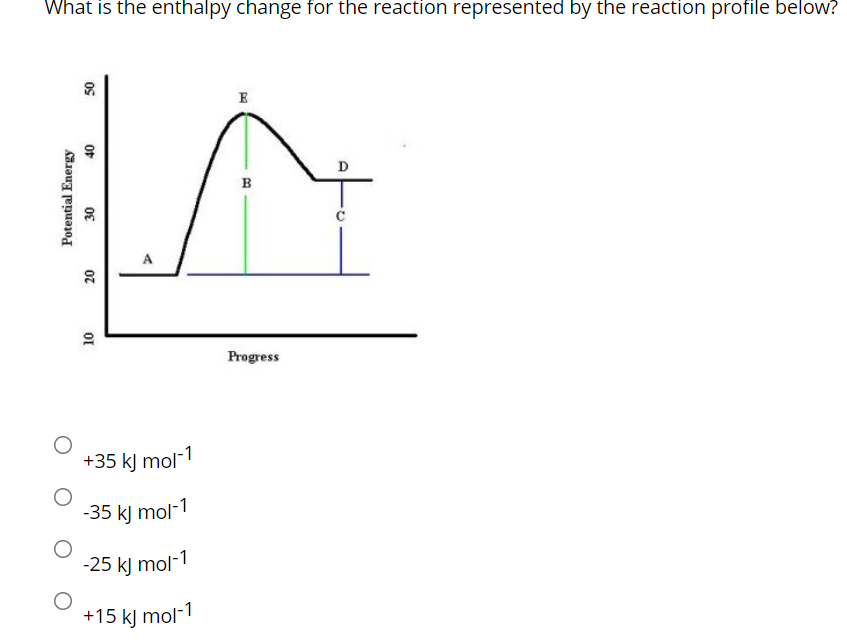
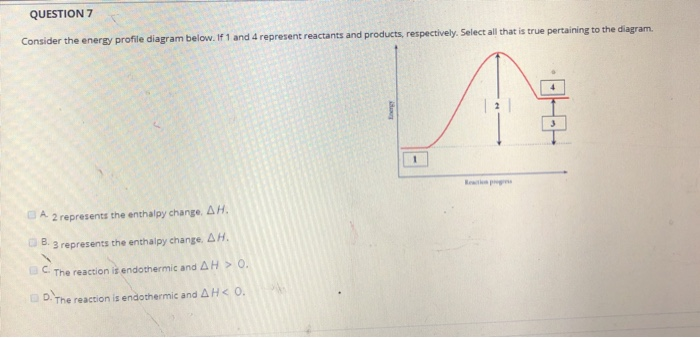
42 which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have
which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the ... The x-axis represents the reaction progress. Chemical reactions proceed (or are read) from left to right. Therefore, looking at the potential energy diagram, the reactants are usually found to the left on the diagram and the products on the right. Niccherip5 and 3 more users found this answer helpful. heart outlined. 5.3 Enthalpy - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax If we have values for the appropriate standard enthalpies of formation, we can determine the enthalpy change for any reaction, which we will practice in the next section on Hess's law. The standard enthalpy of formation of CO 2 (g) is −393.5 kJ/mol. This is the enthalpy change for the exothermic reaction:
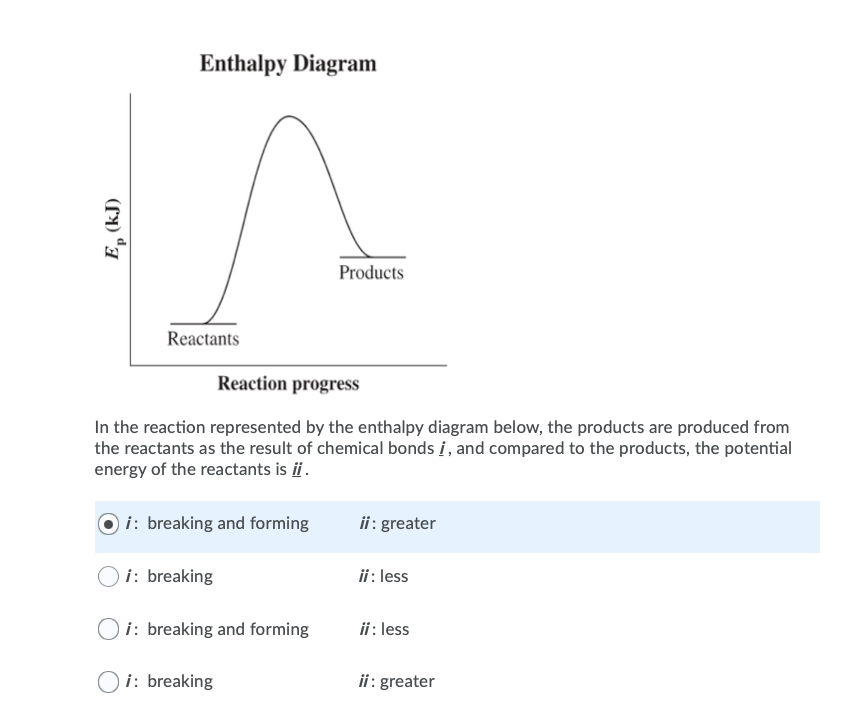
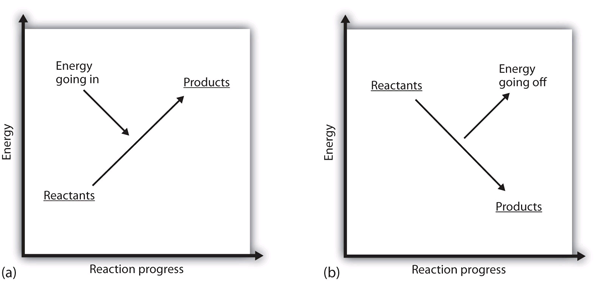
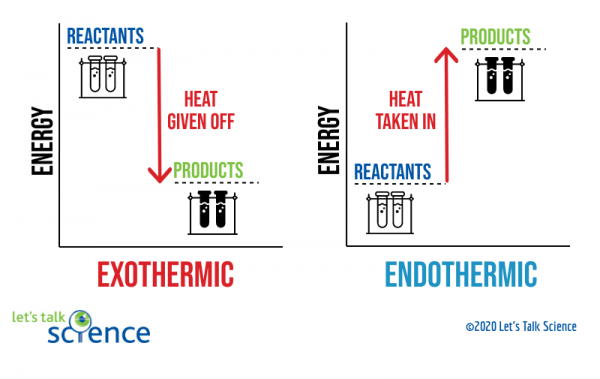
Chemistry chapter 6 smartbook Flashcards - Quizlet The arrow in the enthalpy diagram points from reactants to products. The direction of the arrow in an enthalpy diagram indicates whether a reaction is exothermic or endothermic. Enthalpy, H, increases up the y-axis. In an endothermic reaction, the reactants will be at the bottom of the enthalpy diagram.

Which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have
For which one of the following equations is Δ H^o ... The heat of formation is defined as the heat generated or absorbed when the compound is formed form its component elements in their standard state. By this defination, B and D are clearly not correct as the starting materials are compounds. A is not correct, since ozone is not correct standard state of oxygen. So, C is the correct answer. Heat of Reaction at Constant Pressure and at ... - QS Study At constant pressure, the heat of reaction is equal to the enthalpy change of the system. Heat of Reaction at Constant Pressure and at Constant Volume. When a reaction is carried out at constant volume as in a bomb calorimeter, the pressure within the calorimeter may change but no