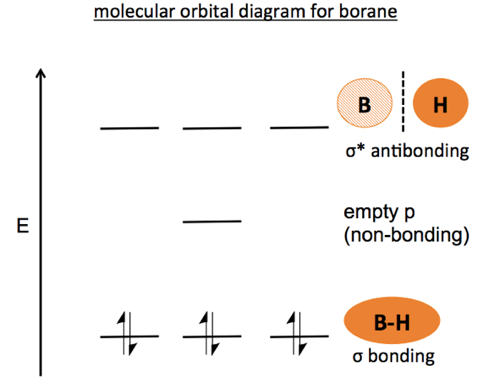
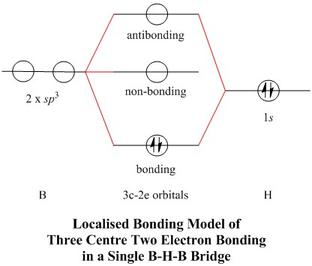
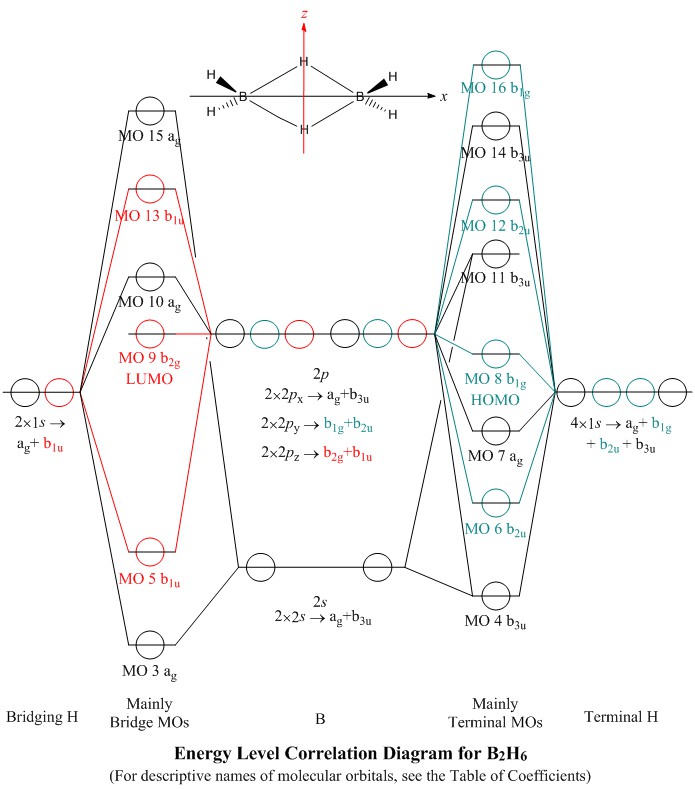
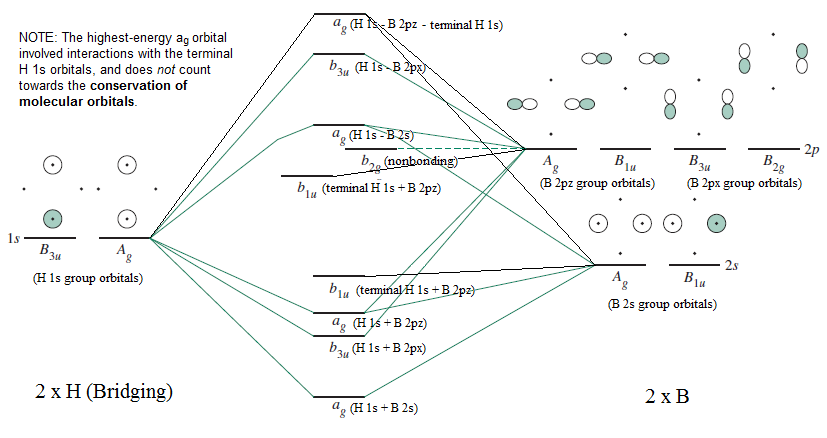
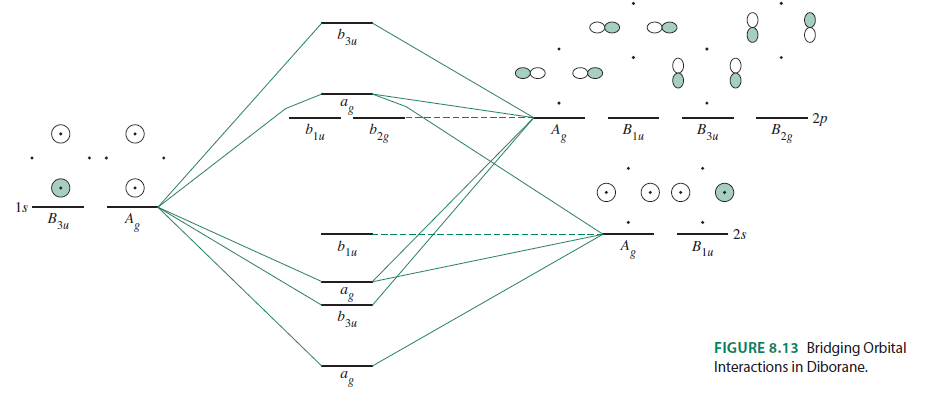
45 bh3 molecular orbital diagram
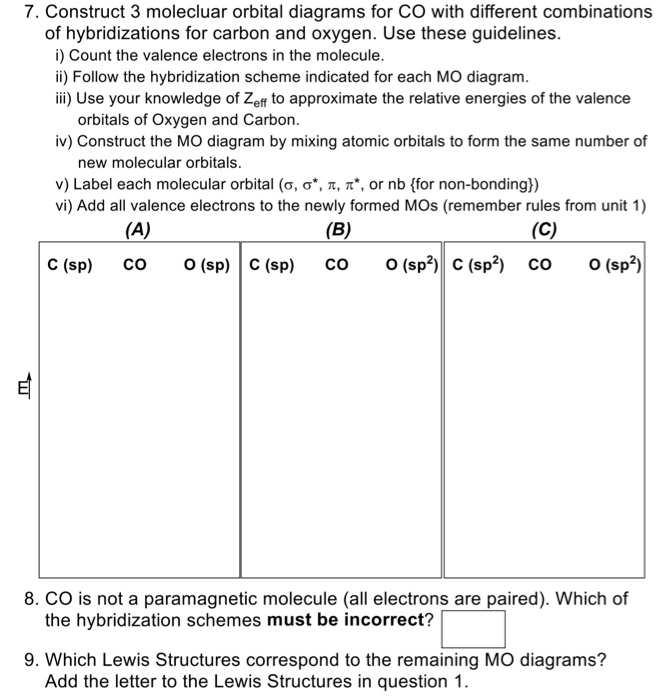
What is the hybridization of AlF3? AlF3 is a trigonal planar compound with a bond angle of 120 degree and a hybridization of sp2. C2H6 in this case each, carbon center are tetrahedral with a bond angle of 109.8 degree and a hybridization of sp3. hybridization of cl in clf2+. 5) The hybridization of the central atom, AL in AlBr3 is a)sp2 b)dsp3 c)sp3 d)d2sp3 e)sp. Total number of orbitals involved in the formation of hybrid orbitals in C l F 2 + is four. Find the hybridization as well identify the pπ-pπ as well as pπ-dπ bonds in $\ce {ClO2}$. 1. E. d2sp3.
This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic orbitals.
