43 circular motion force diagram
Grade 8 Circular Motion Worksheet Sheet 2.pdf - Grade 8 1 ... (a) Name the force labelled in the diagram that causes the ball to move in a circle? (1) Tension Weight Air resistance Circular path of swing ball (b) Choose the correct response: (i) The force needed to make the ball move in a circular path is larger if Circular Motion - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics On the force diagram for the particle, indicate the direction of the centripetal acceleration a c (toward the center of the circular motion). 2. In writing the relationship expressing Newton's second law, enter the magnitude of the forces that are in the direction of a c with positive signs, enter the magnitudes of the forces that are opposite to a c with negative signs, and equate their sum to mv 2 / r .
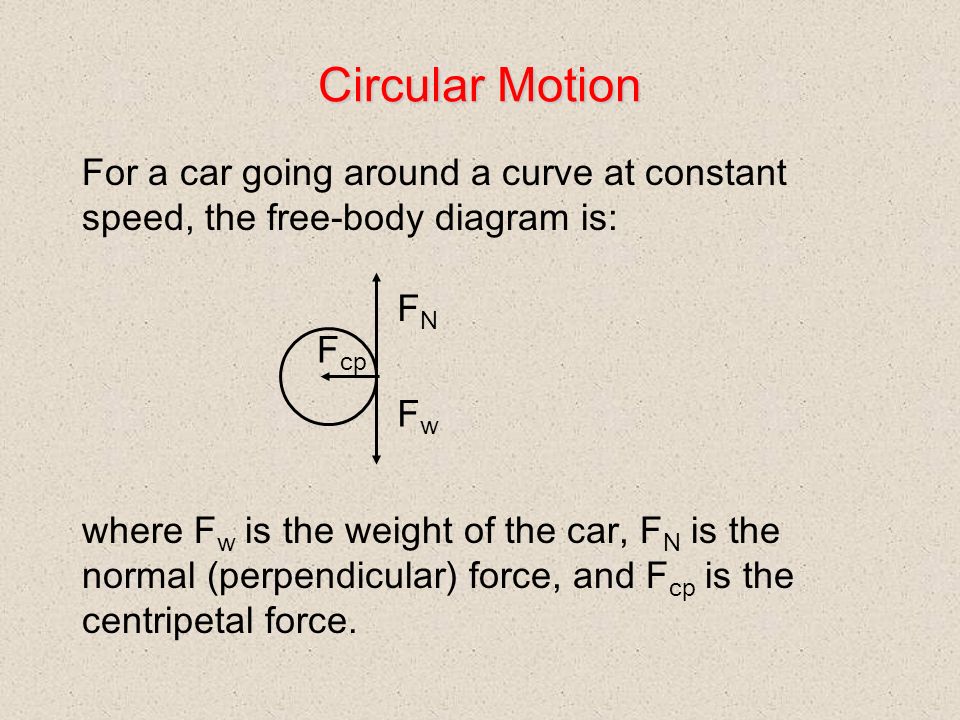
centripetal force - Circular motion, free-body diagram ... The actual question is easy to solve using uniform circular motion equations (and has nothing to do with my question). In the free-body diagram below, what is the balancing force in the question mark? centripetal-force. Share. Cite. Improve this question. Follow edited May 6, 2017 at 15:00. ...