work is done. The heats of reaction in such cases correspond to ∆U. Ordinarily, reactions are carried out in open vessels under constant pressure conditions. ∆H and ∆U are, however, related by the equation PDF Calorimetry Question - Weebly low density. Hydrogen gas can be produced by the reaction represented by the following overall equation. and 2. metal catalyst CH4(g) + 2 H20(g) C02(g) + 4 H2(g) The enthalpy change for the reaction represented by the equation above is the enthalpy change per mole of hydrogen is ii The statement above is completed by the information in row Row
Which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have. How would you calculate the standard enthalpy change for ... In other words, you can express the enthlapy change of reaction by using each individual reaction that corresponds to the standard enthalpy change of formation for the products and for the reactants. ΔH ∘ rxn = ∑(n × ΔH ∘ f products) − ∑(m ×ΔH ∘ f reactants) Here n, m represent the stoichiometric coefficients of the compounds in the reaction. PDF 2. The alcohol 2-methylpropanQ-ol, (CH3)3COH, reacts to form esters that are used as flavourings by the food industry. The alcohol can be oxidised to produce carbon dioxide and water. A student carried out an experiment on a pure sample of 2-methylpropan-2-ol to determine its enthalpy of combustion. A sample of the alcohol was placed into a CHEM 1411 STUDY-GUIDE-for-TEST-2 (CHAPTERS 4, 5 and 6) 24. Identify the Brønsted acid in the following reaction. NH 3 + H 2 O NH 4 + + OH- Ans: H 2 O 25. Write the balanced molecular and net ionic equations for the reaction that would occur between CuCl 2 (aq) and Pb(s). Be sure to include the correct states in your final equations. If no reaction is expected, write "no reaction." ChemTeam: Hess' Law - using three equations and their ... The enthalpy of a given chemical reaction is constant, regardless of the reaction happening in one step or many steps. Another way to state Hess' Law is: If a chemical equation can be written as the sum of several other chemical equations, the enthalpy change of the first chemical equation equals the sum of the enthalpy changes of the other ...
