron configuration for the following pictorial ...
DOC LAB: Electron Configuration Orbital Diagram Lab. Background. The electrons in an atom occupy distinct . principal. ... according to increasing atomic number. ... The size of the charge is equal to the number of electrons that have been gained. For example, a nitrogen atom has 5 valence electrons; when the nitrogen atom gains 3 additional electrons, a nitrogen ion is ...
8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science Molecular orbital diagram of diatomic nitrogen. Homonuclear molecular orbitals are formed between two elements that are the same, meaning that they are naturally symmetrical and will perfectly overlap. However, before we fill out this diagram, Compare this MOD to the one above, particularly in the 2p region.
Molecular orbitals in Nitrogen - ChemTube3D Molecular orbitals in Nitrogen. Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals. There are four molecular orbitals derived from the 1s and 2s orbitals. Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals. The p orbitals combine to produce a sigma and two ...
Electron Configurations & The Periodic Table As we progress from lithium (atomic number=3) to neon (atomic number=10) across the second row or period of the table, all these atoms start with a filled 1s-orbital, and the 2s-orbital is occupied with an electron pair before the 2p-orbitals are filled. In the third period of the table, the atoms all have a neon-like core of 10 electrons, and shell #3 is occupied progressively with …
Atomic orbital - Wikipedia In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus.The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be ...
Hydrogen(H) electron configuration and orbital diagram The electron configuration of all the elements can be done through orbital diagram. Electron configuration of hydrogen(H) through orbital . Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f. …
Lewis structure - Wikipedia Lewis structures, also known as Lewis dot formulas, Lewis dot structures, electron dot structures, or Lewis electron dot structures (LEDS), are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule, as well as the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule. A Lewis structure can be drawn for any covalently bonded molecule, as well as coordination compounds.
Electron Configuration for Nitrogen (N) - UMD In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for N goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining three electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Therefore the N electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3.
Orbital Filling Diagram For Nitrogen - wiringall.com In the same way, the orbital filling diagram for nitrogen will be. Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s. Use orbital filling diagrams to describe the locations of electrons in an atom.
Solved Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. - Chegg Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. Start by adding the appropriate subshells. For example, boron is in the 2p block of the periodic table, and so you need to show the 2p subshell and everything below it. Next, click the orbitals to add electrons (represented as arrows). For boron, you would need to show a total of five electrons.
Orbital Diagram of All Elements (Diagrams given Inside) Atomic no. Orbital Diagram of All Elements Diagrams; 1: Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2: Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3: Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram ...
4.1 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations ... The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +1 2 m s = + 1 2 ).
orbitals - What is the origin of the differences between ... S-p mixing is the primary cause of the difference in the molecular orbitals of nitrogen and oxygen, which is influenced by the initial atomic orbital energies. The lighter second period elements (prior to oxygen) have a relatively small difference in energy between the 2s and 2p orbitals.
Molecular orbital energy level diagrams -Hydrogen ... The molecular orbital energy level diagram of He 2 (hypothetical) is given in Fig. Here, N b = 2 and N a = 2. Bond order = N b -N a / 2 = 2-2 / 2 = 0. As the bond order for He 2 comes out to be zero, this molecule does not exist. 3. Nitrogen molecule (N 2). The electronic configuration of nitrogen (Z=7) in the ground state is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1x 2p ...



















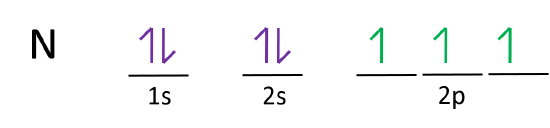




0 Response to "45 Atomic Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen"
Post a Comment