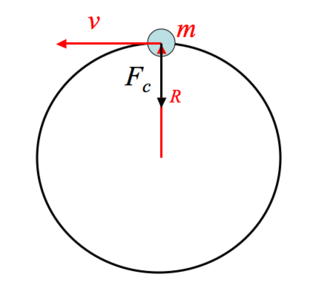
Circular motion force diagram
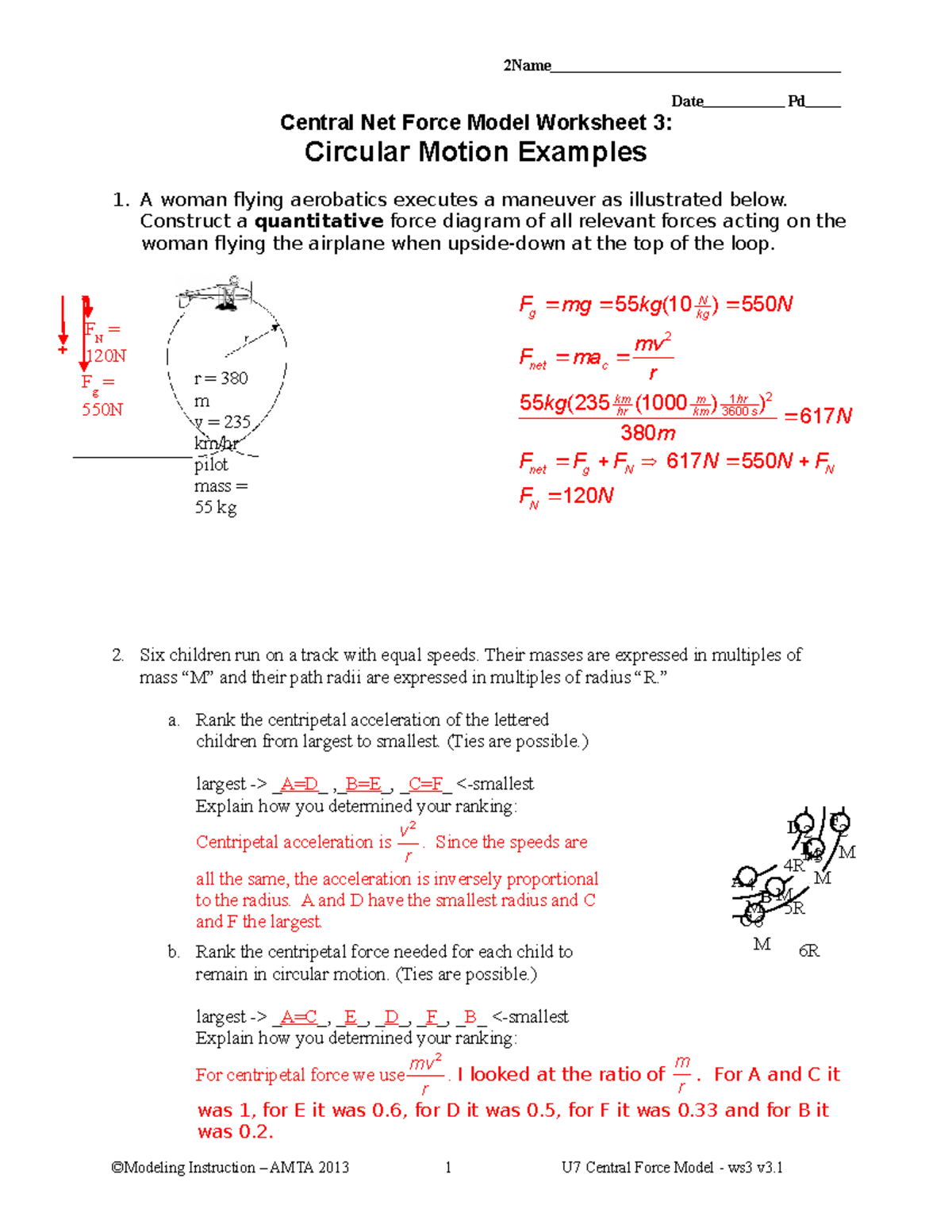
40 circular motion and inertia worksheet answers ... A body in a circular motion tends to move forward due to inertia but centripetal fore which acts towards the center changes its direction and the body moves along the circumference of the circle. Circular Motion Worksheet Answers - Worksheet Blog Circular motion worksheet answer sheet a. Topic 2 uniform circular motion. PDF 5-8 Vertical Circular Motion - WebAssign 5-8 Vertical Circular Motion A common application of circular motion is an object moving in a vertical circle. Examples include roller coasters, cars on hilly roads, and a bucket of water on a string. ... We then draw a free-body diagram, which shows an upward normal force and a downward force of gravity. The system can be you or the car ... Physics Simulation: Uniform Circular Motion The Uniform Circular Motion Interactive is shown in the iFrame below. There is a small hot spot in the top-left corner. Clicking/tapping the hot spot opens the Interactive in full-screen mode. Use the Escape key on a keyboard (or comparable method) to exit from full-screen mode. There is a second hot-spot in the lower-right corner of the iFrame ...
