41 gram positive bacteria diagram
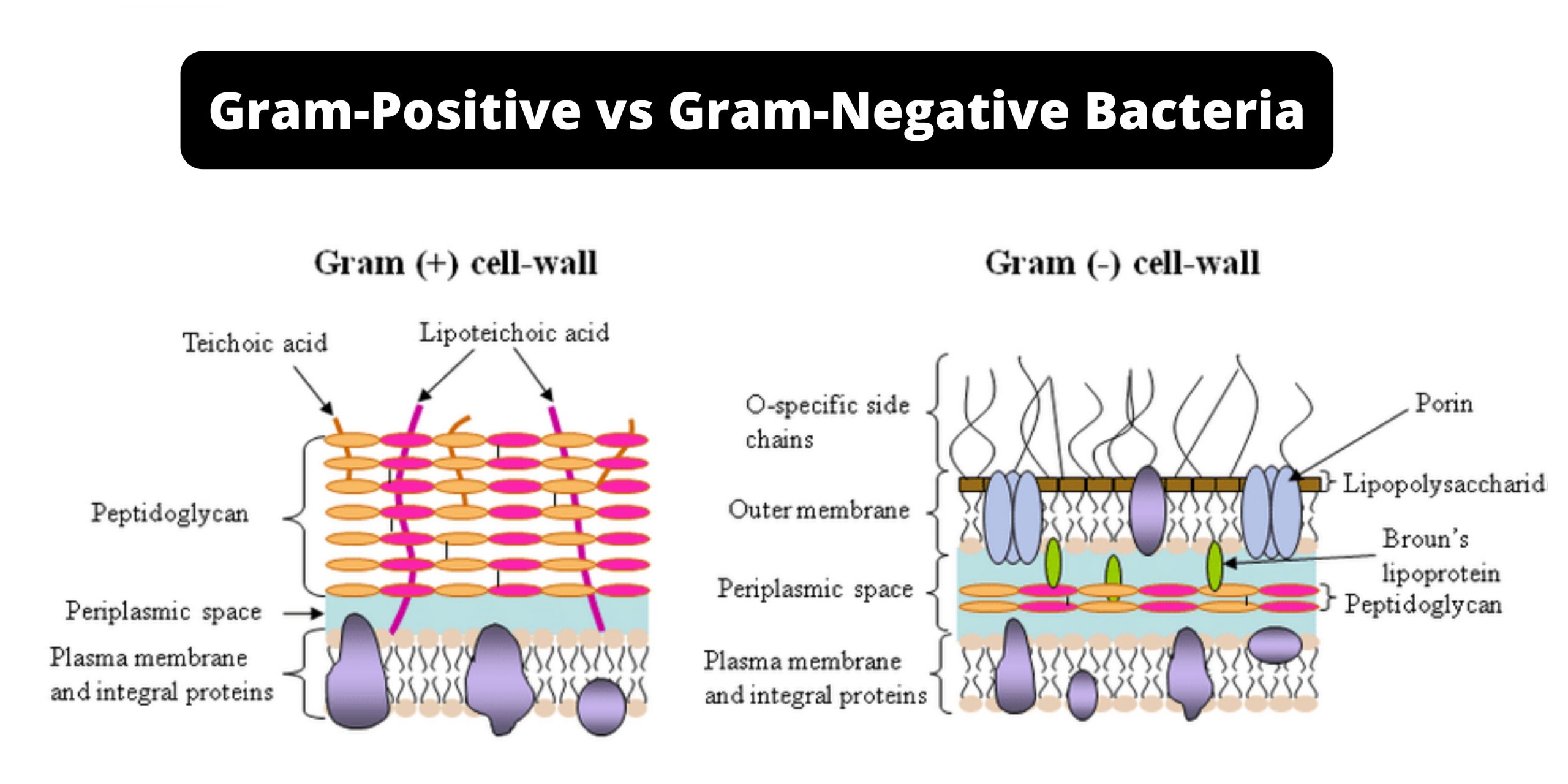
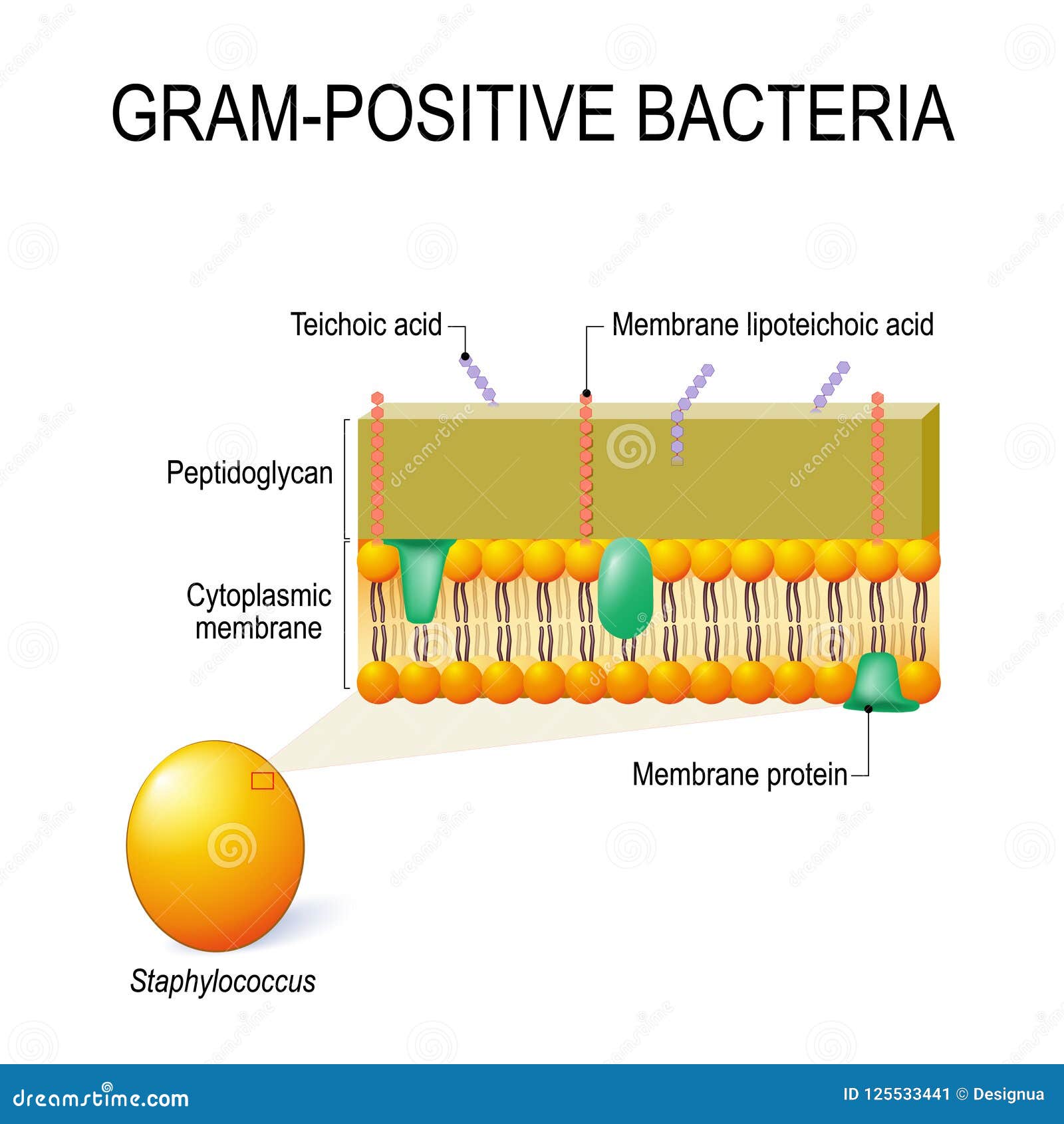
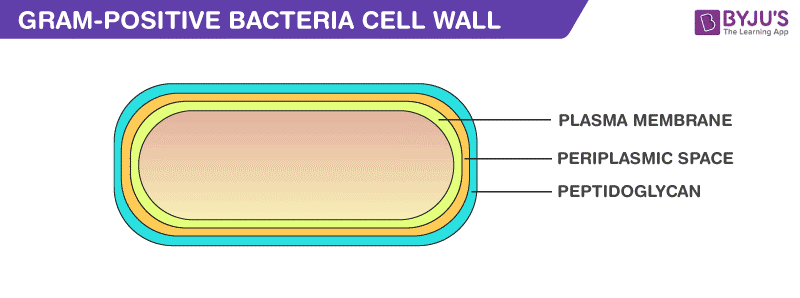
Why Do Gram Positive And Negative Bacteria Stain ... Why Do Gram Positive And Gram-Negative Bacteria Stain Differently? Due to variations within the thickness of a peptidoglycan layer within the cell membrane between Gram optimistic and Gram damaging micro organism, Gram optimistic micro organism (with a thicker peptidoglycan layer) retain crystal violet stain in the course of the decolorization course of, whereas Gram damaging micro organism ... Gram positive bacterial cell wall by Russell Kightley Media Picture of Gram +ve bacterial cell wall. The image above is 400 pixels across and the original is 2,000 pixels across. The Gram positive cell wall has a thick peptidoglycan (orange red in this picture) layer outside the plasma membrane.There may be a gap or periplasmic space between the peptidoglycan layer and the plasma membrane.Various membrane proteins can be seen floating in the plasma ...
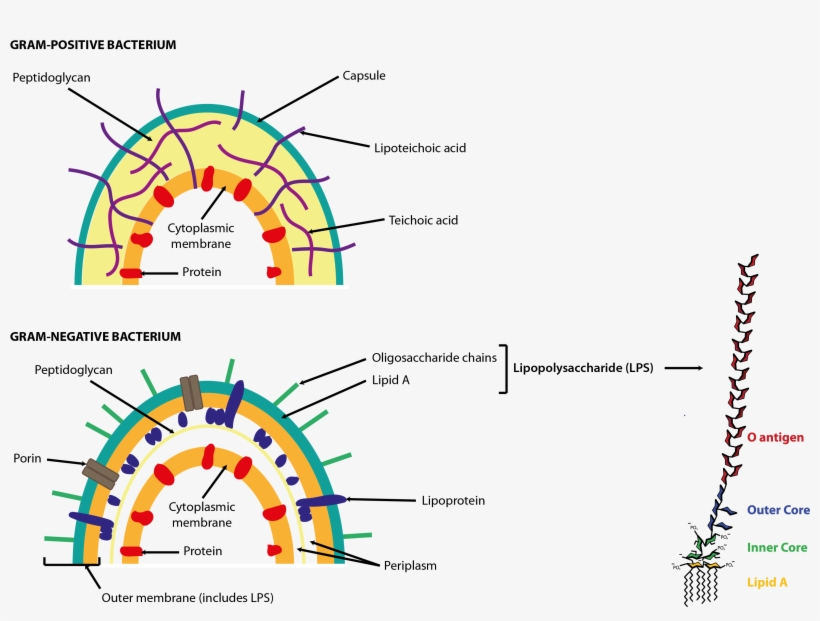
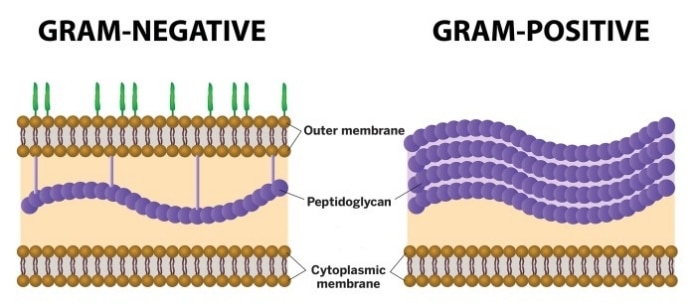
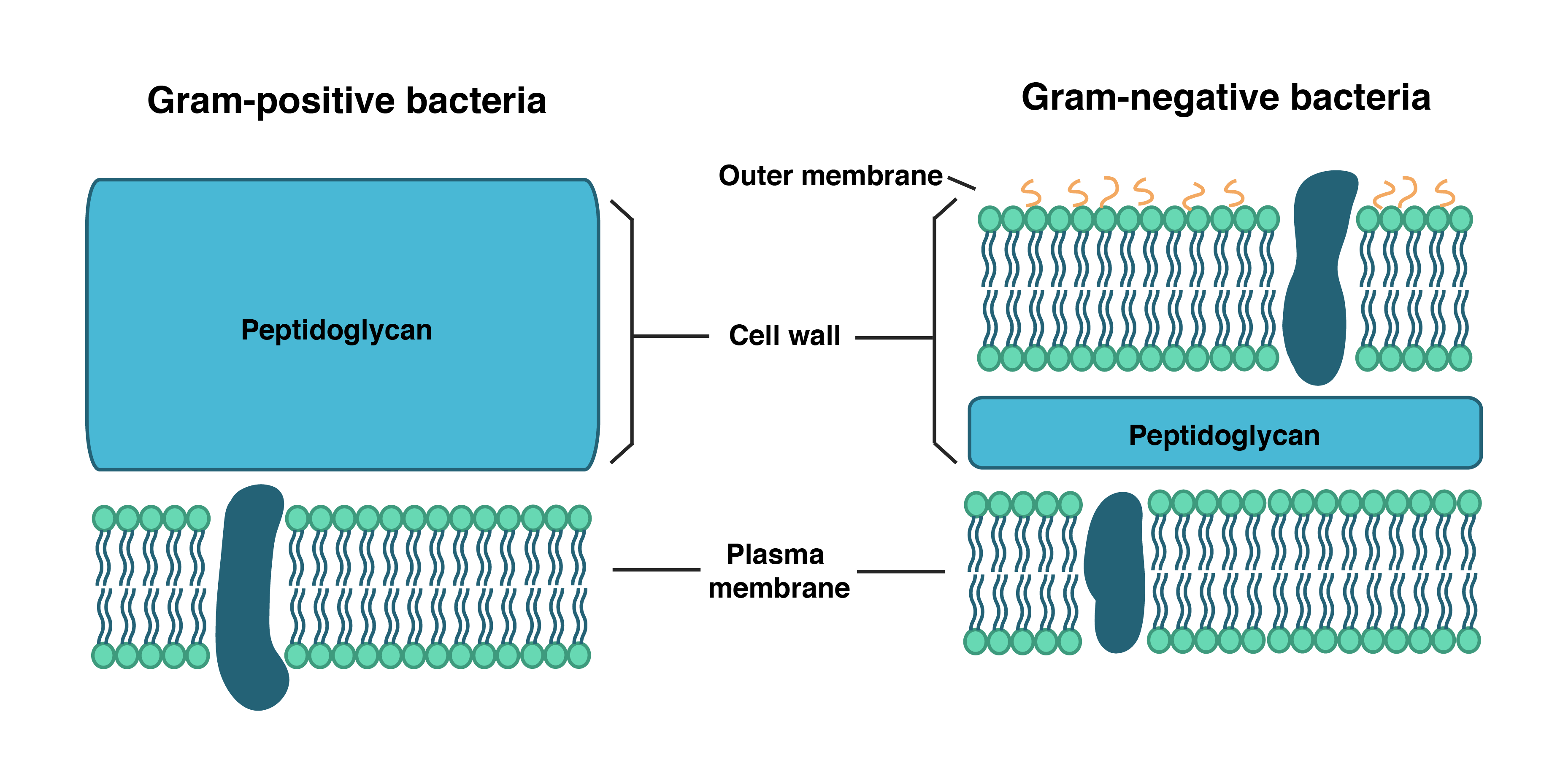
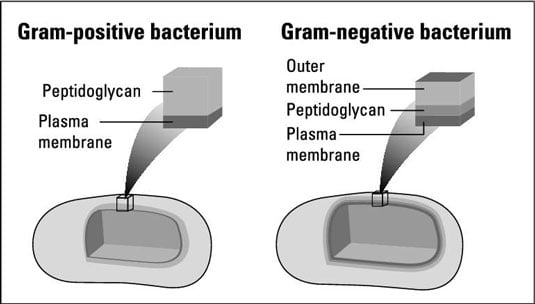
Peptidoglycan Function & Structure | What is Peptidoglycan ... A diagram showing the difference between the cell envelope of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Peptidoglycan Functions Peptidoglycan functions for bacteria are numerous.
