41 sulfur dioxide phase diagram
by BC Smith · 1965 · Cited by 6 — Phase diagrams of some aromatic hydrocarbon–sulphur dioxide binary mixtures. B. C. Smith and G. H. Smith. Abstract. The first page of ... in the previous video we looked at the dot structure for sulphur dioxide 9 through out two resonance structures so the resonance structure on the left and the resonance structure on the right and some people disagreed with me and said that's not the dot structure for sulphur dioxide the dot structure for sulphur dioxide has sulphur with a double bond to an oxygen on the left and two lone pairs ...
Sulfur dioxide. Formula: O 2 S. Molecular weight: 64.064. IUPAC Standard InChI: InChI=1S/O2S/c1-3-2. Copy Sheet of paper on top of another sheet. IUPAC Standard InChIKey: RAHZWNYVWXNFOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N. Copy Sheet of paper on top of another sheet. CAS Registry Number: 7446-09-5.

Sulfur dioxide phase diagram
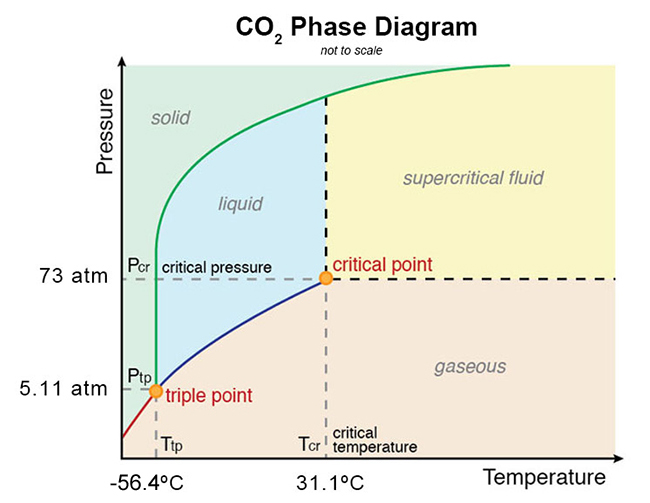
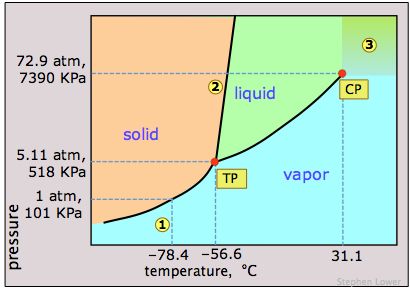
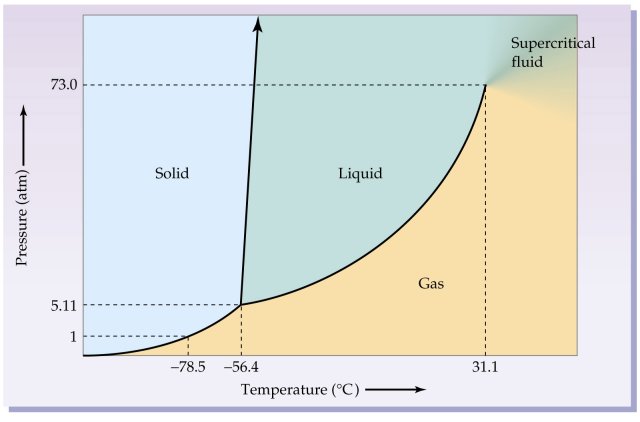
Phase Diagrams: Problem 10.82: Look at the phase diagram of CO 2 in Figure 10.29 and tell what phases are present under the following conditions: Before answering the questions below, we first bring up the phase diagram. ... Sulfur dioxide: T c = 157.8°C and P c = 77.7 atm 1) The boiling point and freezing point of sulfur dioxide (SO2) are -10 oC and -72.7 oC (at 1 atm), respectively. The triple point is -75.5oC and 1.65 x 10-3 atm, and its critical point is at 157 oC and 78 atm. On the basis of this information draw a rough sketch of the phase diagram of SO2. Label your axes. Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ...