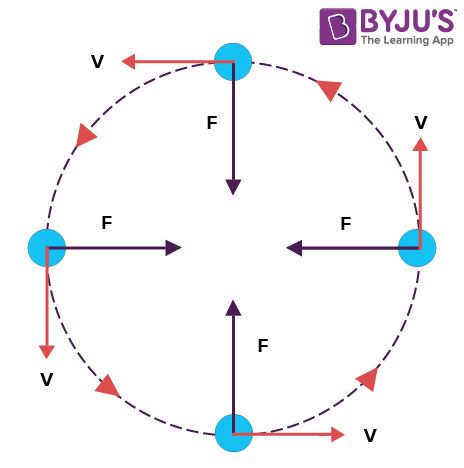
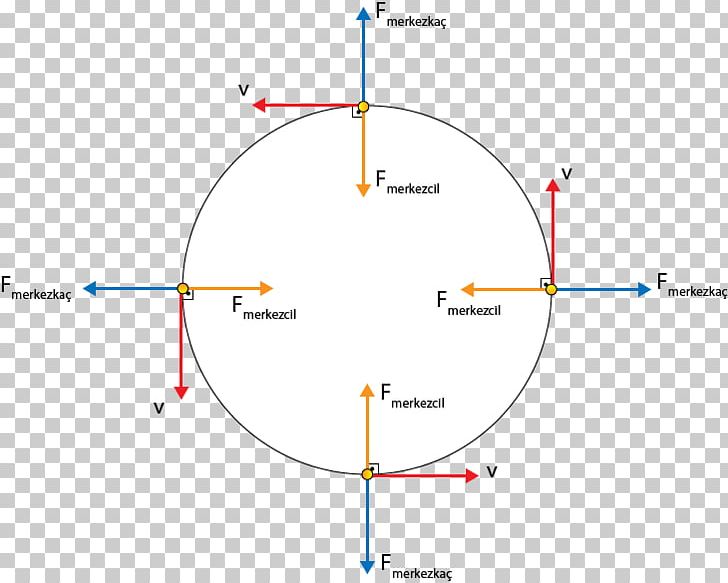
Circular motion force diagram. Lecture 6 Circular Motion - School of Physics Note that centripetal force is the name given to the resultant force: it is not a separate force in the free-body diagram. The centripetal acceleration has to be provided by some other force (tension, friction, normal force) in order for circular motion to occur. 10 • PhysicsLAB: Uniform Circular Motion: Centripetal Forces Friction is the unbalanced central force that is supplying the centripetal force necessary to keep the car moving along its horizontal circular path: f = F c = ma c. Since f = μN and N = mg on this horizontal surface, most problems usually ask you to solve for the minimum coefficient of friction required to keep the car on the road. Identifying Free-Body Diagrams for Objects in Uniform ... The free-body diagram above is of an object orbiting the earth in a uniform circular motion. The force of gravity arrow points towards the center of the orbit. One thing to notice is that the... Circular Motion (and other things) Circular Motion Newton's Second Law applied to a ... Rather, make a clear diagram and then apply F net ac where ac is the centripetal ... from the rider. As always, the normal force may also be called the rider's "apparent weight" for this is the force of the seat on the rider and also describes what the rider "feels" (in addition ...
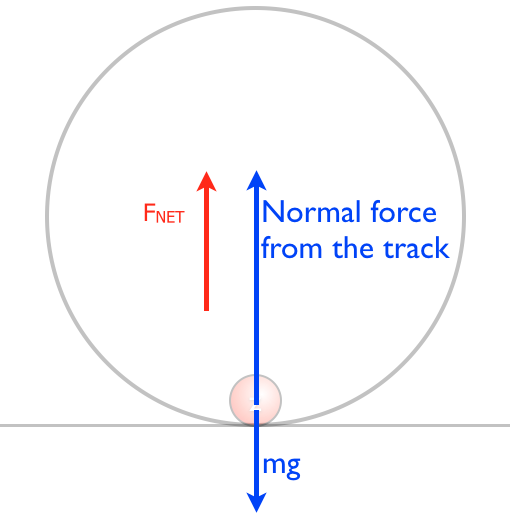
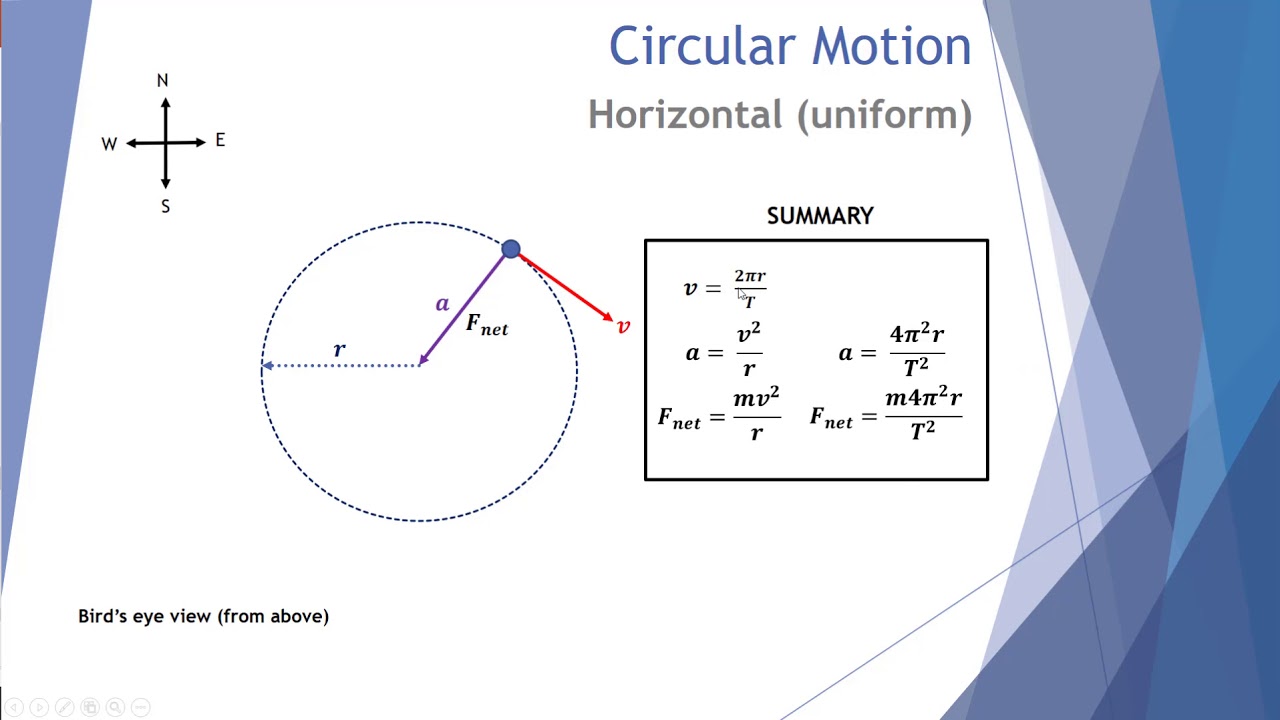
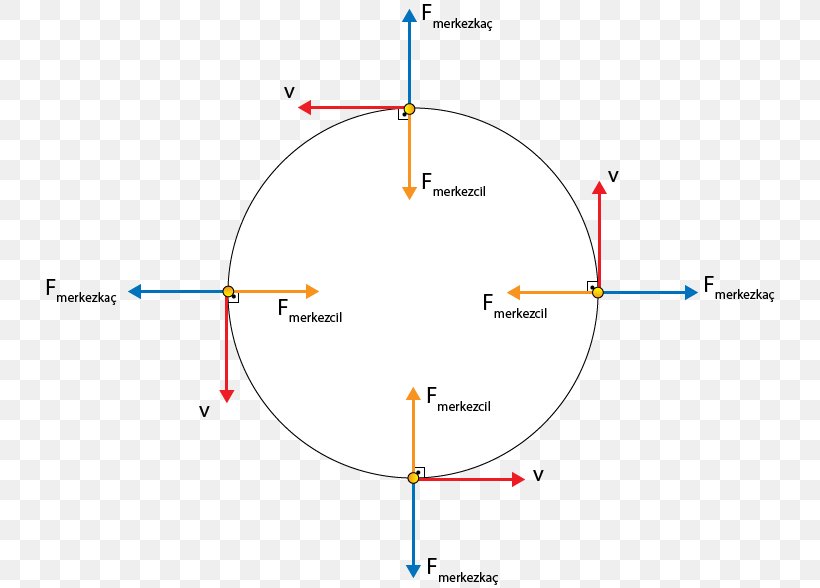