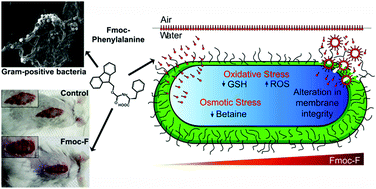
Gram positive bacteria diagram
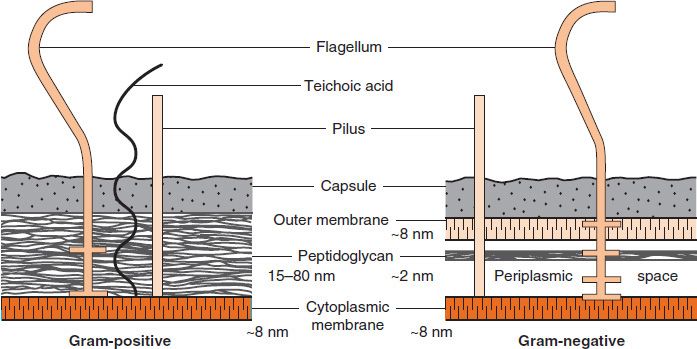
Bacterial Cell Wall Structure: Gram-positive & negative In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycan makes up as much as 90% of the thick cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane. Gram Staining! During Gram staining, these thick, multiple layers (20-80 nm) of peptidoglycan retain the dark purple primary stain crystal violet, whereas Gram-negative bacteria stain pink. PDF Bacterial Classification, Structure and Function Gram positive bacteria have a large peptidoglycan structure. As noted above, this accounts for the differential staining with Gram stain. Some Gram positive bacteria are also capable of forming spores under stressful environmental conditions such as when there is limited availability of carbon and nitrogen. Spores therefore allow bacteria to ... Difference Between Gram positive and Gram negative Bacteria The cell wall of bacteria Gram-positive and negative bacteria differ in their thickness. It is an important layer to understand the structure and difference between Gram-positive and negative bacteria, which we will understand later in this write-up. The third layer is the Capsule which is the sticky outer layer for attachment and protection.