Sulfur dioxide phase diagram. Determining the State of Carbon Dioxide Using the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in (Figure), determine the state of CO 2 at the following temperatures and pressures: (a) −30 °C and 2000 kPa. (b) −60 °C and 1000 kPa. (c) −60 °C and 100 kPa. (d) −40 °C and 1500 kPa. (e) 0 °C and 100 kPa. (f) 20 °C and 100 kPa. Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 11.5.5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a ... Phase Diagrams • Indicate phases as function of T, Co, and P. • For this course:-binary systems: just 2 components.-independent variables: T and Co (P = 1 atm is almost always used). • Phase Diagram for Cu-Ni system Adapted from Fig. 9.3(a), Callister 7e. (Fig. 9.3(a) is adapted from Phase Diagrams of Binary Nickel Alloys , P. Nash Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ...
In the gas phase sulfur dioxide is oxidized by reaction with the hydroxyl radical via a intermolecular reaction: SO 2 + OH· → HOSOHOSO 22 · which is followed by: HOSO2· + O2→ HO 2 · + SO 3 In the presence of water sulfur trioxide (SOIn the presence of water sulfur trioxide (SO 3) is converted) is converted rapidly to sulfuric acid: SO 3 ... by DL Hogenboom · 1996 · Cited by 4 — In our first data run pure sulfur dioxide melted at a temperature of 206.5 K ... Phase diagram of SO2 (bold solid curves) plotted with two lotherms (dashed ... Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ... Sulfur dioxide irritates the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs. High concentrations of SO 2 can cause inflammation and irritation of the respiratory system, especially during heavy physical activity. The resulting symptoms can include pain when taking a deep breath, coughing, throat irritation, and breathing difficulties.
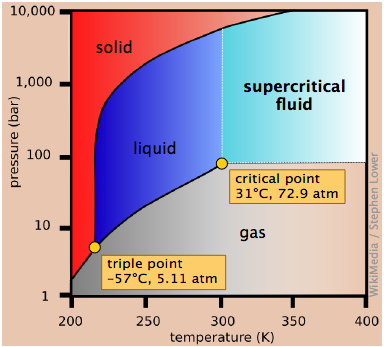
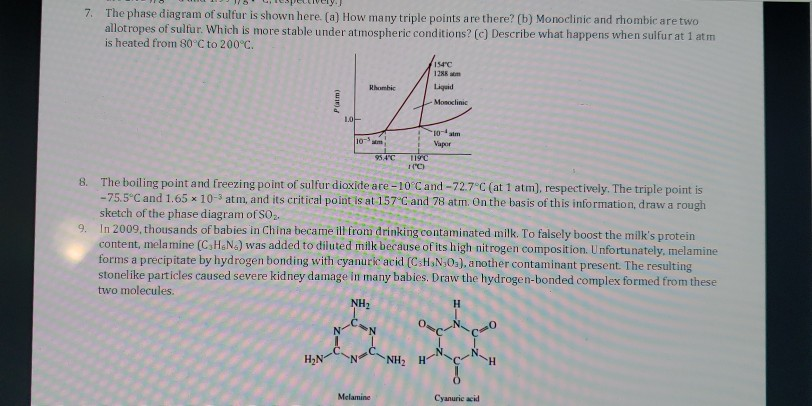
Recall that a phase diagram shows the transition of matter between solid, liquid, and gas phases as temperature and pressure changes. In a phase diagram, the ...1 answer · Top answer: In this problem, we are asked which of the three red points would SO2(g) most closely approach ideal-gas behavior.We can use the phase diagram to answer ... A phase diagram is a chart that shows the conditions of pressure and temperature at which distinct phases occur and coexist at equilibrium.. The lines on a phase diagram divide into regions - solid, liquid, and gas. The phase diagram of sulfur is. The diagram is complicated by the fact that sulfur can exist in two crystalline forms: rhombic and monoclinic. • The phase diagram for sulfur dioxide, SO 2, is shown below. Marks 4 Io, the innermost of the four Galilean moons orbiting Jupiter, is the most geologically active body in the solar system. Its surface is covered with a frost of solid SO 2. Dot and cross diagram of so2 and so3 · Structure and bonding Well it's hard to draw in a dot cross because of the resonance, but a google. The Sulfur Dioxide which is also known as Sulphur Dioxide is the entity of a bond between Sulfur and Oxygen atoms. Here we will provide an explanation of SO2 molecular geometry, SO2 electron geometry, SO2 ...