Uniform circular motion - Boston University You do NOT put a centripetal force on a free-body diagram for the same reason that ma does not appear on a free body diagram; F = ma is the net force, and the net force happens to have the special form when we're dealing with uniform circular motion. The centripetal force is not something that mysteriously appears whenever an object is traveling in a circle; it is simply the special form of the net force. Circular Motion - University of Michigan velocity just so that a circular trajectory is followed. This means that the total radial force must have the correct magnitude for circular motion or F T F net radial rope g, ,radial must equal 2 v mr r or equivalently mr rZ2. This is a very important point: the sum of the radial forces on an object in circular motion must be equal to. Chapter 7: Circular Motion & Rotation - Granbury ISD Chapter 7: Circular Motion & Rotation 163 Objectives 1. Explain the acceleration of an object moving in a circle at con-stant speed. 2. Define centripetal force and recognize that it is not a special kind of force, but that it is provided by forces such as tension, gravity, and friction. 3. Solve problems involving calculations of centripetal force. 4. Calculate the period, frequency, … Mathematics of Circular Motion - Physics Classroom Mathematics of Circular Motion. There are three mathematical quantities that will be of primary interest to us as we analyze the motion of objects in circles. These three quantities are speed, acceleration and force. The speed of an object moving in a circle is given by the following equation. The acceleration of an object moving in a circle ...