Gram positive bacteria diagram. Microbiology: Gram-Negative Bacilli Flashcards - Quizlet A culture from an infected dog bite on a small boy's finger yielded a small, gram-negative coccobacillus that was smooth, raised and beta-hemolytic on blood agar. The isolate grew on MAC forming colorless colonies. The organism was motile, catalase positive, oxidase positive, reduced nitrate, and was urease positive within 4 hours. Gram Negative Bacteria Flow Chart - Reviews Of Chart Solved Gram Positive Flow Chart The Graphic Below Is Able Move Your Mouse Over An Item On And If Arrow Turns Into A Hand Cl Course Hero. Gram Negative Flowchart Docx Bacteria Quynh Dinh Oxidase Test Mr Urease Enterobacter Aerogenes Course Hero. Flow diagram of bloodstream infection gram negative bacterial isolates scientific dichotomous key ... Microbiology: Compare and contrast gram-positive and gram ... Start studying Microbiology: Compare and contrast gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Bacteria: Cell Walls - General Microbiology 4 Bacteria: Cell Walls . It is important to note that not all bacteria have a cell wall.Having said that though, it is also important to note that most bacteria (about 90%) have a cell wall and they typically have one of two types: a gram positive cell wall or a gram negative cell wall.. The two different cell wall types can be identified in the lab by a differential stain known as the Gram stain.