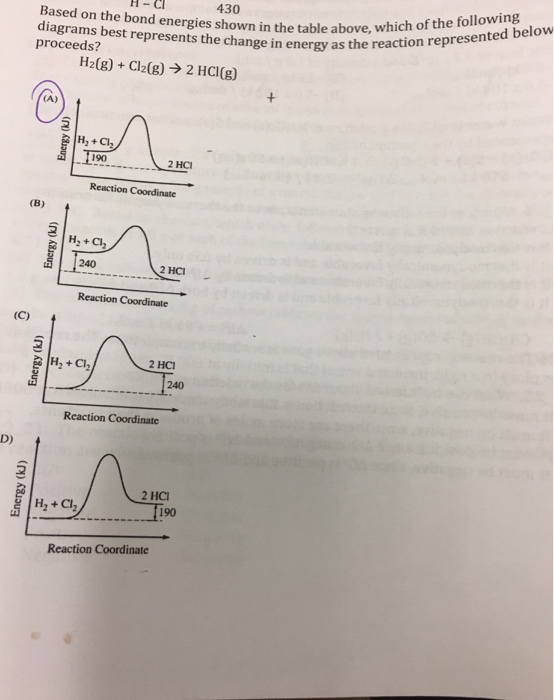
36 what is the enthalpy of reaction from the following ... Energy diagrams for these processes will often plot the enthalpy (H) instead of Free Energy for simplicity. Enthalpy, or heat energy, is represented by ΔH (Δ is the delta sign, which means change). If there is a negative change in energy, or -ΔH, an exothermic reaction is taking place and energy is released🔥 from the system to the surroundings. Chemistry 12 - Unit 3 Quiz - Nelson Which of the following representations of enthalpy changes in chemical reactions is inconsistent with the rest? a. CH 3 OH (l) + O 2(g) CO 2(g) + 2 H 2 O (g) H = -638.0 kJ Enthalpy of Chemical Reactions - Nassau Community College reaction. Consider the following general type of reaction . reactant Æ products . The ∆H is defined as the difference between the enthalpies of products and the reactants. Thus . ∆H = Hproducts - Hreactants . The enthalpy of reaction can be positive or negative or zero depending upon whether the heat is gained or lost or no heat is lost or ... Heat of Neutralization: HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) | Chemdemos Since the solutions are mostly water, the solutions are assumed to have a density of 1.0 g/mL and a specific heat of 4.18 J/g°C. The reaction of an aqueous hydrochloric acid solution with an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution is represented by the neutralization chemical equation. HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H 2 O(l) + heat
