44 O3 Molecular Orbital Diagram
O3 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry... - Techiescientist O3 Molecular Orbital Diagram (MO). The molecular orbital theory is one of the major revolutionary concepts of chemical bonding. It uses quantum mechanics to give us a detailed almost explanatory diagram of the bonding nature inside a molecule. PDF Lecture 1 Octahedral ML6 molecular orbital energy diagram. Lecture 3: p-acceptor ligands and synergic bonding. PES shows that all three iridium complexes have similar d-orbital energies indicating that the formal oxidation state is not the actual charge on the metal. ii) metal d-electron count.
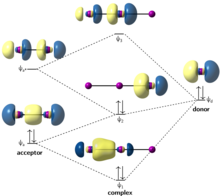
Introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory This section illustrates pictorially molecular orbitals for several organic and inorganic molecules. If possible - the energy level diagram is included and clicking upon the relelvant level will generate the accompanying molecular orbital in the right-hand frame.
O3 molecular orbital diagram
PDF Figure 9.32: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for • The following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the... PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory.ppt... Each orbital wavefunction (φ ) is most easily described in two parts radial term - which changes as a function of distance from the nucleus angular terms - which changes as a function of angles. Lecture 4 Revision of hybridisation Molecular orbital theory and diatomic molecules. Tutorial on Chemical Bonding, Part 8 of 10 (Molecular orbitals) The simplest molecule: H2+. Bonding and antibonding orbitals. Simple molecular orbital diagrams. The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative calculations, including those that lead...
O3 molecular orbital diagram. 8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 8). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - Symmetry-and-Molecular-Orbitals.htm polyatomic molecules. The concept of Hybridization is developed to explain different geometry variations. Describes molecular geometry easier. • Using Delocalization and Resonance to explain extended distribution of electrons over many atoms in a substance. Molecular Orbitals - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The molecular orbital diagram for even a simple octahedral complex looks complicated ( Figure 5 ), but most of the time the information needed may be obtained by just considering the circled region, containing five orbitals: t 2g with threefold degeneracy and e g with twofold degeneracy. PDF PowerPoint Presentation | VB Theory and Orbital Hybridization Molecular Orbital Diagrams. An MO diagram, just like an atomic orbital diagram, shows the relative energy and number of electrons in each MO. molecule has opposite effects: N2+ has a weaker longer bond than N2, but O2+ has a stronger, shorter bond than O2.
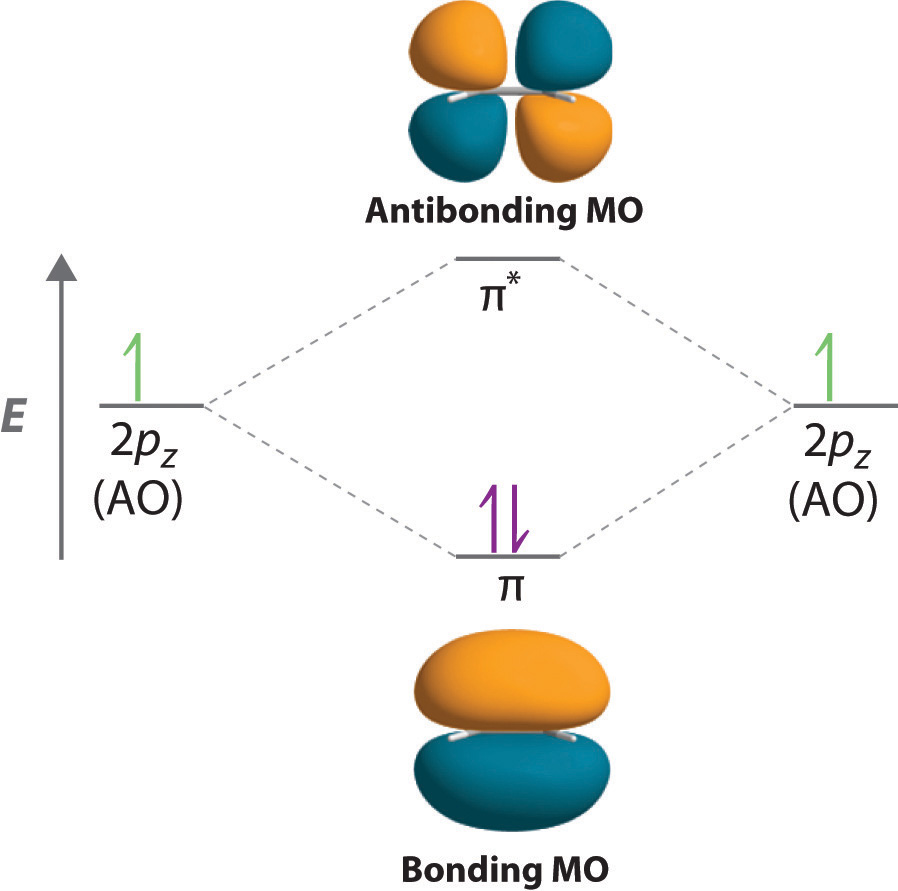
MO Diagrams | Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory is the final theory pertaining to the bonding between molecules. The diagram will end up as such: Notice the effect that this has on the overall bonds. Recall from earlier that electrons in bonding orbitals will stregnthen bonds whereas electrons in antibonding orbitals will... PDF Molecular Orbitals in | 9-2 Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the left) to form two MOs. Diagrams such as these are used to describe the bonding in a molecule in MO terms. Electrons occupy MOs according to the same rules developed... 8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
Molecular Orbital Theory - GeeksforGeeks The molecular orbital function can be used to calculate the space in a molecule where the probability of finding an electron is greatest. According to molecular orbital theory, some types of molecular orbitals are formed by the linear combination of atomic orbitals. PDF Chapter 5 | 5.2.2 Orbital Mixing Molecular orbital theory uses group theory to describe the bonding in molecules; it comple-ments and extends the introductory bonding models in Chapter 3 . In molecular orbital theory the symmetry properties and relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how these orbitals interact to form... MO Diagrams | Molecular Orbital Diagram Maker A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified | by Megan A. Lim | Medium Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms.
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry/Molecular Orbital Theory... Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
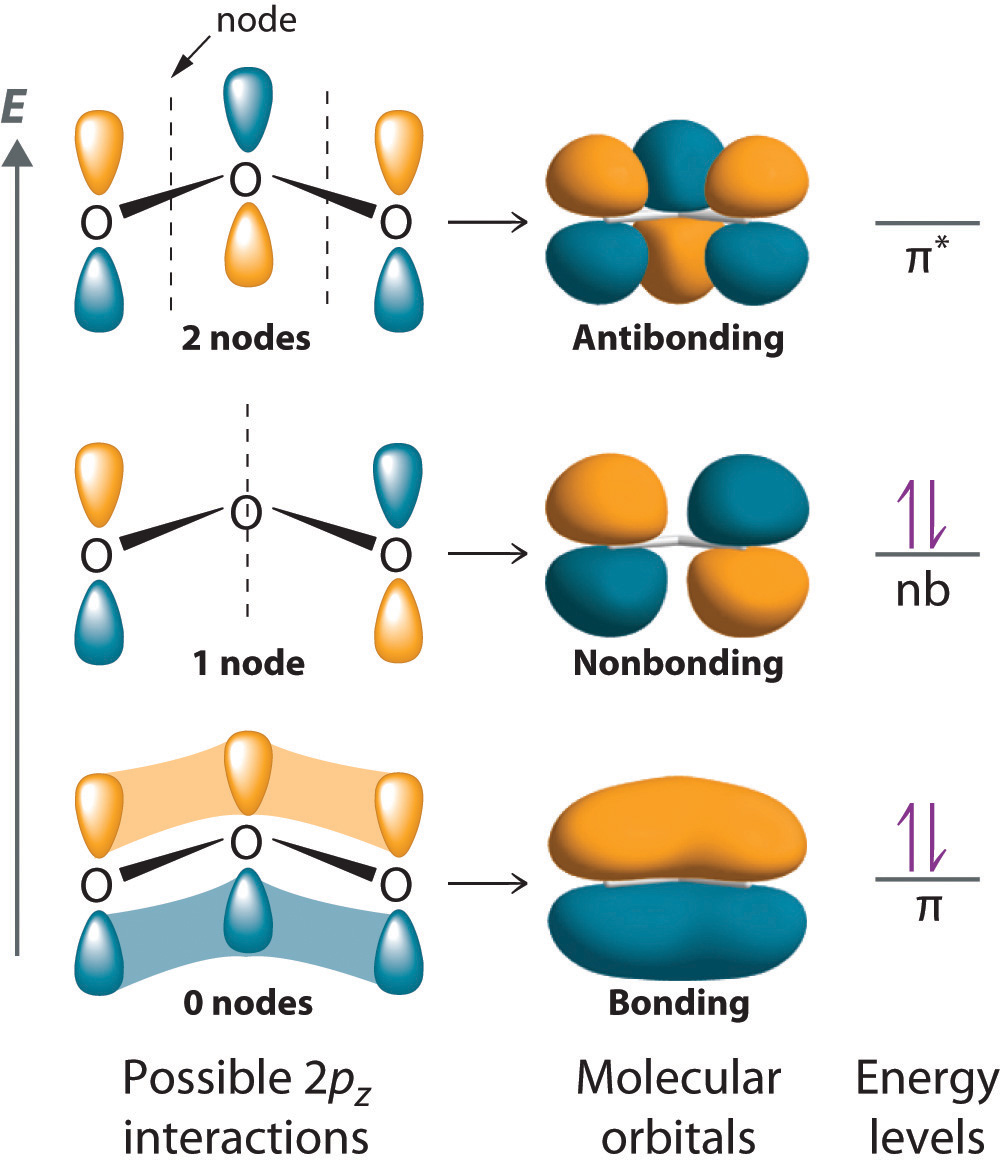
Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry | Socratic Molecular orbital theory is a method for determining molecular structure. Molecular Orbital theory starts by assuming that the three atomic p orbitals on the O atoms overlap to form three molecular π orbitals that extend over the whole How do you draw an atomic level diagram for 2S+3O2=2SO3 ?
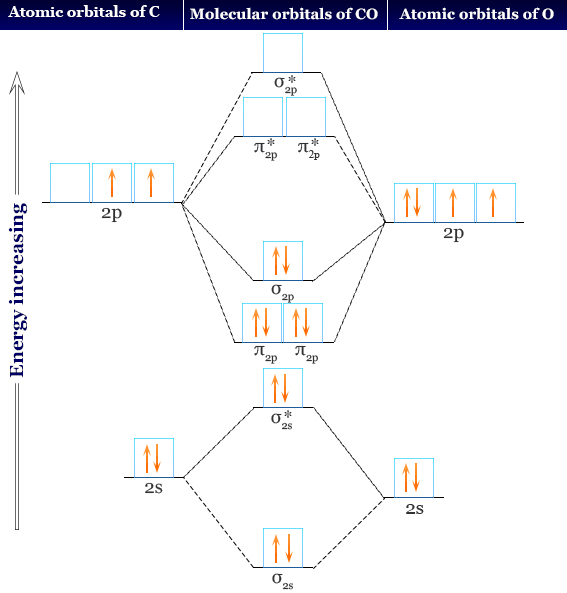
Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT), Chemistry Study... | eMedicalPrep The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. No. 9 Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO. Analysis done by Bond Order. If value of bond order is positive, it indicates a stable molecule and if the value is negative or zero, it means that the molecule is unstable.
Building Molecular Orbital Diagrams for Homonuclear and... General Notes on Molecular Orbital Diagrams. The Y-axis of a MO diagram represents the total energy (not potential nor Gibbs Energy) of the orbitals. Individual atomic orbitals (AO) are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram. Overlapping atomic orbitals produce molecular orbitals...
Understanding Molecular Orbital Theory - YouTube Molecular Orbital Theory allows us to predict the distribution of electrons within a molecule. This allows us to predict properties such as bond order...
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory... MO diagram of homonuclear diatomic molecules. The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. Molecular Orbital Theory - BH3. The BH3 molecule exists in the gas phase, but dimerizes to B2H6 (which we will look at a bit...
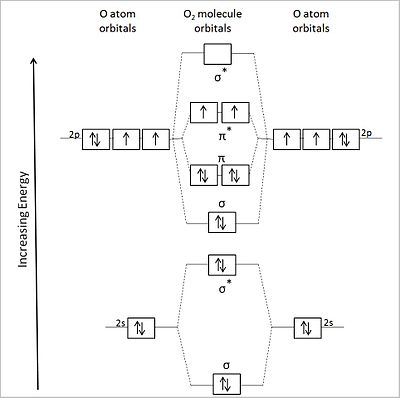
Molecular Orbital Theory The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and The result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give the diagram shown in the figure below.
Molecular Orbital diagram of NO(nitric oxide) molecule Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of C2 molecule : Number of electrons in C2 molecule = 12.
Molecular Orbitals: Molecular Orbital Theory | SparkNotes Molecular orbital theory posits the notion that electrons in molecules likewise exist in different orbitals that give the probability of finding the electron at Notice that the orbitals of the separated atoms are written on either side of the diagram as horizontal lines at heights denoting their relative energies.
What is the molecular orbital diagram for oxygen? - Quora From the molecular orbital diagram, we observe that oxygen has two unpaired electrons which is consist with the paramagnetic nature of oxygen. Whilst this is the MO diagram for N₂: If we compare such diagrams for the diatomic molecules on the Second Period (Li₂, Be₂, B₂, C₂, N₂, O₂, and F₂), the...
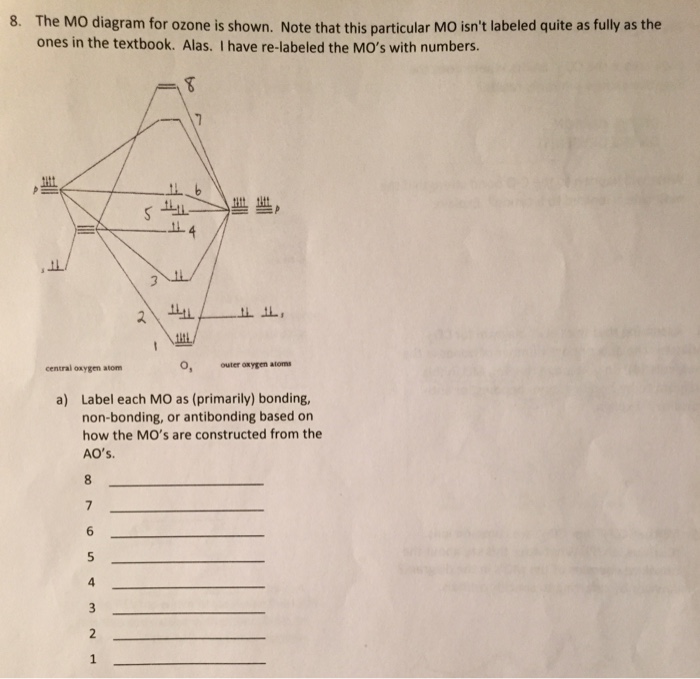
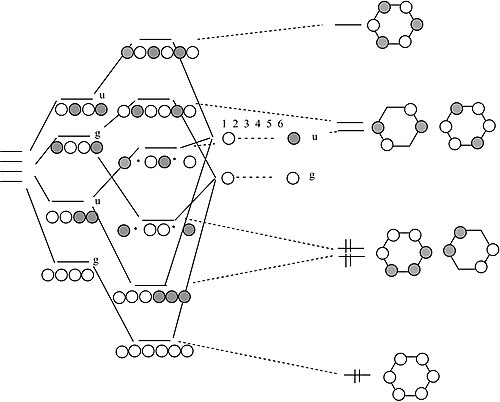
Schematic molecular orbital diagram of O 3 and O ϩ 3 illustrating the ... molecular orbitals of ozone relevant for the interpre- tation of the photoelectron spectrum are depicted in Fig. 1. Early ab initio calculations of its electronic structure already showed that several configurations contribute to the elec- tronic wave function of the ground state of O 3...
Tutorial on Chemical Bonding, Part 8 of 10 (Molecular orbitals) The simplest molecule: H2+. Bonding and antibonding orbitals. Simple molecular orbital diagrams. The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative calculations, including those that lead...
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory.ppt... Each orbital wavefunction (φ ) is most easily described in two parts radial term - which changes as a function of distance from the nucleus angular terms - which changes as a function of angles. Lecture 4 Revision of hybridisation Molecular orbital theory and diatomic molecules.
PDF Figure 9.32: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for • The following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the...