Physics Simulation: Barrel Ride Lesson 1 of the Circular Motion and Satellite Motion Chapter of the Tutorial is a perfect accompaniment to this Interactive. The following pages will be particularly useful in the early stages of the learning cycle on Circular Motion: Speed and Velocity Acceleration The Centripetal Force Requirement The Forbidden F-Word Mathematics of Circular ... TOPIC 1.5: CIRCULAR MOTION - Province of Manitoba Students can draw free-body diagrams to illustrate forces acting on a sphere or a coin moving in a uniform circular motion. In each case, they should indicate the force(s) responsible for the centripetal force. The relative length of the vectors corresponding to the forces should be drawn to scale. Symbols: F g— Weight F T— Tension F f— Friction F PDF PY105 Uniform and Vertical Circular Motions circular motion is counter-clockwise. Below, we show the vector diagram for when it is clockwise. v. 2. −. v. 1. Δ. v. Δθ Δ. V = V. 2 - V. 1. v. 1. v. 2. Δθ Δ. v. The above drawings show that the acceleration vector . a (which is parallel to Δ. v) is still pointing towards the center of the circle. Coins on a turntable . Two identical coins are placed on a flat turntable that is Circular Motion: Introduction, Centripetal Force, Videos ... The Motion of a Car Circular Motion on a Level Road. Refer to the diagram below to observe the motion of a car on a level road. Primarily, three forces are acting on the car. They are. The weight of the car; Normal Reaction; Frictional Force (f) In the diagram, it is clear that the vertical direction does not have any acceleration. Hence, N-mg=0; Therefore, N= mg
Forces and Circular Motion – Learn – ScienceFlip The diagram below represents the forces acting on a vehicle in uniform circular motion on a banked track, including the friction force. The forces are the weight force,, the normal reaction force, and the friction force, . The forces are unbalanced and the resulting force is the centripetal force keeping the vehicle in uniform circular motion.
Centripetal Acceleration & Force - Circular Motion, Banked ... This physics video tutorial explains the concept of centripetal force and acceleration in uniform circular motion. This video also covers the law of univers...
Forces and Free-Body Diagrams for Circular Motion Forces and Free-Body Diagrams in Circular Motion. The Forces in Circles Concept Builder provides learners with the challenge of identifying the free-body diagrams for situations involving the motion of objects in circles. Learners are presented with a short verbal description of an object's motion. They toggle through a set of free-body diagrams until they find the one that they thinkg is the matching diagram for the description.
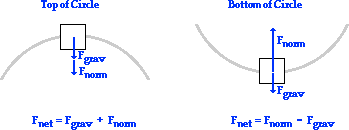
Free-Body Diagrams for Objects in Uniform Circular Motion ... This gives us a net force equation of Fnet = Fn - Fg. The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the left of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed rightwards and Force of Gravity is pointed downwards. This gives us a net force equation of Fnet = Fn.
Newton's Laws - Force Diagrams - Physics Classroom Mission NL5: Force Diagrams. Mission NL5 involves the comparison of the relative magnitude of the individual forces that act upon an object in various physical situations. The mission consists of 39 questions organized into 11 Question Groups. You must answer one question from each Question Group to complete the mission.
Chapter 10. Uniform Circular Motion acceleration and centripetal force to the solution of problems in circular motion. • • Define and apply concepts of frequency and period, and relate them to linear speed. • • Solve problems involving banking angles, the conical pendulum, and the vertical circle. Uniform Circular Motion Uniform circular motion . Uniform circular motion is motion along a circular path in which …
What is the net force acting on an object moving in ... What is the net force acting on an object moving in circular motion? This net force is often called the centripetal force. Since the acceleration of an object undergoing uniform circular motion is v2/R, the net force needed to hold a mass in a circular path is F = m (v2/R)….Force and Circular Motion.
