44 Buoyant Force Free Body Diagram
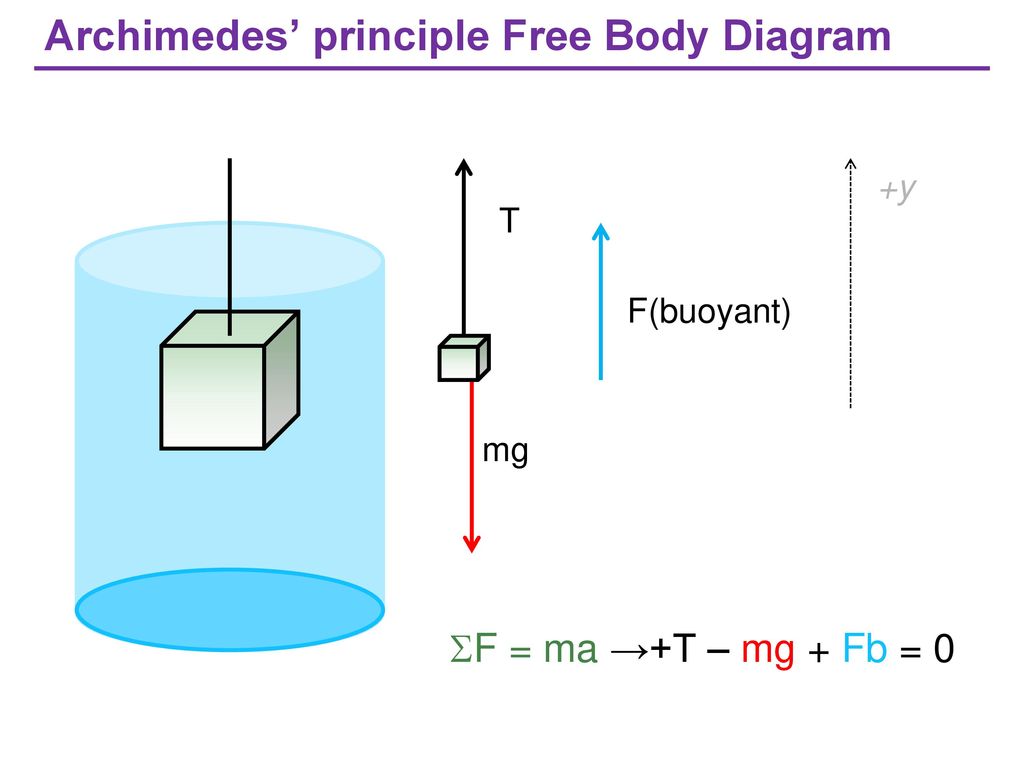
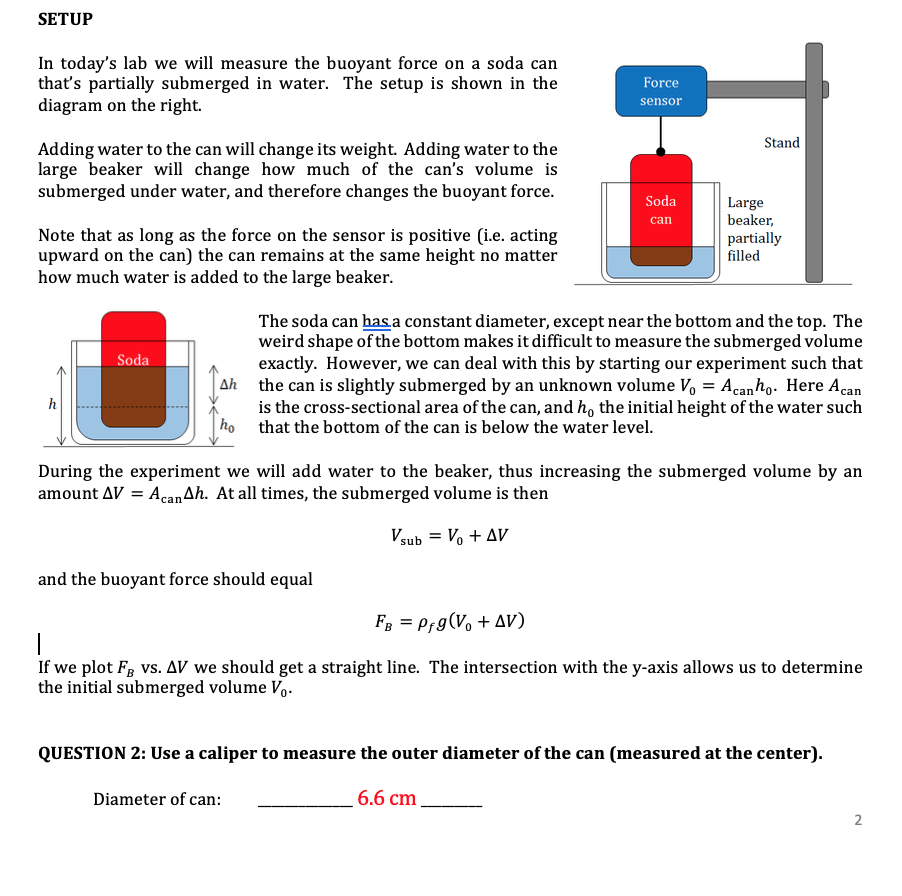
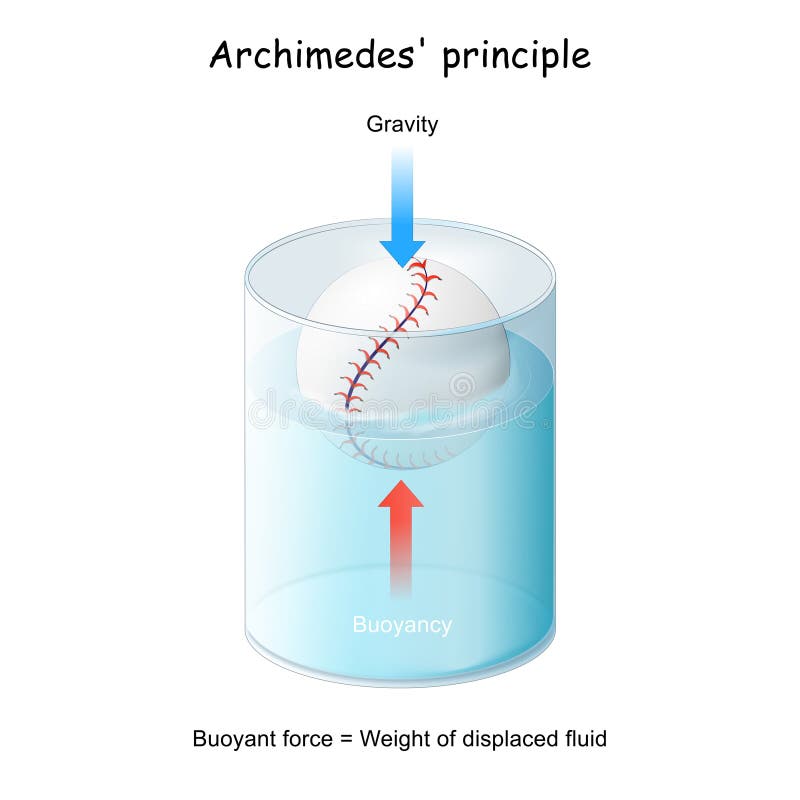
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › BuoyancyBuoyancy - Wikipedia More tersely: buoyant force = weight of displaced fluid. Archimedes' principle does not consider the surface tension (capillarity) acting on the body, [6] but this additional force modifies only the amount of fluid displaced and the spatial distribution of the displacement , so the principle that buoyancy = weight of displaced fluid remains valid. PDF Physics 203 - Lab 7 - Buoyancy second weight, called the "apparent weight" differs from the first due to the buoyant force. Draw the corresponding Free Body Diagram and use it to determine the forces involved, and to solve for the density of the submerged object. Calculate the buoyant force and the density from your measurements.
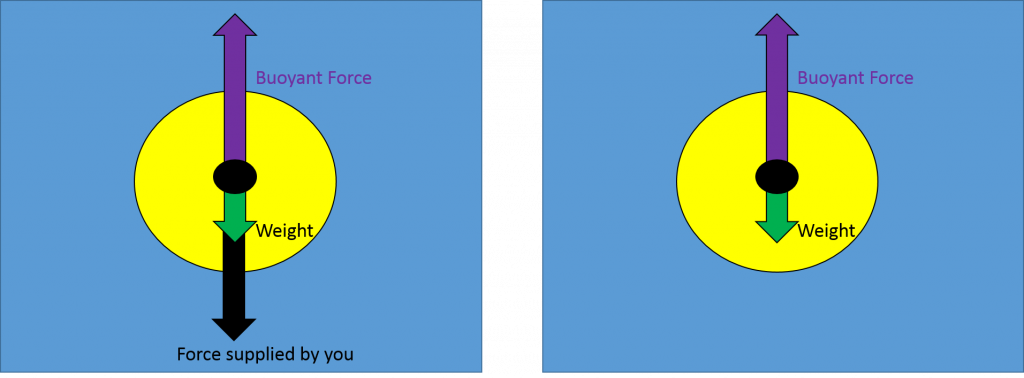
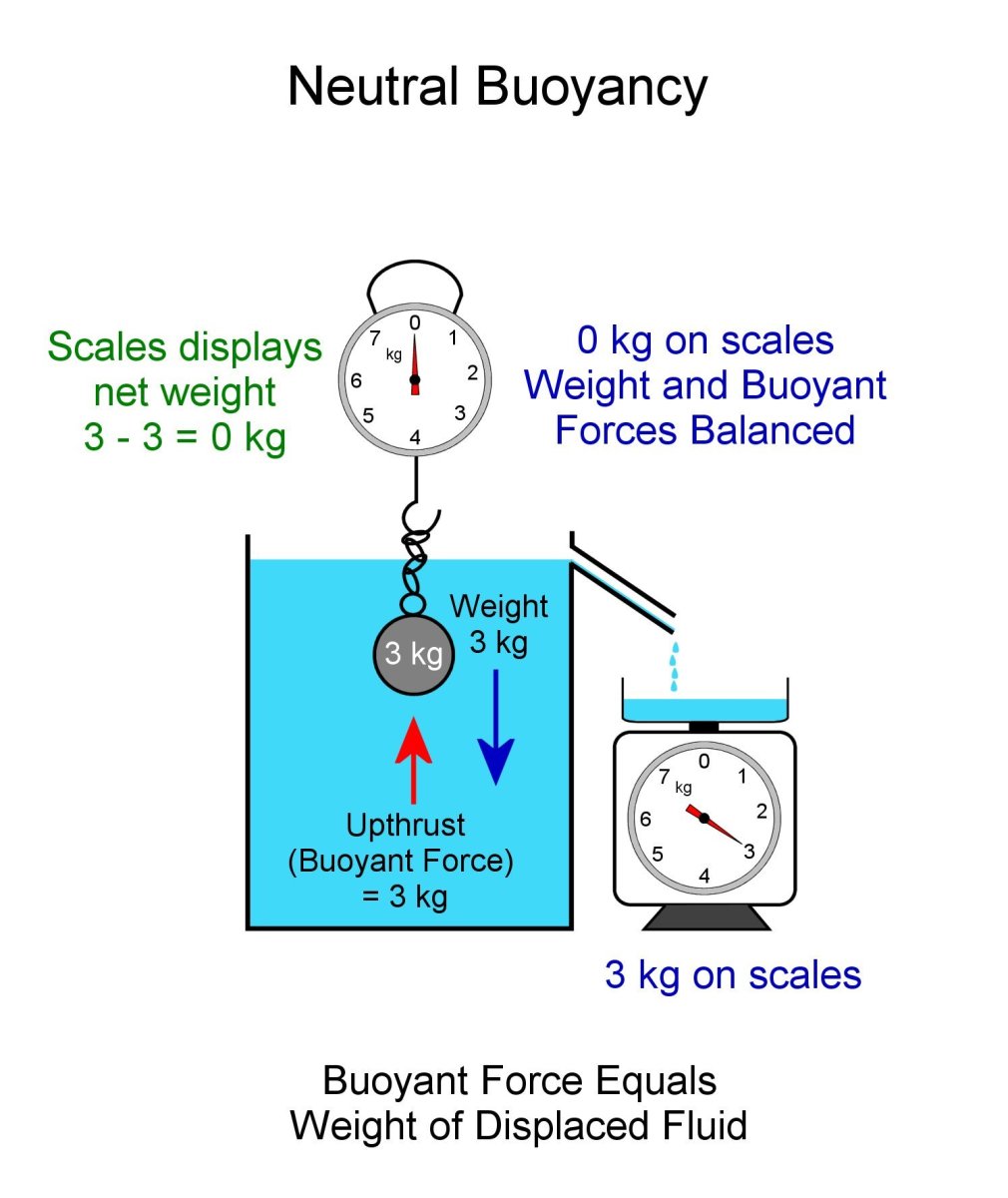
Buoyant Force and FBD - Physics Forums Well, that's correct, but your free body diagram technically has 3 forces acting on the object: its weight down (30N), The buoyant force up (F_b), and tension in the scale's cord acting up (20N). So your FBD equation using Newtyon 1 is from which 20 + F_b -30 = 0, that is, F_b = 10N up, whuch is what you got, but don't take shortcuts.
Buoyant force free body diagram
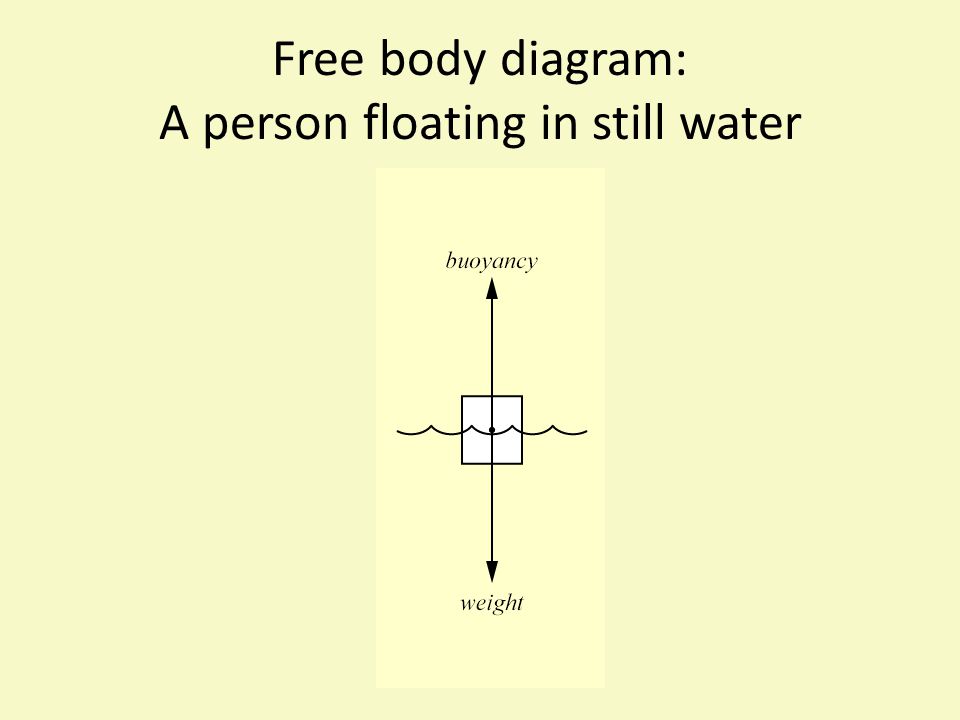
PDF Subject: Forces (Free Body Diagrams; F = ma) Often a Free Body Diagram is useful or necessary to solve a problem that involves forces. Follow these steps, and you'll solve any problem with little difficulty. 1. Draw one Free Body Diagram for each object (see below for what is a good FBD). 2. Break the forces up into components. 3. PDF Fluid Forces on Curved Surfaces; Buoyancy Draw a free body diagram of the container to assist in the solution. 6 Solution. The water exerts a compressive force on the container, but no vertical force, so ... If an object is floating in a fluid, the analysis hardly changes: the buoyant force on the object must still balance the downward force of the object's weight and any other ... openoregon.pressbooks.pub › bodyphysics › chapterUnder Water Weight – Body Physics: Motion to Metabolism Free body diagram of an object hanging from a scale, submerged in water. The length of the weight arrow is equal to the combined lengths of the force supplied by the scale and the buoyant force. A scale will read the weight that it must supply, therefore it will read an apparent weight for submerged objects that is less than the actual weight.
Buoyant force free body diagram. PDF PHY 221 LAB 04-5 { Buoyant force - High Point University uid. This force is called a buoyant force. Materials 1. a force sensor 2. a graduated cylinder 3. water 4. a cylinder with a hook 5. string Background A cylinder hangs by a string and it is completely immersed in water. Sketch a picture, and sketch a free-body diagram for the cylinder. lab 6.docx - Buoyant Force and Archimedes Principle PRE ... Apply Newton's second law to your free body diagram in Pre-Lab Question 2 to solve for the magnitude of the buoyant force. ©eScience Labs, 2018 Buoyant Force and Archimedes Principle Newtons second law , which is that the sum F y=0 of the magnitude , force B , is equal in magnitude to the gravitational force which is moving it down . PDF DENSITY, BUOYANCY AND FORCE DIAGRAMS - Weebly Buoyant * * mg object * m F a net Procedure: PhET Simulations Play With Sims Physics Density Take a few minutes and familiarize yourself with the simulation before moving on. Free Body Diagrams for Floating Objects: Grab the various blocks, lift them over the water and drop into the water a few times. study.com › learn › free-body-diagram-questions-andFree Body Diagram Questions and Answers | Study.com A loaded elevator with very worn cables has a total mass of 2300 kg, and the cables can withstand a maximum tension of 2.70x10^4 N. Draw the free-body force diagram for the elevator. (Assume that ...
Buoyant Force Problem: Boat With Cargo - Physics ... Why isn't normal force included on the free body diagram? Normal force is the contact force between two surfaces. It pushes out from the surfaces and keeps them from falling into each other. In this case, the raft and the chests are in a fluid, and the force due to the pressure of a fluid is called the buoyant force. Buoyant Force - Definition, Demonstration, Buoyant Force ... Buoyant Force. Buoyancy is the tendency of an object to float in a fluid. All liquids and gases in the presence of gravity exert an upward force known as the buoyant force on any object immersed in them. Buoyancy results from the differences in pressure acting on opposite sides of an object immersed in a static fluid. Force Diagrams KS3, KS4 - Buoyancy concept| STEM Crew Forces as pushes or pulls, arising from the interaction between 2 objects. Using force arrows in diagrams, adding forces in 1 dimension, balanced and unbalanced forces. Moment as the turning effect of a force. Forces: associated with deforming objects; stretching and squashing - springs; with rubbing and friction between surfaces, with ... › lab › genlabExperiment 10: Archimedes’ Principle 18. Draw a free-body diagram for this object submerged in water. PART 5: Buoyant Force - Floating Object 19. Although you need to modify or omit certain steps, repeat Part 1 through Part 3 for the wood cylinder: • Omit Step 6, Step 11, and Step 16. • Modify Step 9 and Step 13: Allow the wood object to float. 20. Draw a free-body-diagram ...
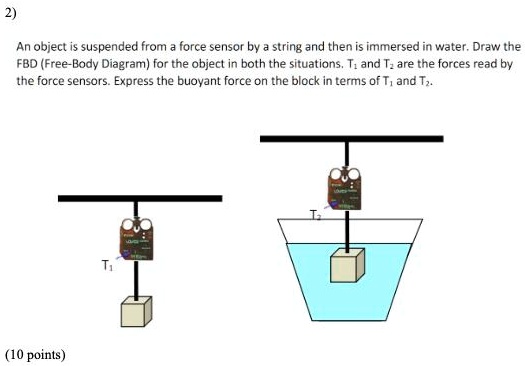
PDF Archimedes' Principle lab Edited 1.9 - UTSA the water, and then write the force summation equation for that free body diagram. In the equation, let the tension in the string be the apparent weight. Algebraically solve this equation for the buoyant force. (10 points) 4. Buoyancy - City University of New York This second weight, called the "apparent weight" differs from the first due to the buoyant force. Draw the corresponding Free Body Diagram and use it to determine the forces involved, and to solve for the density of the submerged object. Calculate the buoyant force and the density from your measurements. Engineering workshop #2: Forces, moments and free-body ... Welcome to part two of a series of 'engineering workshop' articles revising the basics of engineering. The subject for this month's piece is: forces, moments and free body diagrams. The first thing to address is the difference between mass and force - mass is proportional to the summation of the number of particles in the material that you are considering (i.e. all atomic nuclei ... PDF DENSITY, BUOYANCY AND FORCE DIAGRAMS - Weebly Density, Buoyancy And Free Body Diagrams Updated: 7-Jan-16 Page 4 of 4 11. The red block in the "Same Volume" floats in water. The blue block sinks in water. Using your data from the chart above and your knowledge of buoyant forces and weights, what volume of the blue block would float above the water line if the blue block was placed on
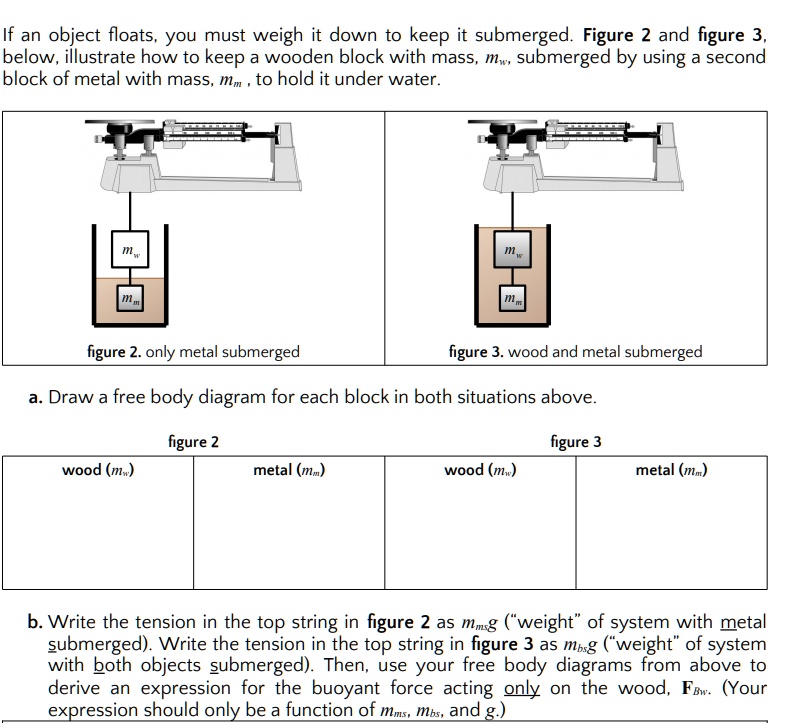
PDF Density and Buoyancy Lab E6 - California State University ... B) In the diagram you made, draw the forces that are acting on the block (i.e. a Free- Body Diagram). Next to your diagram, apply Newton's 2nd Law and then solve algebraically for the buoyant force. You should conclude that FB = W.If this is not your conclusion then go back and check your work.
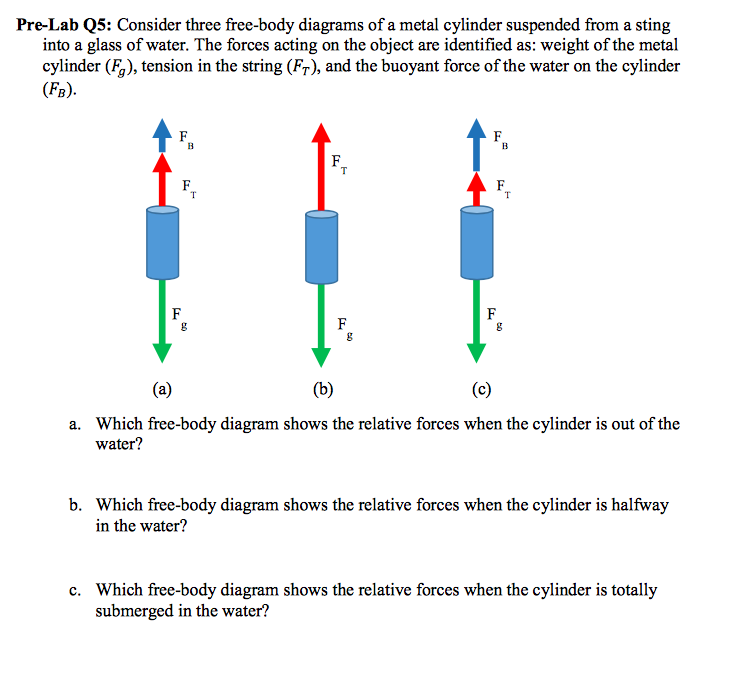
Solved Lab 13 Buoyant Force and Archimedes Principle Pre ... Lab 13 Buoyant Force and Archimedes Principle Pre-Lab Questions 1. Draw a free body diagram of a hanging mass before it is submerged in water. Make sure to label your forces. 2. Draw a free body diagram of a hanging mass after it is submerged in water. Make sure to label your forces. Which force is the force you measure with the spring scale? 3.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ForceForce - Wikipedia In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a push or a pull. A force has both magnitude and direction, making it a vector quantity.
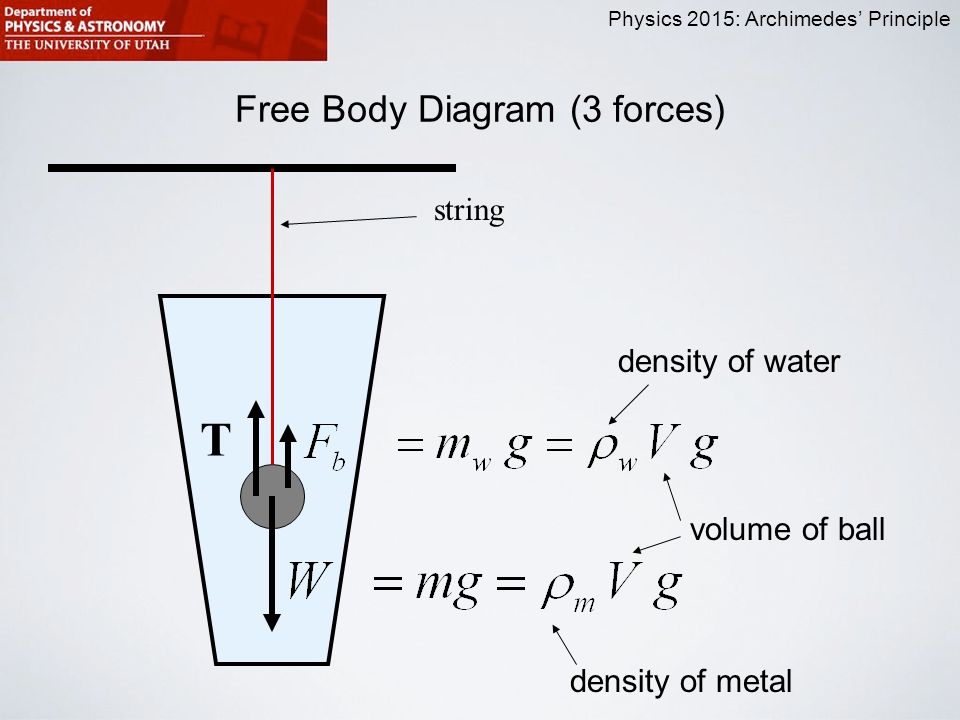
PDF Lab 7 Buoyancy - University of Hawaiʻi The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the displaced fluid. This can be restated in terms of the density of the fluid, ρf, and the volume of the object, V: FB=!fgV (8-3) The free body diagram of an object submerged in a fluid under the influence of gravity is given in Fig. 8-1. Figure 0-1 The free body diagram of an object submerged in a ...
free body diagram - Wood in water and buoyant force ... forces free-body-diagram density fluid-statics buoyancy. Share. Cite. Improve this question. Follow edited Oct 22 2018 at 20:21. ... Archimedes' principle states that the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid, whether fully or partially submerged, ...
PDF Lab 8.Buoyancy - Washington State University CHAPTER 8. BUOYANCY 82 where r w is the density of water (1:000 103 kg/m3). Buoyant force on an object more dense than water Before beginning, draw a free-body diagram showing the forces on an object (more dense than
Solved Draw a free body diagram of a hanging mass before ... Draw a free body diagram of a hanging mass after it is submerged in water. Make sure to label your forces. Which force is measured with the spring scale? Apply Newton's second law to your free body diagram in Pre-Lab Question 2 to derive a general equation for the buoyant force. Show your work.
27.6: Archimedes' Principle - Buoyant Force - Physics ... Because the density of the air is much less that the density of the fluid, we can neglect the buoyant force of the air on the object. Figure 27.9: Free-body force diagram on floating object The buoyant force of the fluid on the object, F → f, o B = ρ f V 1 g k ^ must exactly balance the gravitational force on the object due to the earth, F → e, ρ g
IP_2020_L13_BuoyantForce.docx - Buoyant Force and ... Draw a free body diagram of a hanging mass after it is submerged in water. Make sure to label your forces. Which force is the force you measure with the spring scale? 3. Apply Newton's second law to your free body diagram in Pre-Lab Question 2 to solve for the magnitude of the buoyant force.
What is buoyant force? (article) | Fluids | Khan Academy This equation, when stated in words, is called Archimedes' principle. Archimedes' principle is the statement that the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. The simplicity and power of this idea is striking. If you want to know the buoyant force on an object, you only need to determine the weight ...
PDF Density and Buoyancy Lab E3 - California State University ... B) In the diagram you made, draw the forces that are acting on the block (i.e. a Free-Body Diagram). Next to your diagram, apply Newton's 2nd Law and then solve algebraically for the buoyant force. You should conclude that F B = W. If this is not your conclusion then go back and check your work. If you still do not get this result
Buoyancy - Purdue University same free body diagram as the fish? Are the forces exerted by the water on the fish any different from the forces exerted on the water that took ... A floating object experiences a buoyant force due only to the submerged portion of the object F buoyant m f= V submergedrg. 3/3/13 3 "Light" versus Regular Coke Why does one sink but the
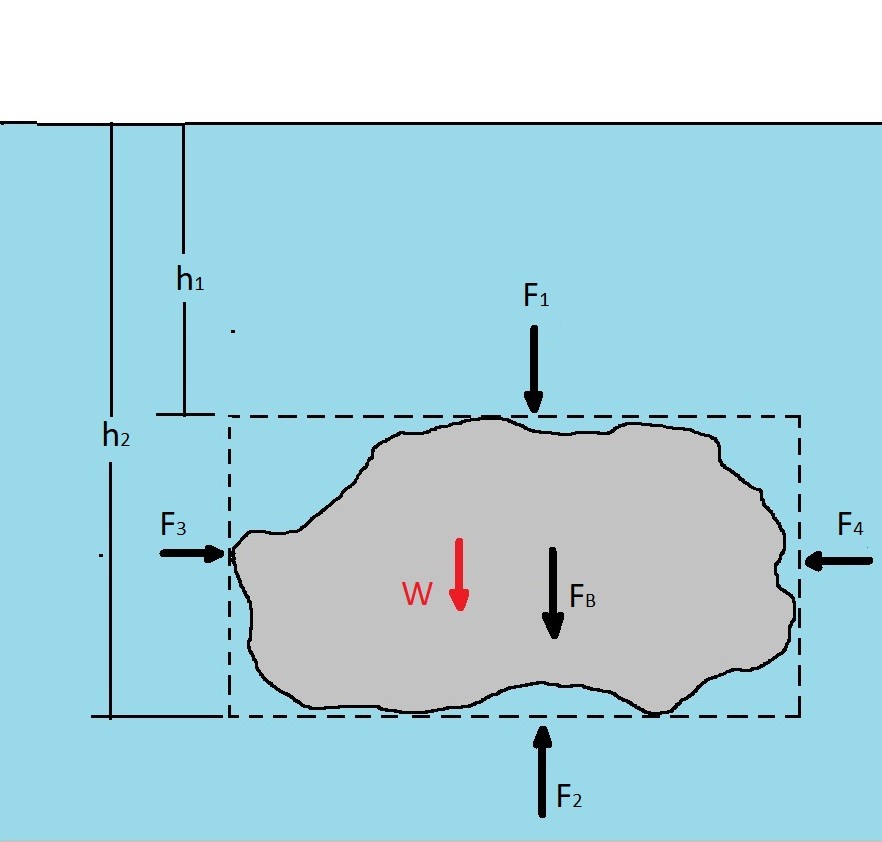
acikders.ankara.edu.tr › pluginfile › 16639FLUID MECHANICS - Ankara Üniversitesi is the buoyant force (N), γ is the specific weight of fluid (N/m3), and ∀ is the volume of the body (m3) The direction of the buoyant force, which is the force of the fluid on the body, is opposite to that shown on the freebody diagram. Therefore, the buoyant force has a magnitude equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body and is
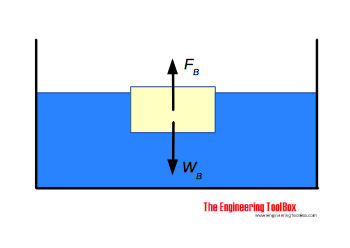
physics.bu.edu › ~duffy › ns542_spring2011_notes02Chapter 9 – Fluids - Boston University (a) On the block's free-body diagram, we draw a downward force of gravity, applied by the Earth. We also draw an upward force of tension (applied by the string), and, because the block displaces some fluid, an upward buoyant force (applied by the fluid). The block is in equilibrium, so there must be no net force acting on the block.
How to Draw a Free Body Diagram for a Fully Submerged ... In this free body diagram of the beach ball, the buoyant force has a far greater magnitude than the force due to gravity. The buoyant force acts upward on the ball while the gravitational force ...
openoregon.pressbooks.pub › bodyphysics › chapterUnder Water Weight – Body Physics: Motion to Metabolism Free body diagram of an object hanging from a scale, submerged in water. The length of the weight arrow is equal to the combined lengths of the force supplied by the scale and the buoyant force. A scale will read the weight that it must supply, therefore it will read an apparent weight for submerged objects that is less than the actual weight.
PDF Fluid Forces on Curved Surfaces; Buoyancy Draw a free body diagram of the container to assist in the solution. 6 Solution. The water exerts a compressive force on the container, but no vertical force, so ... If an object is floating in a fluid, the analysis hardly changes: the buoyant force on the object must still balance the downward force of the object's weight and any other ...
PDF Subject: Forces (Free Body Diagrams; F = ma) Often a Free Body Diagram is useful or necessary to solve a problem that involves forces. Follow these steps, and you'll solve any problem with little difficulty. 1. Draw one Free Body Diagram for each object (see below for what is a good FBD). 2. Break the forces up into components. 3.


















0 Response to "44 Buoyant Force Free Body Diagram"
Post a Comment