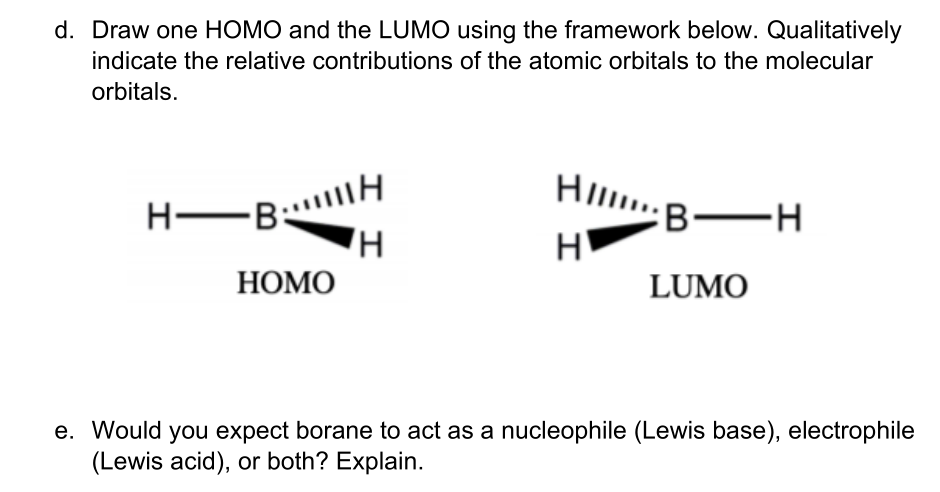
Bh3 molecular orbital diagram
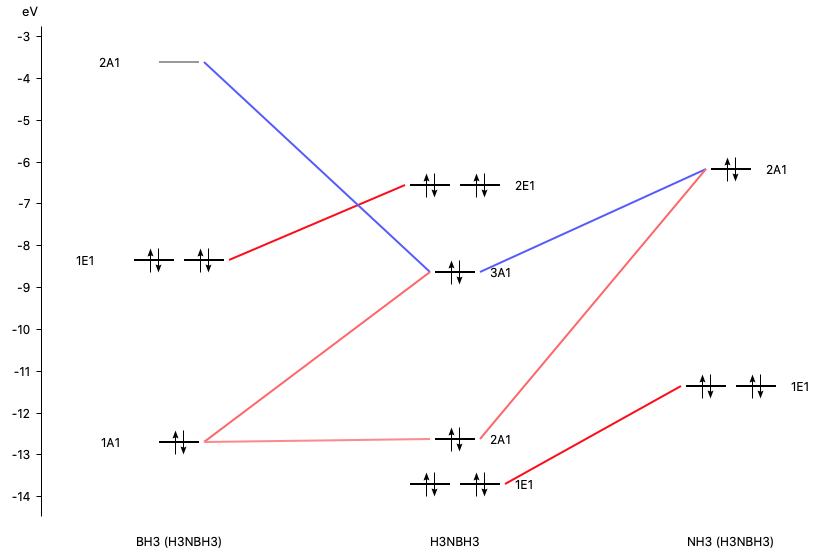
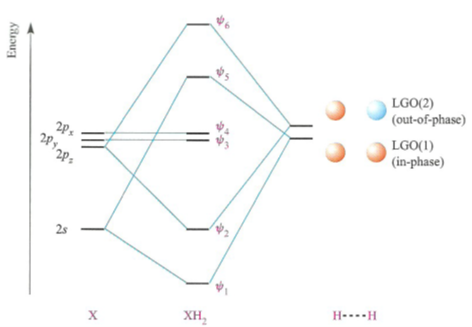
An advanced molecular orbital diagram of beh2 beryllium hydride for the inorganic or physical chemistry student. Molecular orbitals and walsh diagram. Walsh correlation diagram is a plot of molecular orbital energy as a function of some systematic change in molecular geometry. Be has 2s and 2p orbitals and it is in the middle. BH3_LGO. BH3_LGO. BH3_LGO. Kasey Devlin explains how to determine the symmetry labels for BH3 ligand group orbitals for a MO diagram. che124a. labels. ligands ... Molecular Orbitals for homonuclear diatomics from H to Ne. Simple description of Molecular orbitals for homonuclear diatomics form H to He . che124a. orbitals. Sp³, sp² and sp hybridization, or the mixing of s and p orbitals which allows us to create sigma and pi bonds, is a topic we usually think we understand, only to get confused when it reappears in organic chemistry molecules and reactions.. When I took general chemistry, I simply memorized a chart of geometries and bond angles, and I kinda/sorta understood what was going on.
Bh3 molecular orbital diagram. This means only one of nitrogen's p orbitals is available to be hybridized, and so the hybridization of nitrogen in HCN is "sp". What is the molecular shape (VSEPR shape) of HCN? Because the carbon is connected to two atoms, with no lone pairs on that central carbon, the geometry is AX2, which is "linear". The bond order can be interpreted from MO diagram s using the following for mula: `" Bond Order" = 1/2 [(" Bond ing "e^-)-("Anti bond ing " e^-)]` One half the difference between the number of electrons present in the bond ing and the anti-bond ing orbitals is bond order Bond order (B.O) =1/2(Nb−Na) Bond order of H2− To tal number of ... Molecular Weight: 60.009. Dates: Modify . 2021-11-20. Create . 2004-09-16. Contents. 1 Structures Expand this section. 2 Names and Identifiers Expand this section. 3 Chemical and Physical Properties Expand this section. 4 Related Records Expand this section. 5 Literature Expand this section. 6 Patents Expand this section. 7 Information Sources. Results #1. Bond order is a concept in the molecular orbital theory. It depends on the number of electrons in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Which of the following statements is true about it ? The bond order Can have a negative quantity Can have a negative quantity Has always an integral value Has always...