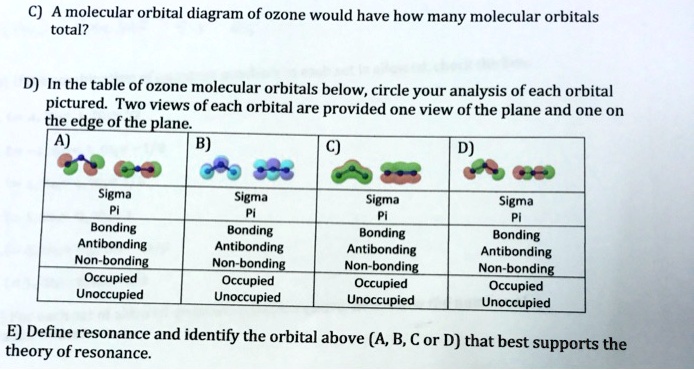
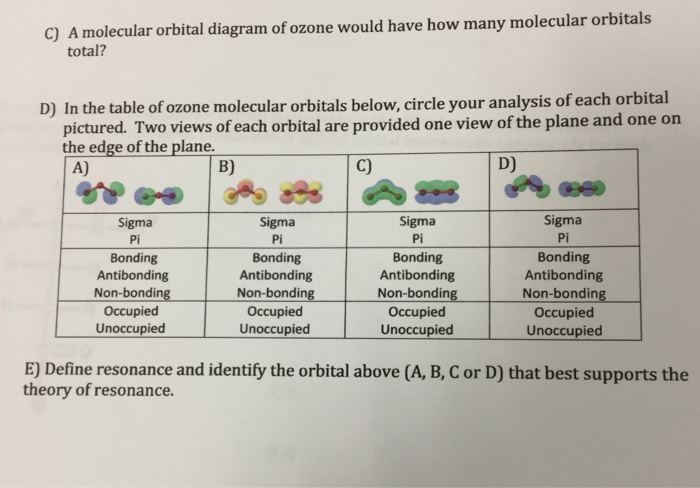




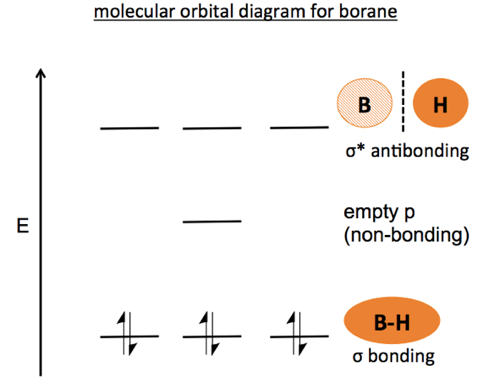
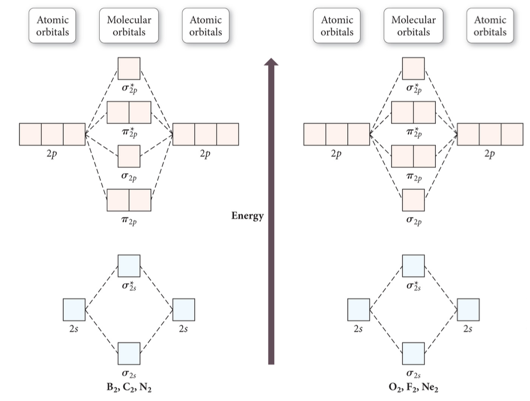

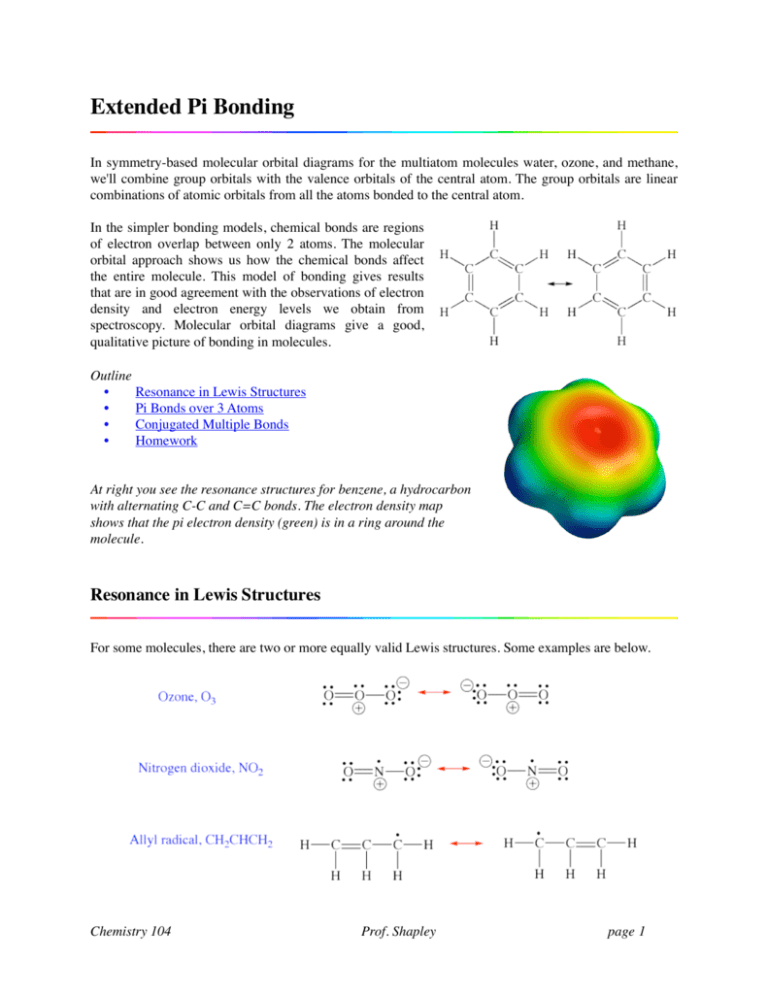