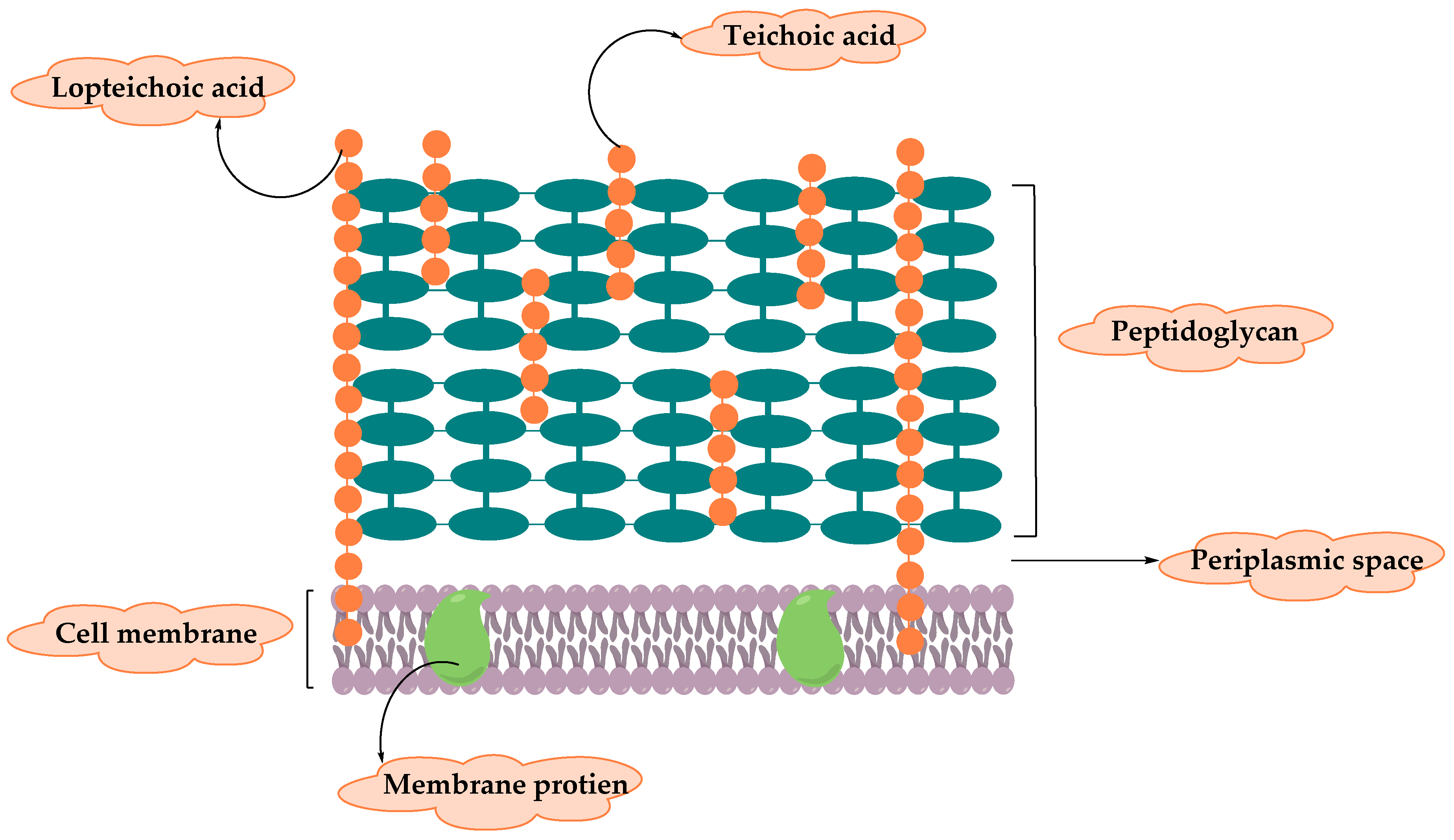
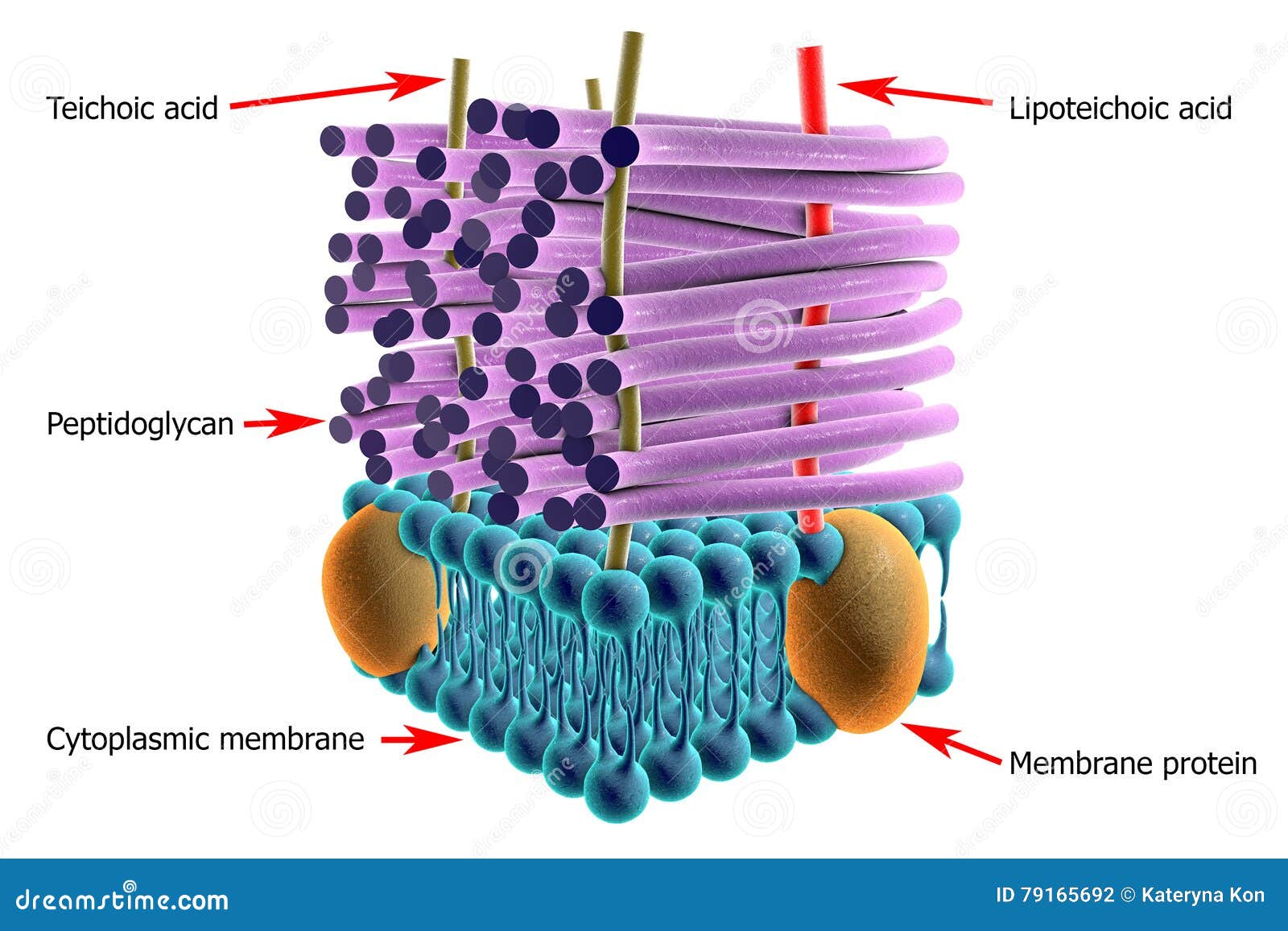
Bacteria Under The Microscope - Types, Morphology and ... Gram-Positive Bacteria Unlike gram-negative, gram positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer that allows them to retain the primary stain/dye (crystal violet stain). Fixing with heat allows the stain to penetrate the layer, which is then retained even when the cells are washed using alcohol. Gram positive bacteria: examples and structure - Jotscroll Gram positive bacteria diagram Diagram of Gram positive bacteria showing the cell wall structure Photo credit: Classification. Gram staining is a differential technique used to differentiate bacterial cells. Hence, these bacterial cells are classified according to the gram staining test result along with the cell ... Solved S. pyogenes is a gram-positive bacterium. | Chegg.com Gram-positive bacteria have structural differences that distinguish them from gram-negative organisms of particular Interest to this case is the fact that these differences in structure can be exploited during treatment Drag each of the labels onto the diagram to correctly label the indicated structures Cell wall Teichoic acid Peptidoglycan ... Gram-Positive Bacteria: Definition, Structure, and Facts Gram-positive living beings have a thicker peptidoglycan cell wall contrasted and gram-negative bacteria. It is a 20 to 80 nm thick polymer while the peptidoglycan layer of the gram-negative cell wall is 2 to 3 nm thick and covered with an external lipid bilayer film. Circulatory system disease death rates have expanded by 78% in only twenty years.
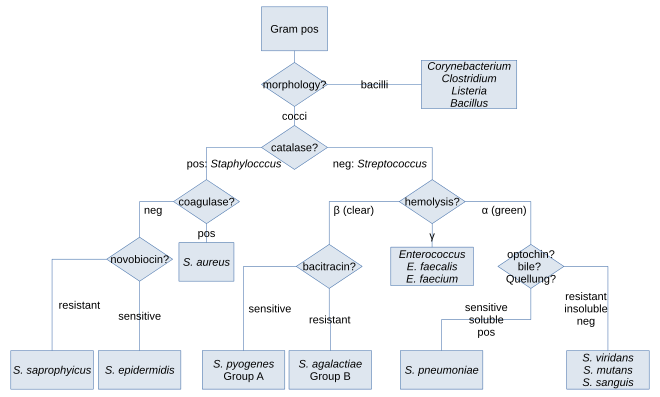
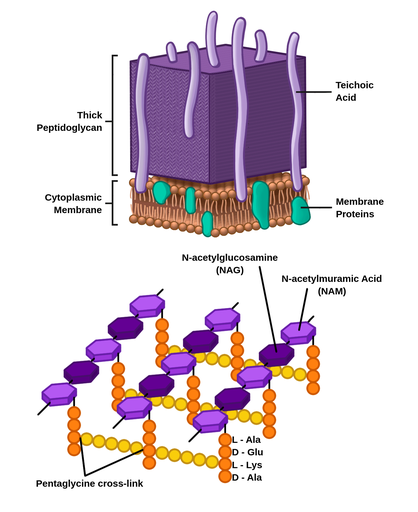
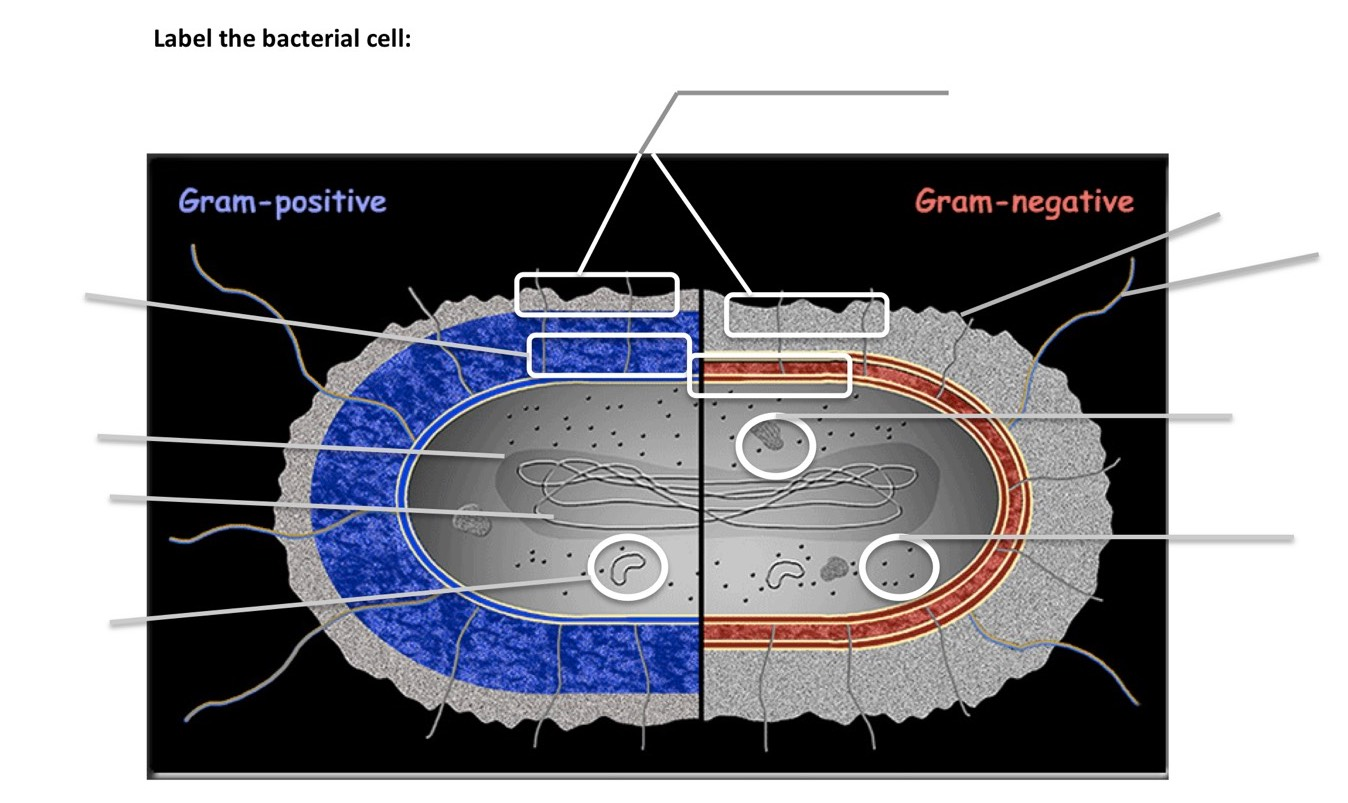