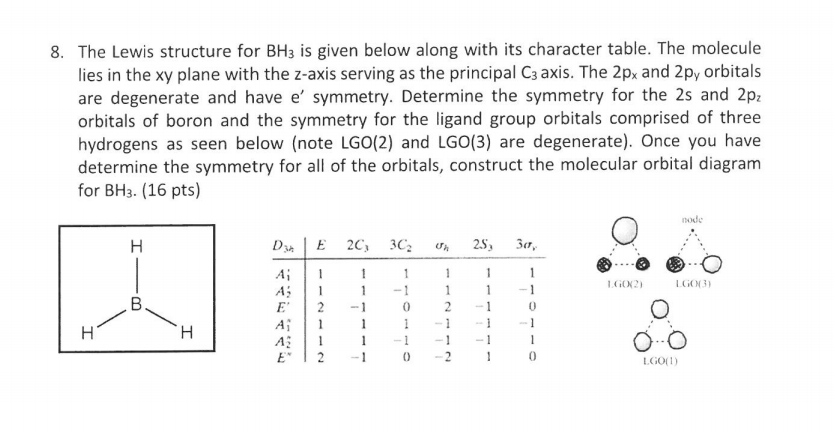
Below is the geometrical structure of the Trihydridoboron (BH3) molecule. Properties of BH3. Borane gas is colorless in appearance. It is unstable in nature therefore highly reactive. Its molecular mass is around 13.83 g·mol−1. Boronium ion is considered to be its conjugate acid. borohydride anion is its conjugate base. NH3 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Bond Angle & Shape. Ammonia is a colorless compound, used in making fertilizers. It is a stable hydride formed of one nitrogen and three hydrogen atoms. The molecule has a pungent smell. It can form an NH4+ ion by accepting a proton. Bh3 molecule is an electron deficient molecule in nature since the 6 electrons are around the 'B' atom. Hydrogen being small in size, plus electron deficient it cannot donate electrons to boron, hence to exist, Bh3 goes under dimerization so as to fulfill the electron deficiency and attain stability. Identify the types of hybrid orbitals found in molecules of the following substances; (8 marks - 2 marks each) a) CCl4(l) b) BH3(g) c) BeI2(s) d) SiH4(g) The polarity of a molecule is determined by bond polarity and molecular shape. a) Compare the polarity of the bonds N-Cl and C-Cl. (2 marks)
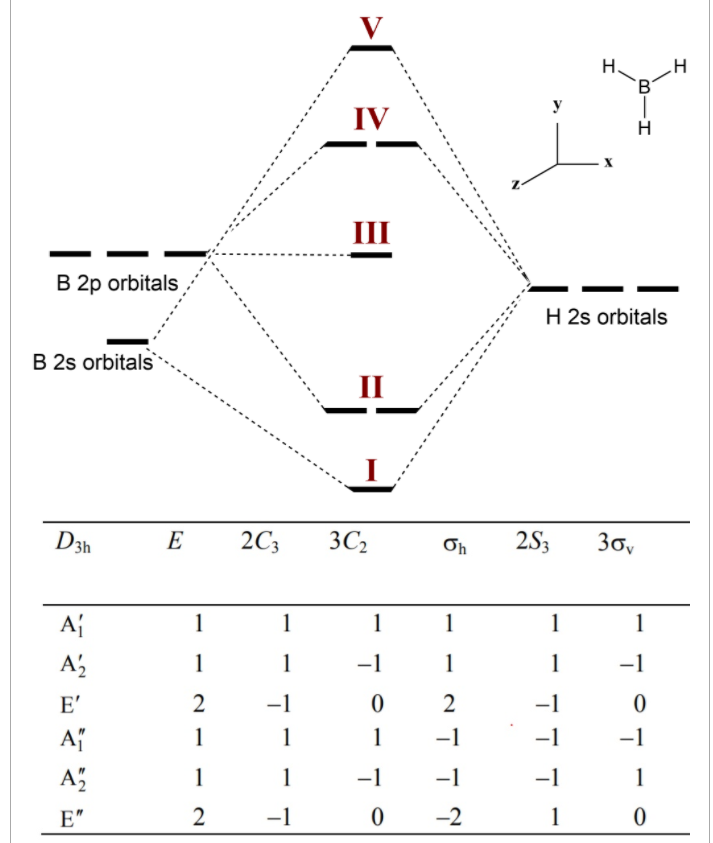