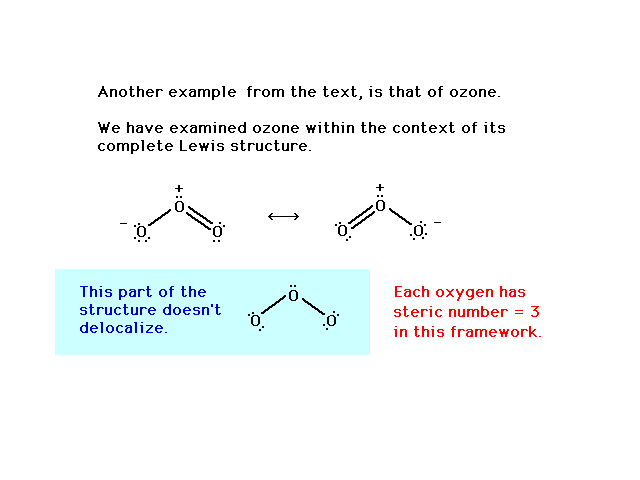
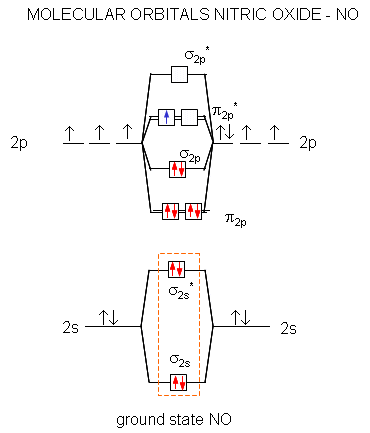



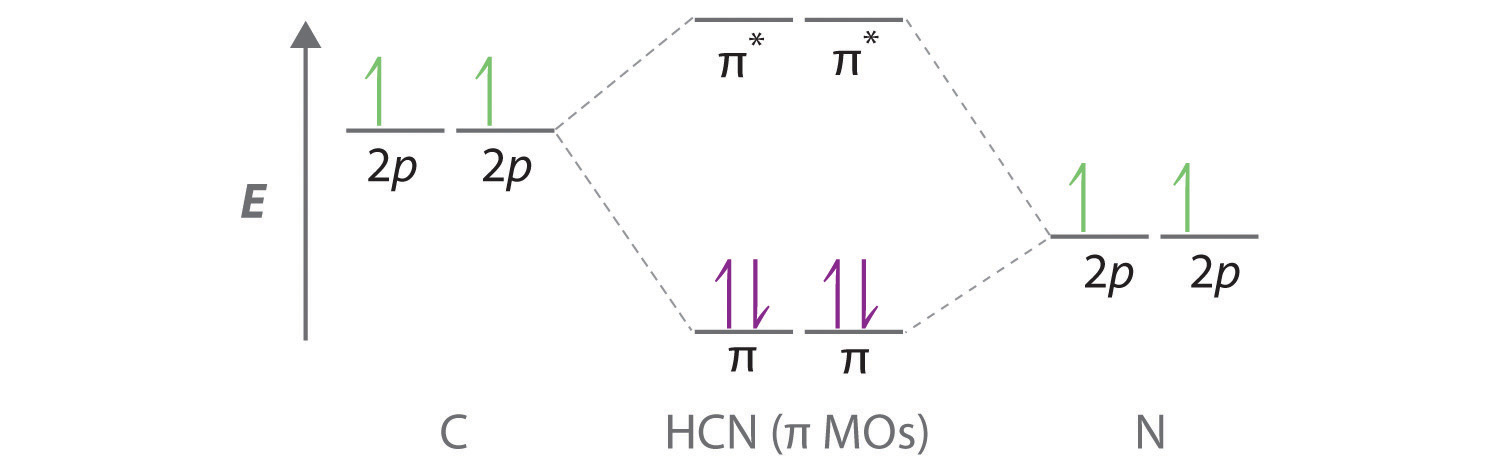

0 Response to "44 O3 Molecular Orbital Diagram"
Post a Comment