40 free body diagram of a car
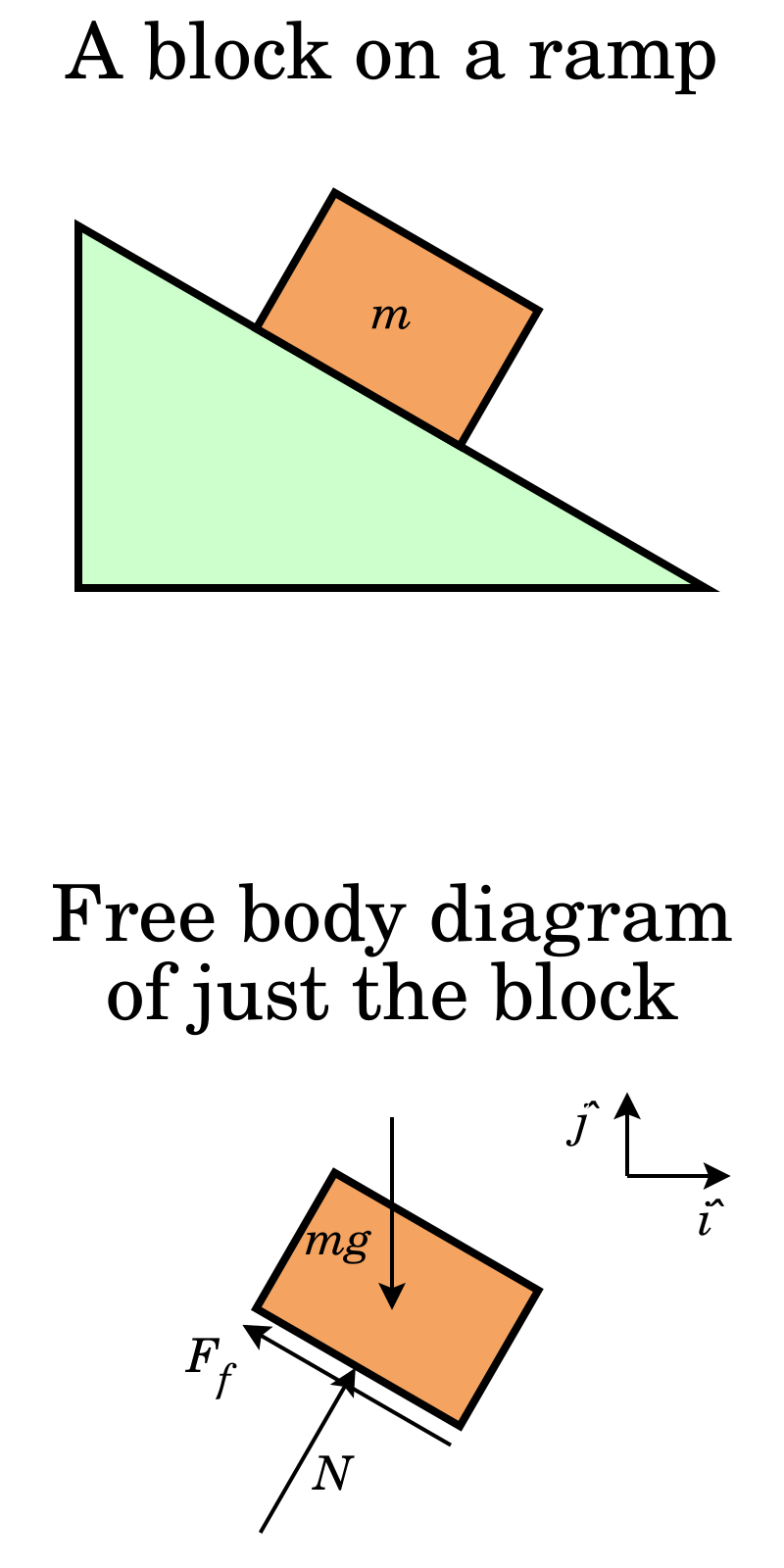
I make a free-body diagram for a car that accelerates to the right. I make a free-body diagram for a car that accelerates to the right. A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram:
The car shown below is moving and then slams on the brakes locking up all four wheels. The distance between the two wheels is 8 feet and the center of mass is 3 feet behind and 2.5 feet above the point of contact between the front wheel and the ground. Draw a free body diagram of the car as it comes to a stop. Public Domain image, no author listed.