Gram Positive Bacilli Flowchart - Chart Examples Unknown organisms shall be two Gram-negative bacteria two Gram-positive bacteria or one of each. The six flow charts well be discussing are. Gram Negative Bacilli. Bacteria from Fishes Dr. Coagulase Test Hemolysis Test Novobiocin Test. Flowchart For Identification Of Anaerobic Gram Positive Bacilli 1 Scientific Diagram. Microbiology Test 2 (Chapter 4: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes ... S. pyogenes is a gram-positive bacterium. Gram-positive bacteria have structural differences that distinguish them from gram-negative organisms. Of particular interest to this case is the fact that these differences in structure can be exploited during treatment. *Drag each of the labels onto the diagram to correctly label the indicated structures. Structure of Bacteria (With Diagram) | Microbiology 8. According to Peberdy (1980) the only compound present in the cell walls of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria is 'peptidoglycan'. The cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria contain up to 95% peptidoglycan and up to 10% teichoic acids. 9. Cytoplasmic membrane is a thin (5-10 nm) layer lining the inner surface of the cell wall. Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria - Structures ... Gram positive bacteria are a group of organisms that fall under the phylum Firmicutes. However, a few species have a Gram negative cell wall structure. As compared to Gram negative bacteria, this group of bacteria is characterized by their ability to retain the primary stain (Crystal violet) during Gram staining (giving a positive result). ...
Gram-Negative Bacteria | List, Characteristics & Types ... Gram-positive bacteria trap the stain more effectively, causing the difference in color. In today's medicine, Gram staining is an important test to identify bacteria and aid in diagnosis.
Gram positive vs gram negative bacteria differences ... Gram positive vs gram negative bacteria diagram showing the color difference after gram staining The diagram above shows a comparison of gram positive vs gram negative bacteria under microscope. Gram-positive bacteria appear purple or pale blue while gram-negative bacteria appear red or pink.
Gram-positive bacteria - Wikipedia In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.. Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope.
Difference Between Gram-positive and Gram-negative Bacteria Gram-positive bacteria, on the other hand, retains the gram stain and show a visible violet colour upon the application of mordant (iodine) and ethanol (alcohol). Gram-positive bacteria constitute a cell wall, which is mainly composed of multiple layers of peptidoglycan that forms a rigid and thick structure.
Gram Staining- Principle, Reagents, Procedure, Steps, Results Feb 04, 2022 · Gram staining is a differential bacterial staining technique used to differentiate bacteria into Gram Positive and Gram Negative types according to their cell wall composition. It is the most widely used and the most important staining technique in bacteriology, especially in medical bacteriology.
Gram Positive vs. Gram Negative Bacteria - ThoughtCo Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive coccus (round) bacteria that is found on the skin and mucous membranes of humans and many animals. The bacteria are usually harmless, but infections can occur on broken skin or within a blocked sweat or sebaceous gland, resulting in boils, pustules and abscesses.
Gram Positive Vs Gram Negative Bacteria: A Comparison ... Christian Gram, a Danish Physician in 1884 developed a staining technique to distinguish two types of bacteria. The two categories of bacteria based on gram staining are Gram positive bacteria and Gram negative bacteria. Bacteria are first stained with crystal violet or gentian violet.