BF3 is SP2 hybridization. For this molecule, It is SP2 because one π (pi) bond is required for the double bond between the Boron and only three σ bonds are formed per Boron atom. The atomic S - orbitals and P - orbitals in Boron outer shell mix to form three equivalent SP2 hybrid orbitals. Answer (1 of 2): Refer to the Lewis structure of BH₃ and NaBH₄ respectively. In BH₃, the central B atom has only 6 electrons in the outermost shell, and it cannot complete its octet. In NaBH₄, the central B atom of BH₄⁻ ion has 8 electrons in the outermost shell, and it completes its octet. O... Molecular geometry is associated with the chemistry of vision, smell and odors, taste, drug reactions and enzyme controlled reactions to name a few. BH3 is non-polar. Molecular Geometry of BF3. 1 decade ago. 5) What is the Molecular Geometry (MG)? Examples of molecular weight computations: C[14]O[16]2, S[34]O[16]2. FIGURE2: Character table for the the point group D3h. B atom in BH3: +s-orbital: with the shape of the sphere, its function is x 2 +y 2 +z 2.Therefore, 2s orbital has a 1 ' symmetry +p-orbital: has 3 orbitals , p x, p y, p z.Therefore, 2p z orbital has a 2" symmetry. 2p x and 2p y orbital are degenerate and have e' symmetry. 3 Hydrogen atoms in BH3: (Ligand group orbitals)
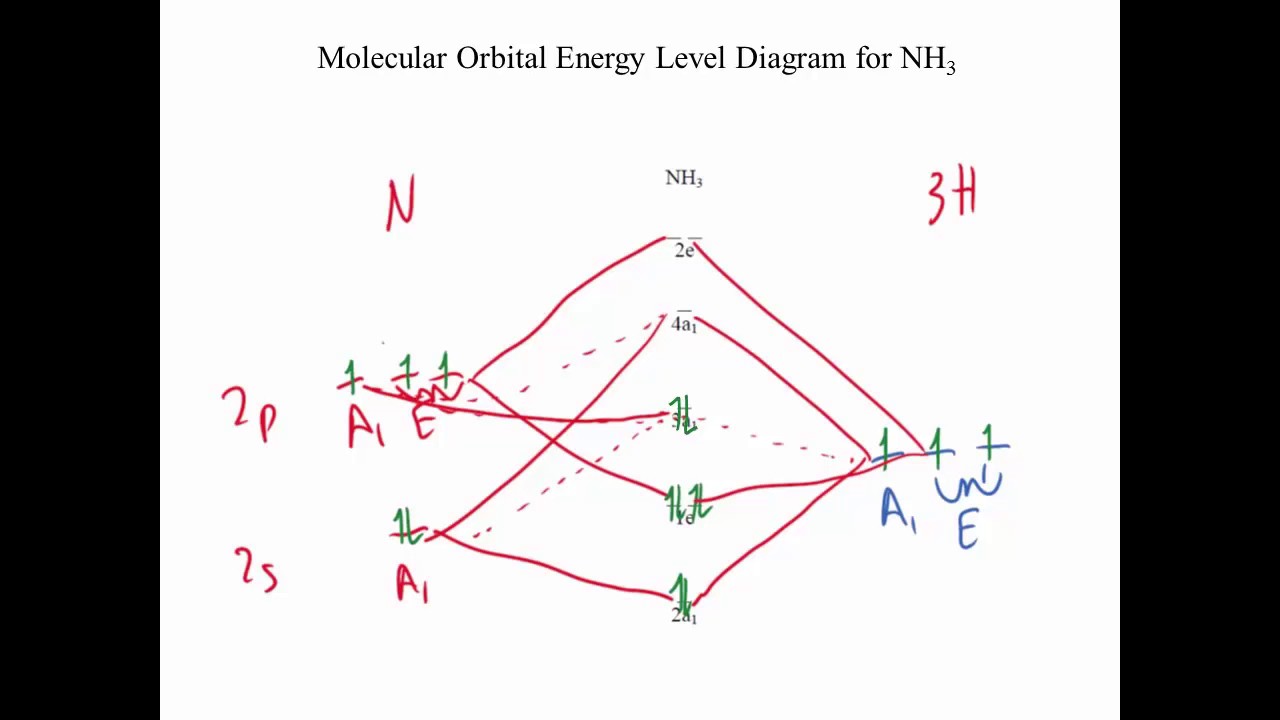
Kasey Devlin explains how to put together a MO diagram of BH3 once you have the BH3 LGO. che124a. orbitals. prime. bonding. thing. bond. 2s. hydrogens. boron. molecule. electrons. a2. symmetry. ... Molecular Orbitals for homonuclear diatomics from H to Ne. Simple description of Molecular orbitals for homonuclear diatomics form H to He ...