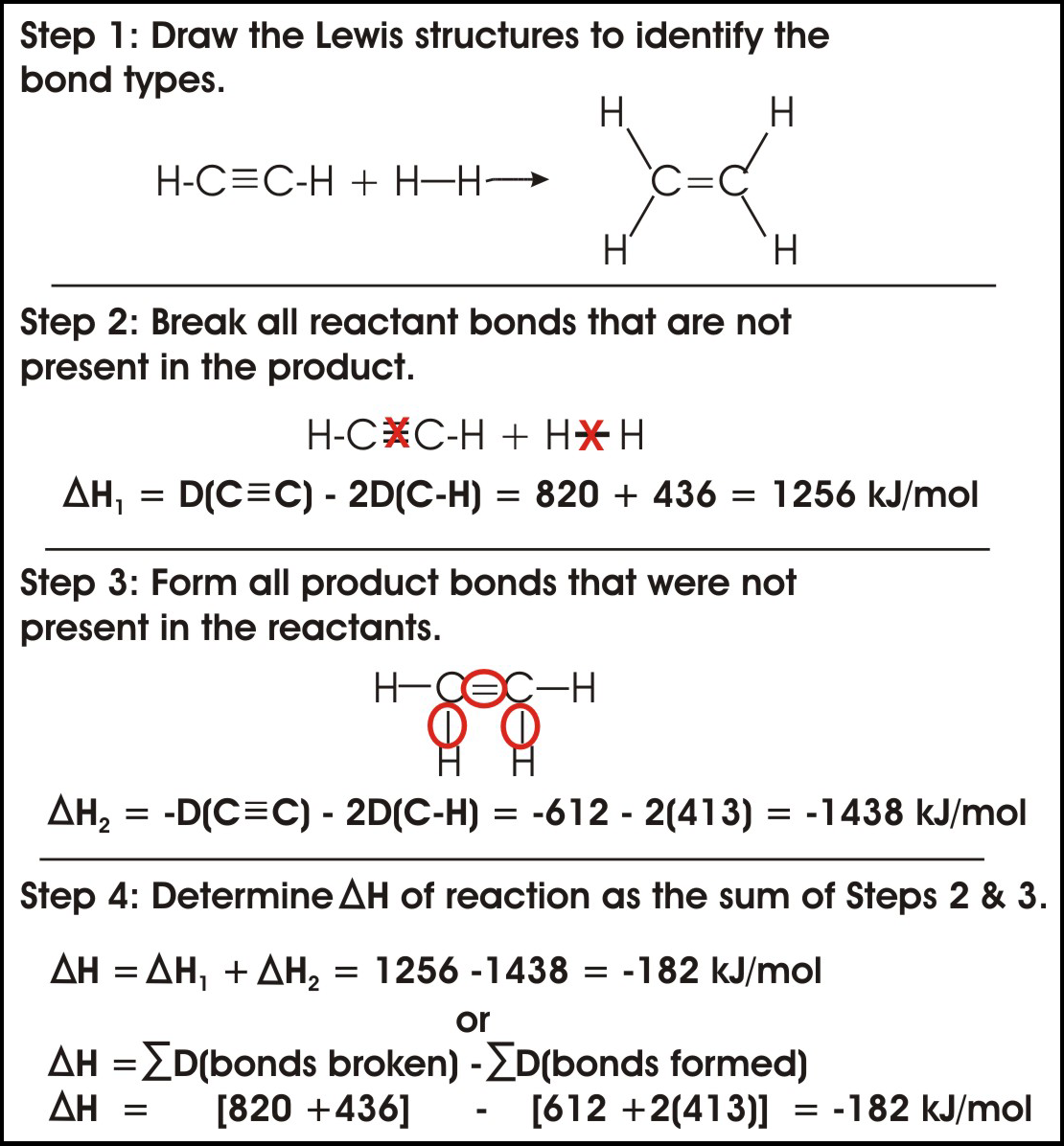
AP Chemistry Practice Test 8 - CrackAP.com AP Chemistry Practice Test 8. Questions 1-5 refer to the following information. 1. In which of the reactions does the amount of energy released by the formation of bonds in the products exceed the amount of energy necessary to break the bonds of the reactants by the greatest amount? 2. In which of the reactions is the value for Δ S the ... How to calculate Delta H - Easy To Calculate The change in enthalpy can be quickly calculated in a given thermodynamic system that has undergone a chemical reaction by the following formula: ∆H = cm∆T. Where ∆H refers to change in enthalpy of a reaction, C refers to the specific heat. It is constant for all substances, m represents the mass and, What is the enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide in KJ ... 1. C (s) + O₂ (g) → CO₂ (g); ΔH = -393 kJ. Our target equation has CO (g) on the right hand side, so we reverse equation 2 and divide by 2. 3. CO₂ (g) → CO (g) + ½O₂; ΔH = +294 kJ. That means that we also change the sign of ΔH and divide by 2. Then we add equations 1 and 3 and their ΔH values. This gives. AP Chemistry: Midterm Review Flashcards - Quizlet The oxidation of carbon monoxide can be represented by the chemical equation 2 CO(g)+O2(g)→2 CO2(g). The table above provides the average bond enthalpies for different bond types. Based on the information in the table, which of the following mathematical expressions is correct for the estimated enthalpy change for the reaction?