Free body diagram of a car
This is a free-body diagram for a car at constant speed. There is. The moment you take your foot off the gas pedal, though, there is no longer an applied force, ... Neglect air resistance. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this. Upward normal force, downward force of gravity. Rightward there is a force applied and force of friction to the left. A car is coasting to the right and slowing down. Neglect air resistance. Diagram the forces acting upon the car. A free-body diagram can be drawn very simply, with squares and arrows, or you can make it much more complex. The only requirement is that you or someone else looking at it should be able to understand what the diagram is telling. A free-body diagram (FBD) is a representation of a certain object showing all of the external forces that acts on it.
Free body diagram of a car. Point mass model. The simplest model of a car is to treat the entire vehicle as a point mass. On a free body diagram we have vertical force balance for a stationary car. When the car accelerates, there is a horizontal forward force on the car, and a corresponding backwards horizontal force on the ground.As the car picks up speed, air resistance produces a backwards force. Free Auto Repair Diagrams. Below we provide access to three basic types of diagrams that will help in the troubleshooting and diagnosis of an automotive related problem. Wiring diagrams are one of the most common these days with all the added electronics. The bells and whistles tend to break the most often. Draw a free-body diagram; be sure to include the friction of the road that opposes the forward motion of the car. A runner pushes against the track, as shown. (a) Provide a free-body diagram showing all the forces on the runner. ( Hint: Place all forces at the center of his body, and include his weight.) $\begingroup$ That's a good free body diagram for a car slamming on the brakes :) $\endgroup$ - Gregor Thomas. Oct 16 at 1:19. Add a comment | 4 Answers Active Oldest Votes. 20 $\begingroup$ The friction forces on the bottom of the tyres should point in the direction of motion, not the opposite direction. ...
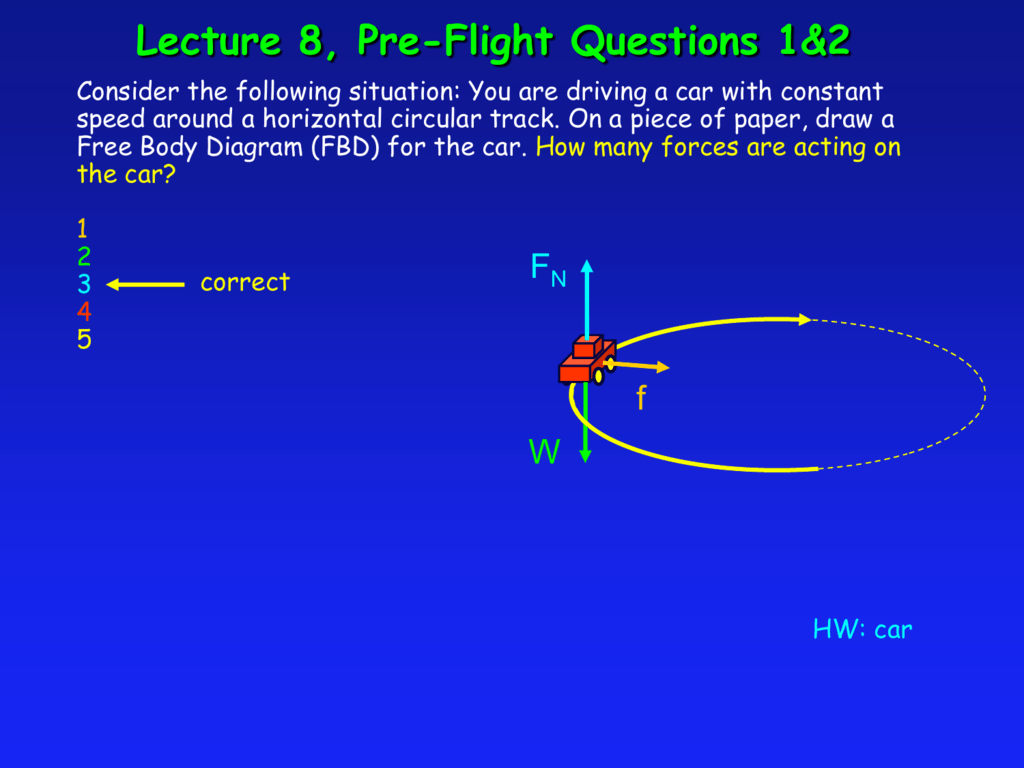
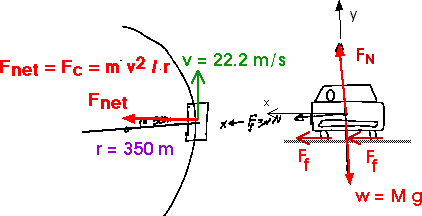
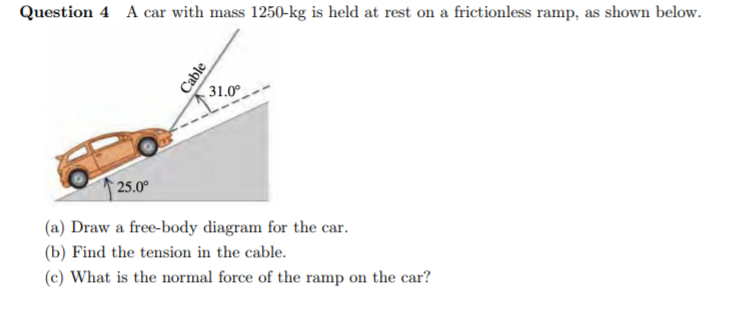
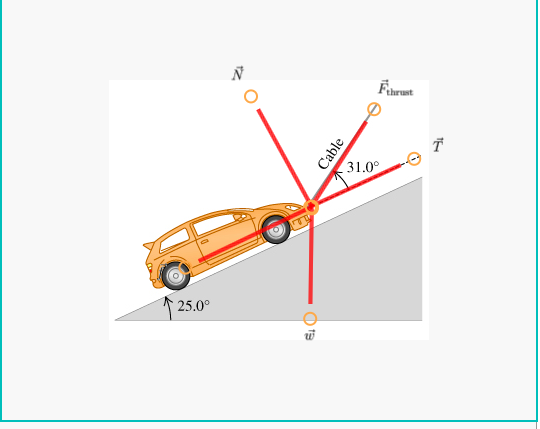
Construct free-body diagrams for the following physical situations. Label all forces (e.g, Fgrav, Fnorm, Fapp, Ffrict, Fair, Ftens, etc. ). a. A physics book rests upon a level table. ... a rightward moving car and it skids to a stop. h. A spider is slowly descending a thin silk thread at constant speed. i. A projectile is moving Learn how to draw the Free Body Diagram(FBD) of a car on a slope. Learn how to draw the Free Body Diagram(FBD) of a car on a slope. A car of mass 1.6 t travels at a constant speed of 72 km/h around a horizontal curved road with radius of curvature 190 m. (Draw a free-body diagram).1 page A free-body diagram for the car is shown at left. Both the normal force, N (blue components) and the friction force, f (red components) have been resolved into horizontal and vertical components. Notice that the friction force acts up the incline, to keep the car from sliding toward the center of the turn.
Free body diagram of the car as the car moves along the circular track with the minimum speed min v. In this case the difference in the normal force and ... A free-body diagram for the car on the banked turn is shown at left. The banking angle between the road and the horizontal is (theta). The normal force, N, has been resolved into horizontal and vertical components (the blue vectors). In the vertical direction there is no acceleration, and: so: A car pushes a block across the floor. (assume that it is moving from left to the right) Draw a free body diagram for the car showing: Force by block on car. Force of friction. Force of Gravity. Normal force. Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution Normal force Straight up, gravity straight down. A free-body diagram is a diagram that is modified as the problem is solved. Normally, a free body diagram consists of the following components: The number of forces acting on a body depends on the specific problem and the assumptions made. Commonly, air resistance and friction are neglected.
Description
Example: The car in Figure 2 is being towed by a force of some magnitude. Construct a free-body diagram showing all the forces acting on ...