PDF Bacterial Cell Structure - Bellarmine University Compare and contrast the cell walls of typical Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. 3. Relate bacterial cell wall structure to the Gram-staining reaction. 37 . 38 Bacterial Cell Wall • Peptidoglycan (murein) -rigid structure that lies just outside the cell plasma membrane
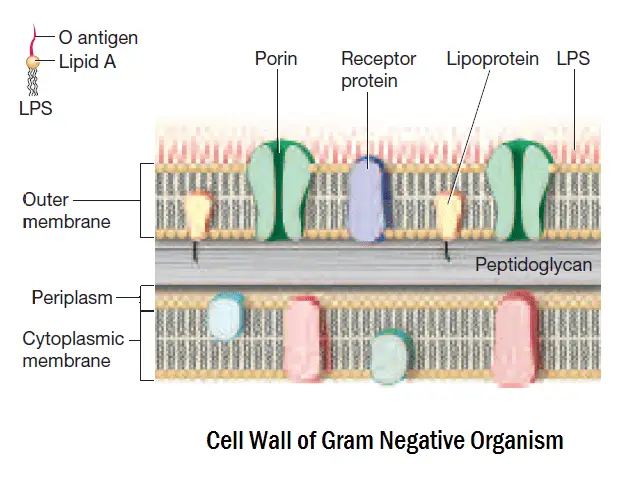
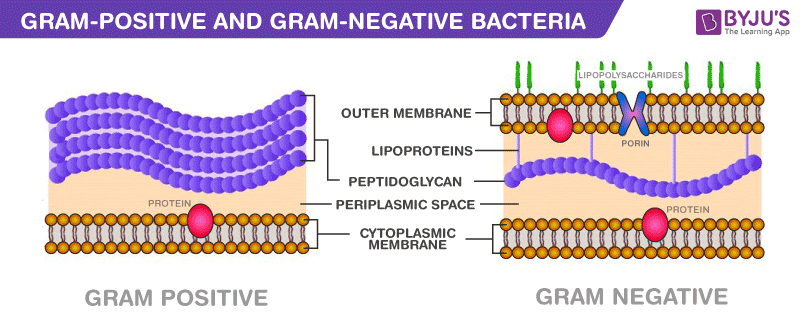
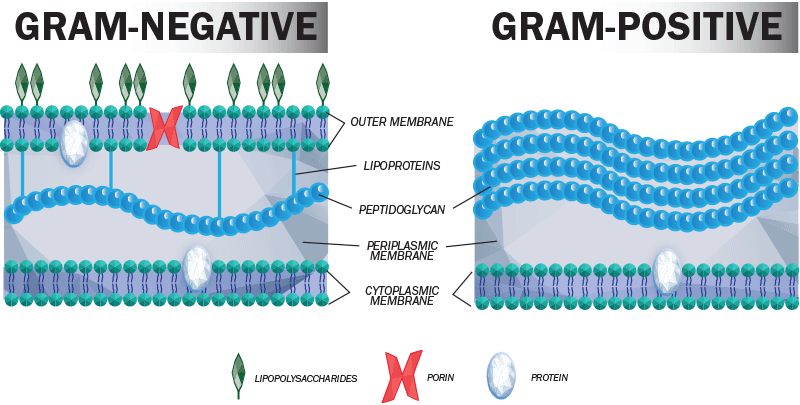
Interactive Bacteria Model - CELLS alive Gram-positive Cell Wall. Gram-negative Cell Wall. Outer Membrane. Cytoplasmic Membrane. Membrane Proteins. Porin
Gram-positive bacteria- cell wall, examples, diseases ... Gram-positive by definition in shape can be classified into two: Cocci - Singular form is known as coccus, which is round or oval shape bacteria measuring 0.5-1.0 um in diameter. They occur in pairs or in chains or clusters or as singles. For example Staphylococcus app, Streptococcus app. Special spaces of cocci include tetrads, Sarcines
Gram Positive Bacteria - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Gram-positive bacteria comprise cocci, bacilli, or branching filaments. Health professionals need to understand the important difference between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria are bacteria classified by the color they turn in the staining method. Hans Christian Gram developed the staining method in 1884.
Gram Positive vs Gram Negative | Technology Networks The diagram below illustrates the differences in the structure of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. The two key features that lead to the differing visualization properties of Gram positive and Gram negative species are the thickness of the peptidoglycan layer and presence or absence of the outer lipid membrane.
Gram Positive Bacteria - Characteristics And Structure Gram-positive bacteria are the genus of bacteria family and a member of the phylum Firmicutes. These bacteria retain the colour of the crystal violet stain which is used during gram staining. These bacteria give a positive result in the Gram stain test by appearing purple coloured when examined under a microscope, hence named, gram-positive ...
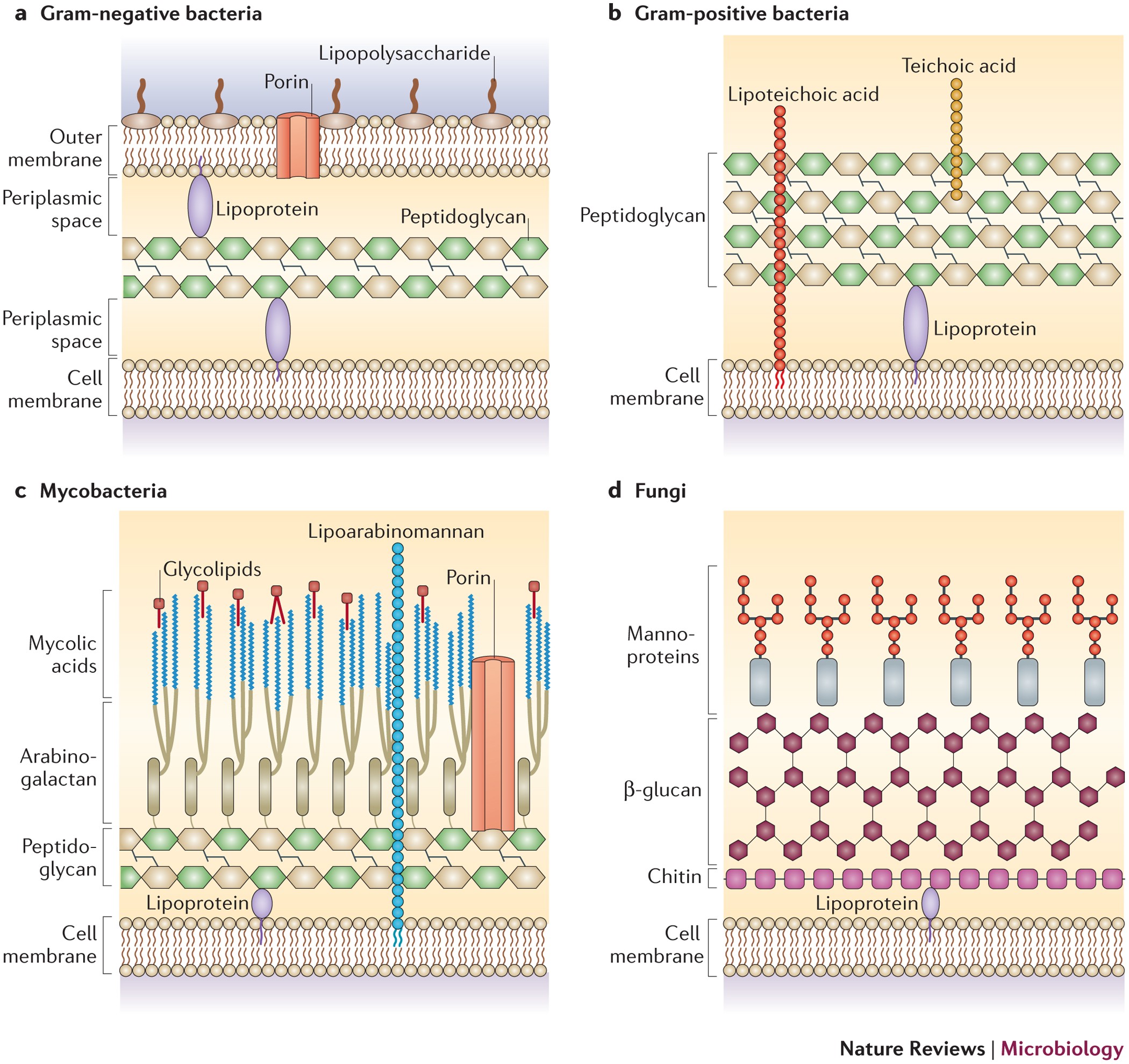
Action and resistance mechanisms of antibiotics: A guide ... The Gram-positive bacteria consists of cytoplasmic membrane surrounded by a tough and rigid mesh called cell wall. In contrast, Gram-negative bacteria consist of thin cell wall that is surrounded by second lipid membrane called outer membrane (OM). The space between the OM and cytoplasmic membrane is referred as periplasm [Figure 1]. The OM is ...