PDF sample Multiple-Choice Questions - Weebly 23 . The enthalpy change for the reaction represented above is ∆H T. This reaction can be broken down into a series of steps as shown in the diagram: A relationship that must exist among the various enthalpy changes is (a) ∆H T - ∆H 1 - ∆H 2 - ∆H 3 = 0 (b) ∆H T + ∆H 1 + ∆H 2 + ∆H 3 = 0 (c) ∆H 3 - (∆H 1 + ∆H 2) = ∆H T (d) ∆H 2 - (∆H 3 + ∆H
Chemistry 4.09 Quiz: Writing Thermochemical Equations ... In which of the following thermochemical equations would the ΔH be considered a heat of solution? NH4Cl (s) → NH4 (aq) + Cl- (aq), ΔH = +14.8 kJ/mol Which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have?
Energy, Enthalpy, and the First Law of Thermodynamics The relationship between the change in the internal energy of the system during a chemical reaction and the enthalpy of reaction can be summarized as follows. 1. The heat given off or absorbed when a reaction is run at constant volume is equal to the change in the internal energy of the system. E sys = q v. 2.
Standard Enthalpy of Formation and Reaction | Boundless ... standard enthalpy of reaction: The enthalpy change that occurs in a system when one mole of matter is transformed by a chemical reaction under standard conditions. The standard enthalpy of reaction, [latex]\Delta H^\ominus _{rxn}[/latex], is the change in enthalpy for a given reaction calculated from the standard enthalpies of formation for all reactants and products.
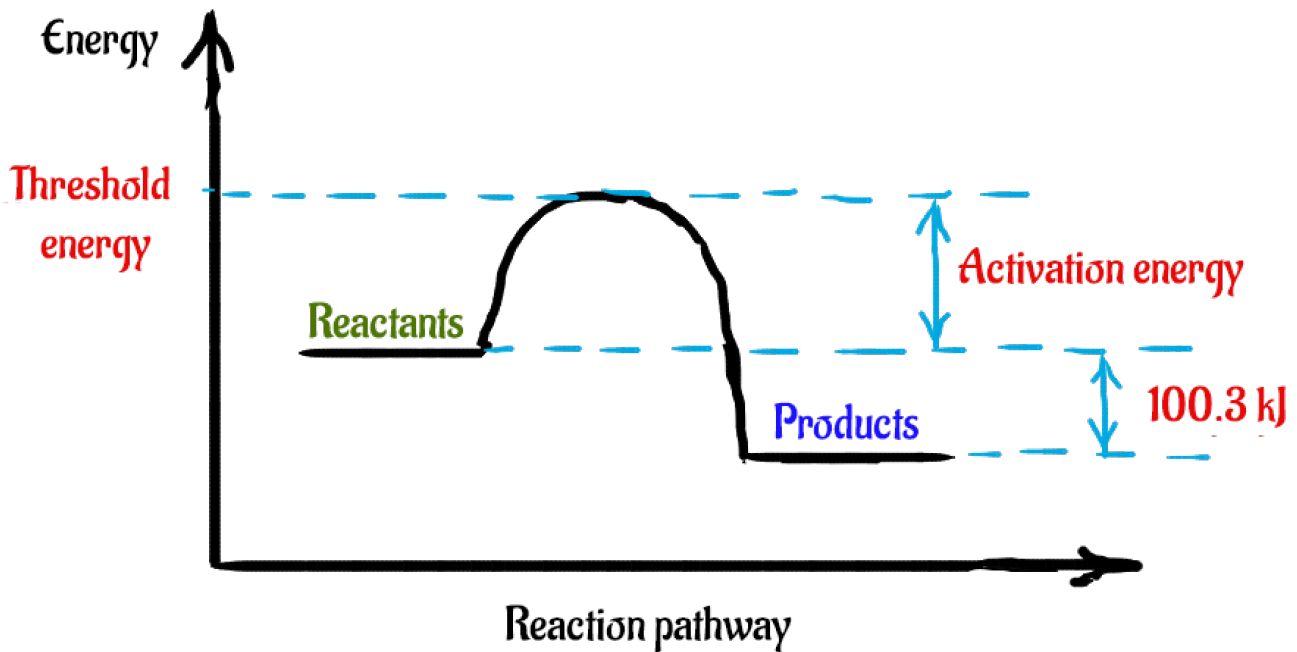
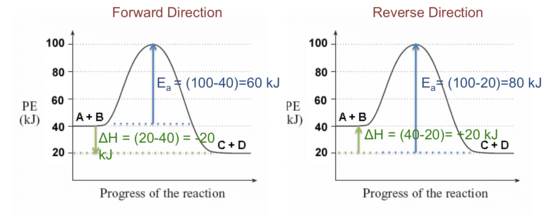
Activation energy of forward and backward ... - Toppr Ask ΔH=E af. . −E ab. . =+20kJ/mol. ΔH is positive, reaction is endothermic. Threshold energy is the energy that a molecule must have to make effective collision. threshold energy is greater than activation energy. For given reaction, threshold energy can be 100 kJ/mol.
PDF Problems - Chapter 14 (with solutions) Find the following: a) The order of the reaction with respect to A and with respect to B. b) The rate constant for the reaction (including correct units). c) The initial rate of the reaction when [A] 0 = 0.01500 M, [B] 0 = 0.0300 M. pa) We assume a rate law of the form rate = k [A] [B]q. To find the reaction order for A we can compare trials 2 and 1
Thermodynamics Conceptual | Chemistry Quiz - Quizizz Diagram 2, because it represents a reaction with a high activation energy barrier for molecules to overcome and a very slow reaction rate, even if it is thermodynamically favorable with ΔG < 0 Diagram 2, because it represents a reaction that is thermodynamically favorable with ΔH < 0 the products formed are unstable and quickly revert to form reactants.
Exam Flashcards - Quizlet Use the standard enthalpies of formation for the reactants and products to solve for the ΔHrxn for the following reaction. (The ΔHf of Ca(OH)2 is -986.09 kJ/mol and liquid H2O is -285.8 kJ/mol.)
5.3 Enthalpy - Chemistry In a thermochemical equation, the enthalpy change of a reaction is shown as a Δ H value following the equation for the reaction. This Δ H value indicates the amount of heat associated with the reaction involving the number of moles of reactants and products as shown in the chemical equation. For example, consider this equation:
PDF Chemistry 102 ANSWER KEY - Los Angeles Mission College ] vs. time give a straight line, this reaction is second order with respect to [NO 2] The rate constant, k, is the slope of the plot. k = = 10 M s 212.8 - 10.0-1 -1 20.0 - 0 8. The reaction 2 N 2 O 5 4 NO 2 + O 2 has an activation energy of 100 kJ/mol and an enthalpy of -23 kJ/mol. Sketch a potential energy diagram for this reaction and
PDF Calorimetry Question - Weebly low density. Hydrogen gas can be produced by the reaction represented by the following overall equation. and 2. metal catalyst CH4(g) + 2 H20(g) C02(g) + 4 H2(g) The enthalpy change for the reaction represented by the equation above is the enthalpy change per mole of hydrogen is ii The statement above is completed by the information in row Row
Heat of Reaction at Constant Pressure and at ... - QS Study At constant pressure, the heat of reaction is equal to the enthalpy change of the system. Heat of Reaction at Constant Pressure and at Constant Volume. When a reaction is carried out at constant volume as in a bomb calorimeter, the pressure within the calorimeter may change but no work is done. The heats of reaction in such cases correspond to ∆U. Ordinarily, reactions are carried out in open vessels under constant pressure conditions. ∆H and ∆U are, however, related by the equation
For which one of the following equations is Δ H^o ... The heat of formation is defined as the heat generated or absorbed when the compound is formed form its component elements in their standard state. By this defination, B and D are clearly not correct as the starting materials are compounds. A is not correct, since ozone is not correct standard state of oxygen. So, C is the correct answer.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endergonic-vs-exergonic-609258_final-2904b2c359574dfcb65a9fca2d54179a.png)










0 Response to "42 which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have"
Post a Comment