Molecular orbital diagram s are diagram s of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked on the sides by constituent AO energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels ranging from low energy at the bottom to high energy at the top. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms ...
Energy Level Diagram for Molecular Orbitals 1s atomic orbitals of two atoms form two molecular orbitals designated as s1s ( Bonding 1 s)and s*1s ( antibonding 1s) In the same manner, the 2s and 2p atomic orbitals (eight atomic orbitals on two atoms) give rise to the following eight molecular orbitals- Antibonding Mos s*2s , s*2pz , p*2px , p*2py .
BH3 is an electron deficient compound which has an empty p orbital or we can say 6 electron in its outermost shell. A PCl3 Is contains three covalent bond which are formed by equal sharing of electron in between phosphorus atom and chlorine atom hence its a covalent molecule.
BF3 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, and Hybridization. Boron Trifluoride (BF3) is an inorganic compound as it lacks a carbon atom or C-H bond in the molecule. Manufactured from the reaction of boron oxides and hydrogen fluoride, the chemical compound BF3 has a pungent smell and is colorless in nature. The compound behaves differently in ...
In the Lewis structure of CH3Cl, Carbon is at the central position and all the other atoms around it. The bond angles of Carbon with Hydrogen and Chlorine atoms are 109.5 degrees. This molecule has a tetrahedral shape, and the central carbon atom has sp3 hybridization.
I think I have the proper shape of the diagram but how do I label the symmetries of the MOs?
Answer (1 of 3): Dear Student Boron is a Group III element with atomic number 5 with 5 electrons. n - Principal Quantum Number Out of these 5 electrons first 2 electrons occupy 1s orbital of K shell (n=1). While remaining outermost valence 3 electrons occupy 2s and 2 p orbital present in L she...
1. Draw on a separate and ungraded paper the Lewis Dot Structure of borane, BH3 and of phosphine, PH3, and list the bond angles. Then, draw the orbitals involved in bonding (valence orbitals) on the boron atom in BH3 and on the phosphorous atom of PH3. Label each orbital (for example: s, p, sp, sp2, or sp3).
Sp³, sp² and sp hybridization, or the mixing of s and p orbitals which allows us to create sigma and pi bonds, is a topic we usually think we understand, only to get confused when it reappears in organic chemistry molecules and reactions.. When I took general chemistry, I simply memorized a chart of geometries and bond angles, and I kinda/sorta understood what was going on.
BH3_LGO. BH3_LGO. BH3_LGO. Kasey Devlin explains how to determine the symmetry labels for BH3 ligand group orbitals for a MO diagram. che124a. labels. ligands ... Molecular Orbitals for homonuclear diatomics from H to Ne. Simple description of Molecular orbitals for homonuclear diatomics form H to He . che124a. orbitals.
An advanced molecular orbital diagram of beh2 beryllium hydride for the inorganic or physical chemistry student. Molecular orbitals and walsh diagram. Walsh correlation diagram is a plot of molecular orbital energy as a function of some systematic change in molecular geometry. Be has 2s and 2p orbitals and it is in the middle.


















0 Response to "45 bh3 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment