43 law of reflection diagram
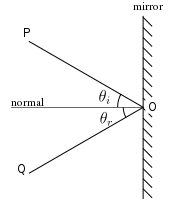
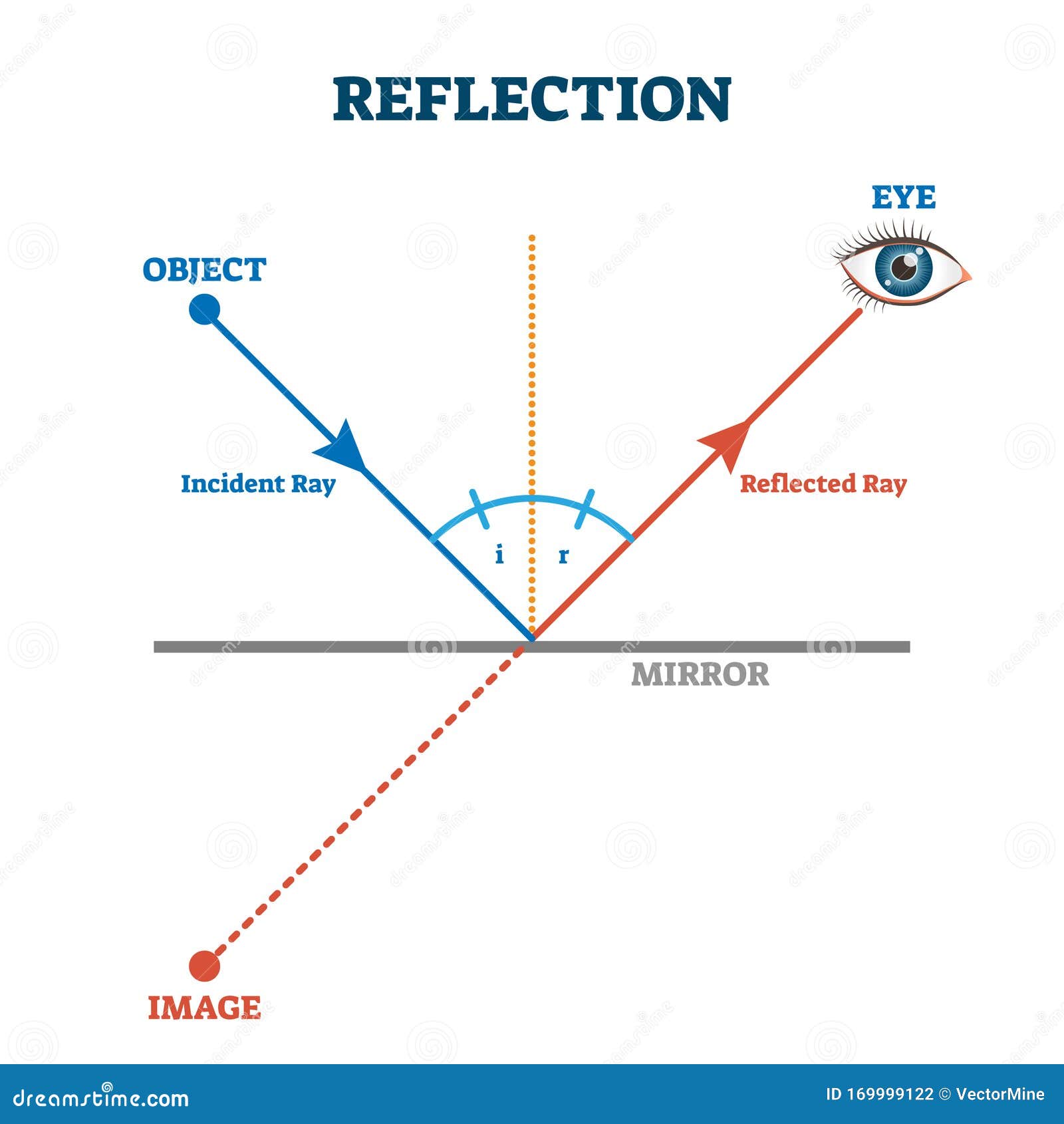
What is Reflection of Light? - Definition, Laws, Types & Video The laws of reflection determine the reflection of incident light rays on reflecting surfaces, like mirrors, smooth metal surfaces and clear water. Let's consider a plane mirror as shown in the figure above. The law of reflection states that The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same plane Sample Problems for The Law of Reflection When light is reflected from a surface, the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection, where both angles are measured from the path of the light to the normal to the surface at the point at which light strikes the surface. This equality is known as the law of reflection. Sample Problem 1:
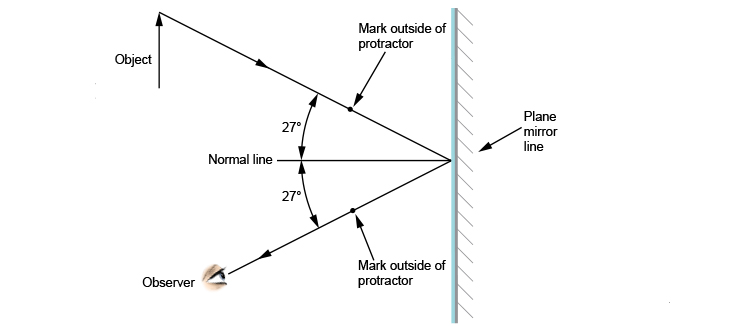
Laws of Reflection | Definition, Examples, Diagrams Aim : To verify the law of reflection. Procedure: 1) Take a drawing board and fix a white paper on it with the help of clamps. 2) Draw a straight line AB at the centre of the paper and also a normal (ON) to AB at point 'O'. 3) Draw a straight line PQ making certain angle (Angle i) with ON. 4) Fix two pins at the points P and Q on the paper ...

Law of reflection diagram
Concave Mirrors And Convex Mirrors - Image Formation, Ray Diagram A ray passing through the center of curvature of the spherical mirror will retrace its path after reflection. Image Formation By Concave Mirror By changing the position of the object from the concave mirror, different types of images can be formed. Balanced vs. Unbalanced Forces Interactive Each interactive concept-builder presents learners with carefully crafted questions that target various aspects of a discrete concept. There are typically multiple levels of difficulty and an effort to track learner progress at each level. Law of reflection - Reflection and refraction of light ... the angle of reflection, r, is the angle between the normal and reflected ray. The law of reflection states that: angle of incidence i = angle of reflection r. For example, if a light ray hits a...