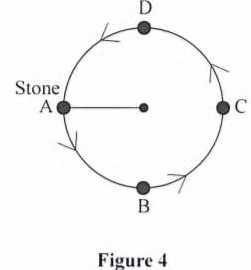
PDF Acceleration and Force in Circular Motion Circular Motion - Slowing down . An object is moving counter-clockwise around a circular path and it is slowing down. The magnitude of its velocity when it passes the first point on the diagram below is 6.0m/s and when it passes the second point is 4.0m/s. Draw the two velocity vectors. Use tail-to-tip method of vector addition to find . V. f. inal - V
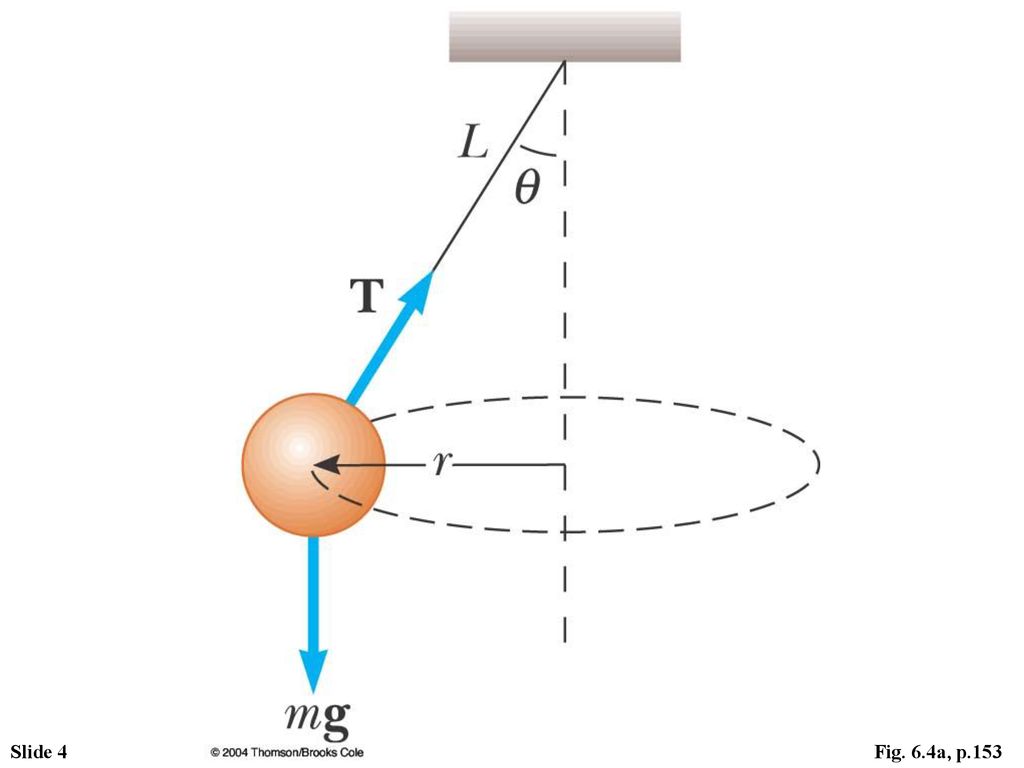
Force and Acceleration in Circular Motion - WebAssign The radius R of the circular path of the ball is given by R = L cos θ. Figure 3 The forces on the ball are gravity and the tension in the string. The tension in the string is directed along the string and the gravity force is straight downward. The free-body diagram for the moving ball is given in Figure 4.
Physics Simulation: Uniform Circular Motion The Uniform Circular Motion Interactive is shown in the iFrame below. There is a small hot spot in the top-left corner. Clicking/tapping the hot spot opens the Interactive in full-screen mode. Use the Escape key on a keyboard (or comparable method) to exit from full-screen mode. There is a second hot-spot in the lower-right corner of the iFrame ...
PDF 5-8 Vertical Circular Motion - WebAssign 5-8 Vertical Circular Motion A common application of circular motion is an object moving in a vertical circle. Examples include roller coasters, cars on hilly roads, and a bucket of water on a string. ... We then draw a free-body diagram, which shows an upward normal force and a downward force of gravity. The system can be you or the car ...
40 circular motion and inertia worksheet answers ... A body in a circular motion tends to move forward due to inertia but centripetal fore which acts towards the center changes its direction and the body moves along the circumference of the circle. Circular Motion Worksheet Answers - Worksheet Blog Circular motion worksheet answer sheet a. Topic 2 uniform circular motion.
























0 Response to "43 circular motion force diagram"
Post a Comment