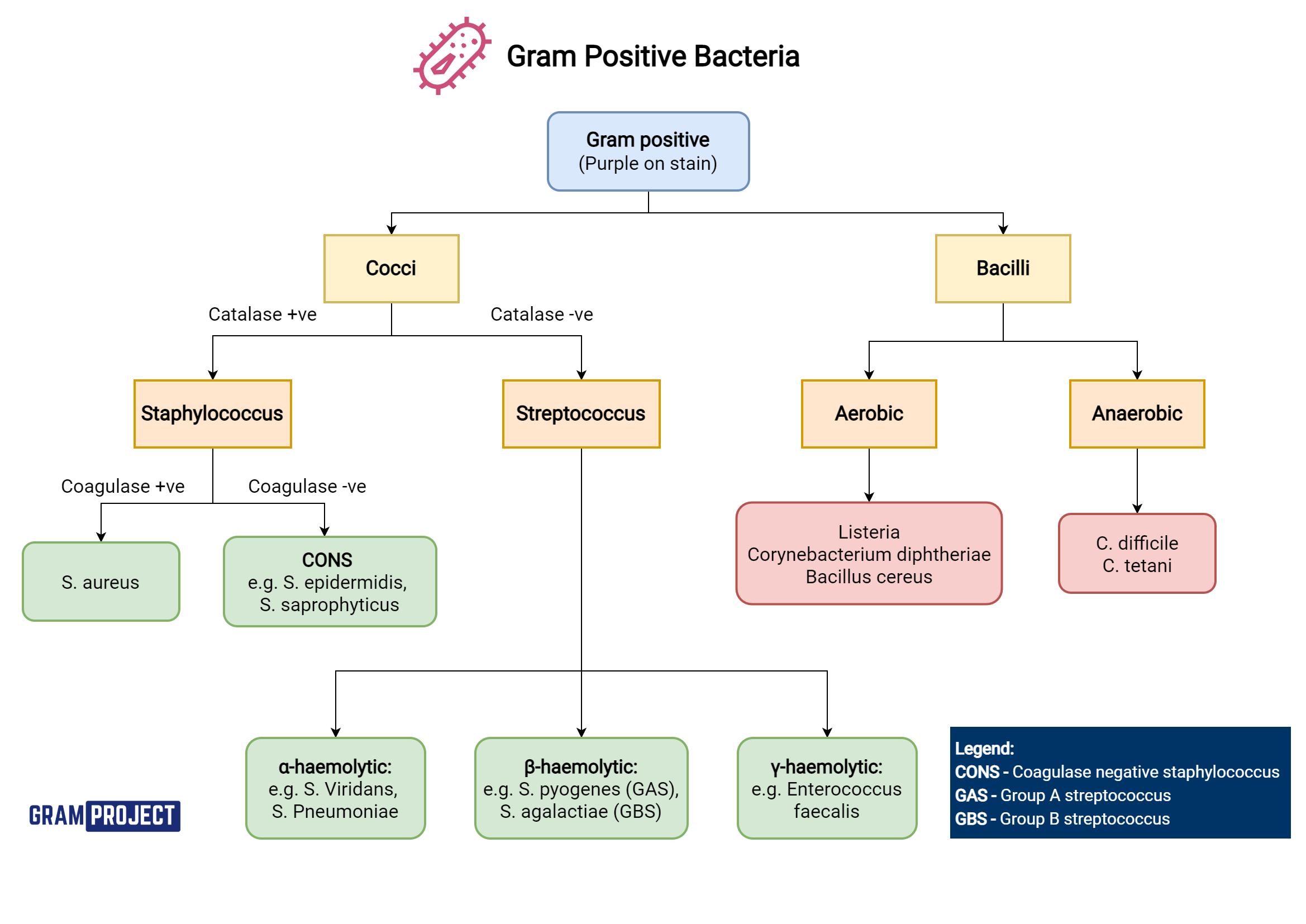
Gram Positive Bacteria - Gram Project Gram positive bacteria types and classification. Gram Project is a medical education resource website containing diagrams, tables and flowcharts for all your quick referencing, revision and teaching needs.
Envelope Structures of Gram-Positive Bacteria - PMC - NCBI by M Rajagopal · 2017 · Cited by 144 — Gram-positive organisms, including the pathogens Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Enterococcus faecalis, have dynamic cell envelopes that ...MRSA: Methcillin-resistant Staphylococcus aur...PGT: Peptidoglycan glycosyltransferasePG: PeptidoglycanLTA: Lipoteichoic acid
Difference Between Gram positive and Gram negative Bacteria The cell wall of bacteria Gram-positive and negative bacteria differ in their thickness. It is an important layer to understand the structure and difference between Gram-positive and negative bacteria, which we will understand later in this write-up. The third layer is the Capsule which is the sticky outer layer for attachment and protection.
PDF Bacterial Classification, Structure and Function Gram positive bacteria have a large peptidoglycan structure. As noted above, this accounts for the differential staining with Gram stain. Some Gram positive bacteria are also capable of forming spores under stressful environmental conditions such as when there is limited availability of carbon and nitrogen. Spores therefore allow bacteria to ...
Bacterial Cell Wall Structure: Gram-positive & negative In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycan makes up as much as 90% of the thick cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane. Gram Staining! During Gram staining, these thick, multiple layers (20-80 nm) of peptidoglycan retain the dark purple primary stain crystal violet, whereas Gram-negative bacteria stain pink.
















0 Response to "41 gram positive bacteria diagram"
Post a Comment