Law of reflection diagram. The Law of Reflection | Physics - Lumen Learning The law of reflection is illustrated in Figure 1, which also shows how the angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray strikes. We expect to see reflections from smooth surfaces, but Figure 2 illustrates how a rough surface reflects light. Since the light strikes different parts of the ... PhysicsLAB: Reflection The ray diagram below shows the reflection of one of the rays that strikes the parabolic mirror. Notice that the law of reflection is obeyed, and the angle of incidence (from the normal, the dashed line) equals the angle of reflection (from the normal). Complete the diagram by drawing the reflected rays of the other three rays that are shown. Physics Tutorial: The Law of Reflection The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The ray of light that leaves the mirror is known as the reflected ray (labeled R in the diagram). Laws of Reflection - First and Secons Law with Examples Law 1 - The primary law of reflection expresses that the reflection point is dependably comparable to the point of incidence. If the episode beam falls on the plane mirror along with the typical, for example, 90°, the reflected beam will go along a similar way.
Addition of Forces - Physics Classroom The above diagram shows what is occasionally a difficult concept to believe. Many students find it difficult to see how 10 N + 10 N could ever be equal to 10 N. For reasons to be discussed in the next section of this lesson, 10 N + 10 N would equal 10 N whenever the two forces to be added are at 30 degrees to the horizontal. State the laws of Reflection along with a suitable diagram. State the laws of Reflection along with a suitable diagram. Easy Solution Verified by Toppr I = Incident ray R = Reflected ray N = Normal ∠ i = angle of incidence ∠ r = angle of reflection There are two basic laws of reflection of light - (i) The incident ray the reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting Huygens' Principle: Proving the Law of Reflection | Study.com To use Huygens' principle to prove the law of reflection, we're going to start by drawing a diagram of two light rays traveling in the same direction and striking a surface at some angle. We can... Laws Of Reflection: Definition, Types, Diagrams ... According to the Law of Reflection, θ = θ r Hence, Angle of Reflection = 60° Q2: A light ray strikes a reflective plane surface at an angle of 54° with the surface. (i) Calculate the angle of incidence. (ii) Calculate the angle of reflection. (iii) Calculate the angle made by the reflected ray and the surface.
What are the laws of reflection? - Quora Answer (1 of 29): What is Reflection of Light? When a ray of light falls on any object (polished, smooth, shiny object), light from that object bounces back those rays of light to our eyes and this is known as "Reflection" or "Reflection of Light". This phenomenon is what enables us to look at t... The Electromagnetic Spectrum Song - YouTube Emerson Foo ( ) & Wong Yann ( ) made an original music video on the Electromagnet... Solved (Ch. 18.2 and Figure 18.9b) State the Law of ... Define all quantities on the diagram that are in the equation, including SI units. Question: (Ch. 18.2 and Figure 18.9b) State the Law of Reflection, provide a diagram showing it in 2- D, and an equation. Define all quantities on the diagram that are in the equation, including SI units. The reflection of light - Boston University In a ray diagram, rays of light are drawn from the object to the mirror, along with the rays that reflect off the mirror. The image will be found where the reflected rays intersect. Note that the reflected rays obey the law of reflection.
Using the law of reflection - Ray diagram rules Using the law of reflection - Ray diagram rules When we observe an object in a convex mirror there are three ways to try to work out how the light rays from an object focus into the eye of an observer. Use the ray diagram flat/plane mirror rules Use the laws of reflection Use new ray diagram rules and create a virtual image
Law of Reflection (Diagram) Diagram | Quizlet The angle measured between the reflected ray and the normal. Mirror Smooth, shiny surfaces make the best mirrors. The flat side on the diagram is the shiny side. Law of Reflection (plane mirror) Angle of incidence = Angle of Reflection Sets with similar terms Light and wave terms 13 terms Caleb_Sowah Energy and It's Transformation 22 terms
PhysicsLAB: Video: Law of Reflection Sample Diagram The Law of Reflection states that when waves are reflected from an interface, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. The purpose of this lab is to experimentally verify this outcome. Given below are a sample screen capture and an accompanying image showing an example of the corresponding ray and angle constructions.
What is the Law of Reflection of Light? - Definition ... To understand what these angles and light rays stand for, consider the following diagram depicting the law of reflection. In this depiction, the blue band represents a mirror, which reflects rays ...
reflection - Louisiana State University 1) Students should be able to state the law of reflection and draw a ray diagram to illustrate it. 2) Students should be able to apply the law of reflection to predict the position of images formed by objects in front of a planar mirror. Material required: 1) Full length mirror hung horizontally
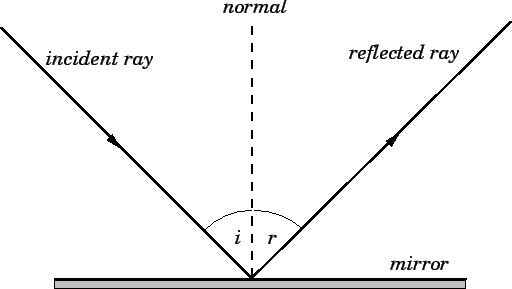
What is the Law of Reflection: Definition and A Simple ... This is basically what the law of reflection is all about. Here's a diagram to help you visualize the law of reflection a bit better: Angle of incidence and angle of reflection In the diagram above, the light ray approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray, while the one that bounces off the mirror is called the reflected ray.
What is law of reflection short definition? - Runyoncanyon ... The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The law of reflection states that when a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. What is reflection example?
Fresnel equations - Wikipedia 1) where E k is the (constant) complex amplitude vector, i is the imaginary unit , k is the wave vector (whose magnitude k is the angular wavenumber), r is the position vector , ω is the angular frequency , t is time, and it is understood that the real part of the expression is the physical field. [Note 1] The value of the expression is unchanged if the position r varies in a direction normal ...
Law of Reflection | Physics Quiz - Quizizz Question 3. SURVEY. 30 seconds. Q. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. answer choices. law of light. law of reflection. law of refraction.
what are the laws of reflection explain with diagram ... The Law of Reflection; Specular vs. Diffuse Reflection; Light is known to behave in a very predictable manner. If a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off of a flat mirror, then the behavior of the light as it reflects would follow a predictablelawknown as thelaw of reflection. The diagram below illustrates the law of ...
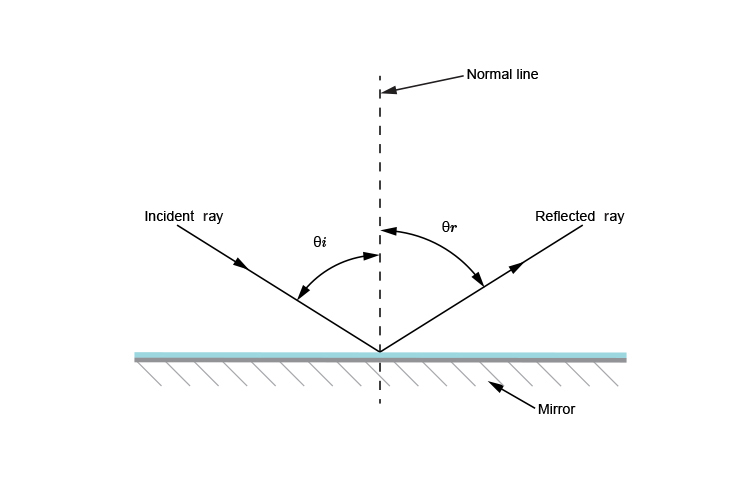
Reflection - Light waves - KS3 Physics Revision - BBC Bitesize The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, i = r. It works for any angle. For example: the angle of reflection is 30° if the angle of incidence is 30 ...
Lesson 26: Reflection & Mirror Diagrams The Law of Reflection says "the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection." These angles are always measured from the normal line so that we have a common reference. In Illustration 1 we see that the angle is 42° coming in and 42° reflecting off. This is an example of regular (specular) reflection.
The three laws of reflection - Mammoth Memory The three laws of reflection Any mirror obeys the three laws of reflection, flat, curved, convex or concave. The three laws of reflection are 1. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the normal 2. The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray are all in the same plane 3.
Mirrors, Law of Reflection, and Ray Diagrams Quiz - Quizizz Q. In the given figure, which of the following holds TRUE? answer choices. The angle of incidence is 10°. The angle of incidence is 80°. The angle of reflection is 10°. The angle of reflection is 90°. The angle of incidence is 10°.. alternatives.
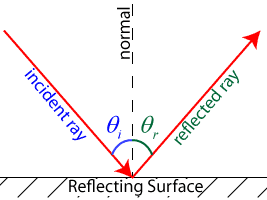
The Laws of Reflection and Refraction First, we consider reflection, as shown in the diagram below for a light wave striking a surface. We identify the incoming ray as the incident ray and the outgoing ray as the reflected ray. Concomitantly, the angle ?i that the incoming ray makes with a line (dashed in the diagram) normal to the surface is called the angle of incidence.
Law of reflection - Reflection and refraction of light ... the angle of reflection, r, is the angle between the normal and reflected ray. The law of reflection states that: angle of incidence i = angle of reflection r. For example, if a light ray hits a...
Balanced vs. Unbalanced Forces Interactive Each interactive concept-builder presents learners with carefully crafted questions that target various aspects of a discrete concept. There are typically multiple levels of difficulty and an effort to track learner progress at each level.
Concave Mirrors And Convex Mirrors - Image Formation, Ray Diagram A ray passing through the center of curvature of the spherical mirror will retrace its path after reflection. Image Formation By Concave Mirror By changing the position of the object from the concave mirror, different types of images can be formed.