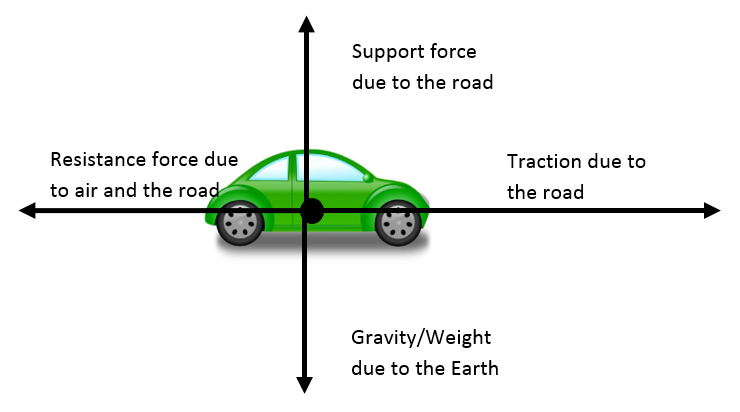
The free body diagram of a car traveling at a constant speed consists mainly of five forces, when considered in an actual situation. These vectors are that of friction, gravity, normal force, air resistance, and engine driving force. In a hypothetical situation without external forces (friction and air resistance), only the three remaining ...
31 May 2020 — Let's consider a car travelling at a constant velocity of 20 miles per hour. NOT a force diagram. (Note: whilst force arrows on situation ...
A car is coasting to the right and slowing down. Neglect air resistance. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: ...
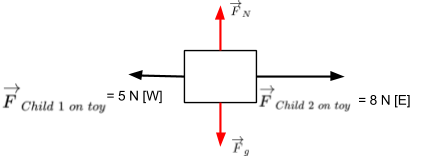
A. The force of gravity on the car. Explanation: A free-body diagram of an object must include all the forces acting on the object itself. Let's analyze each statement separately. A. The force of gravity on the car. --> This is one of the forces acting on the car, so it must be included in the free-body diagram. B.
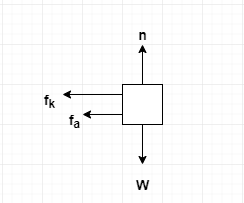
Free Body Diagrams When objects slow down (decelerate), they move in the direction OPPOSITE the net force. Example: A car coasts rightward while slowing down. MOTION F friction F gravity Fnormal Since the car is coasting to the right, there is no force being applied to the right.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
A free-body diagram can be drawn very simply, with squares and arrows, or you can make it much more complex. The only requirement is that you or someone else looking at it should be able to understand what the diagram is telling. A free-body diagram (FBD) is a representation of a certain object showing all of the external forces that acts on it.
Neglect air resistance. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this. Upward normal force, downward force of gravity. Rightward there is a force applied and force of friction to the left. A car is coasting to the right and slowing down. Neglect air resistance. Diagram the forces acting upon the car.
This is a free-body diagram for a car at constant speed. There is. The moment you take your foot off the gas pedal, though, there is no longer an applied force, ...























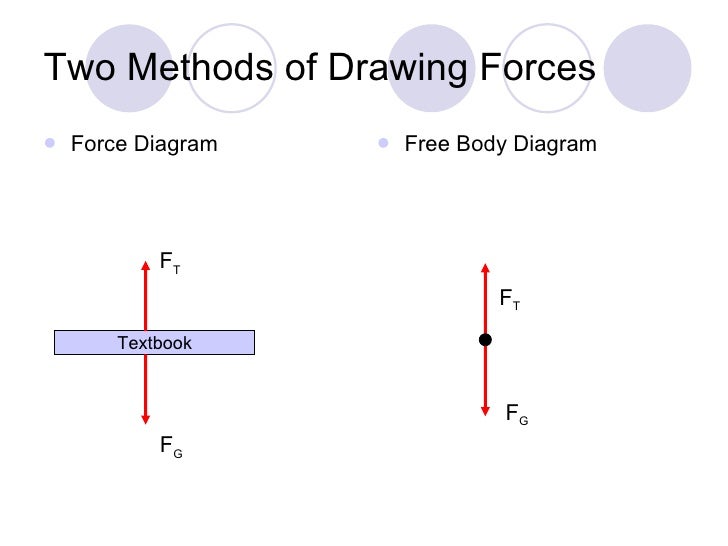
0 Response to "40 free body diagram of a car"
Post a Comment