![Solved 2) Law of reflection [35 points] a. [10 points] On ...](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media%2F1eb%2F1ebb8037-d34b-45a6-a7dd-e7d711b040c5%2FphpB6Fcqx.png)



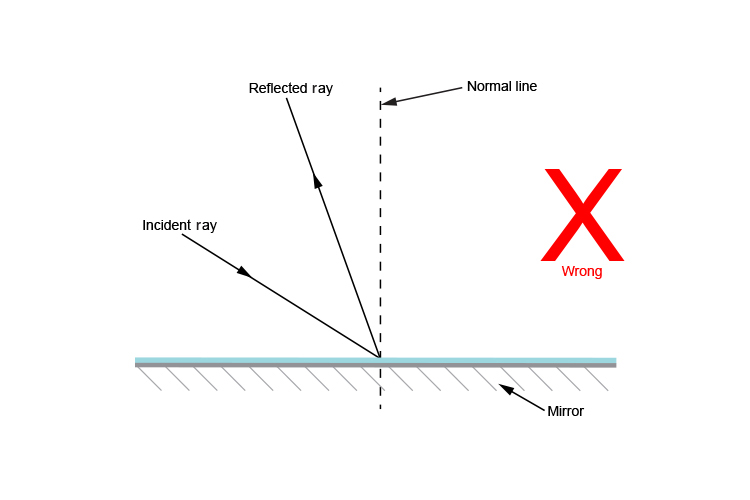

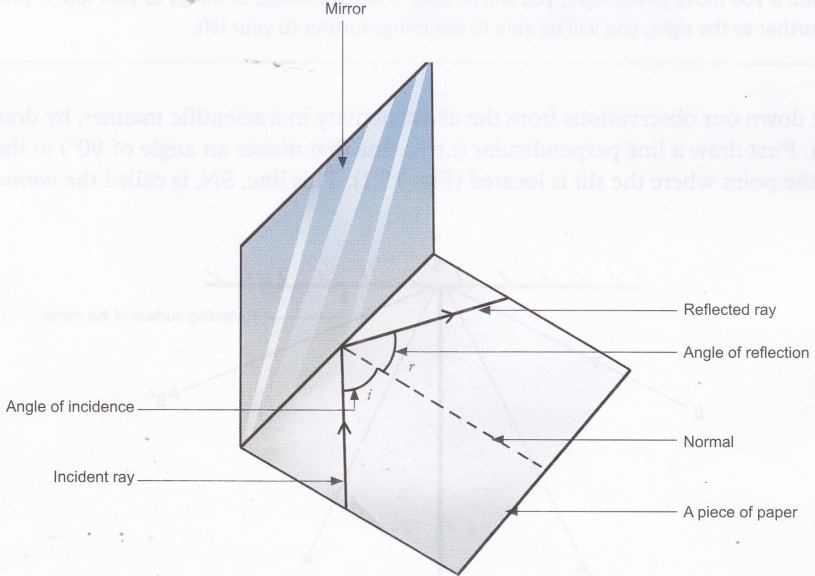

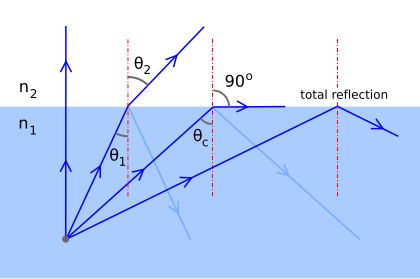




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ReflectionLaw-5946c6dd5f9b58d58a2f2efc.png)






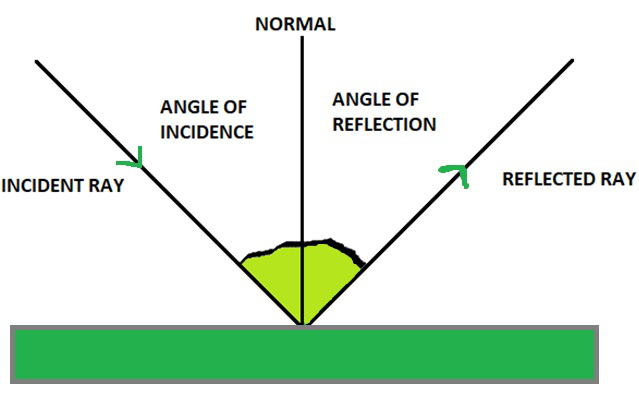


0 Response to "43 law of reflection diagram"
Post a Comment