Volumetric Properties And Phase Behavior Of Sulfur Dioxide Carbon Disulfide And Oxygen In High Pressure Carbon Dioxide Fluid Sciencedirect
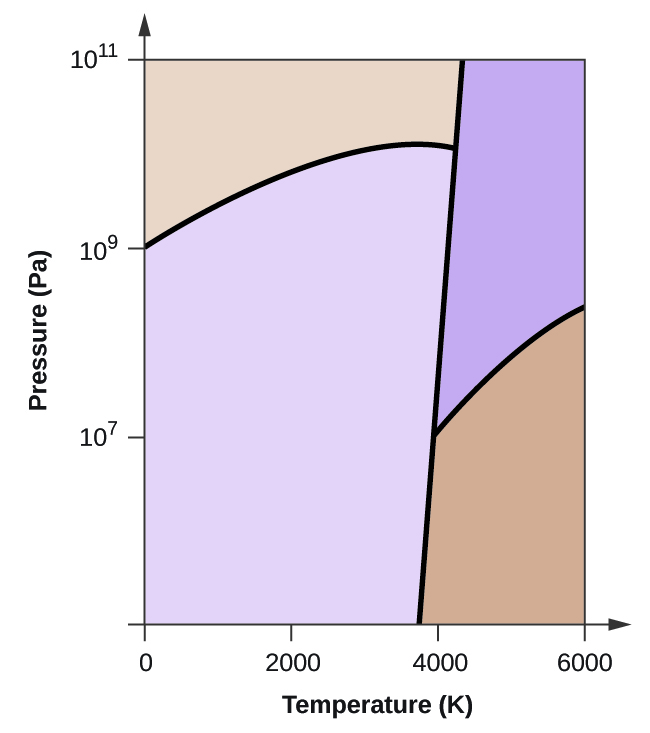
Is it possible to liquefy nitrogen at room temperature (about 25 °C)? Is it possible to liquefy sulfur dioxide at room temperature? Explain your answers. Elemental carbon has one gas phase, one liquid phase, and three different solid phases, as shown in the phase diagram: On the phase diagram, label the gas and liquid regions.

The Geological Availability And Emissions Of Sulfur And So2 From The Typical Coal Of China Aerosol And Air Quality Research
Carbon dioxide, CO 2, is a colourless and odorless gas. It is relatively nontoxic and noncombustible, but it is heavier than air and may asphyxiate by the displacement of air. When CO 2 is solved in water, the mild carbonic acid, is formed.Cooled CO 2 in solid form is called dry ice.. Carbon dioxide phase diagram
From the phase diagram for carbon dioxide in Figure 10.34, determine the state of CO2 at: -80 °C and 1500 kPa. ... The critical temperature is 430.5 K for sulfur dioxide, which is above room temperature. It can be liquefied at room temperature. Elemental carbon has one gas phase, one liquid phase, and three different solid phases, as shown in ...
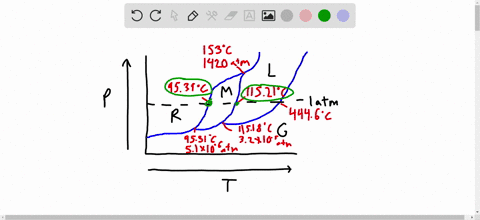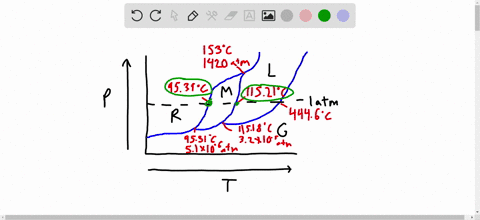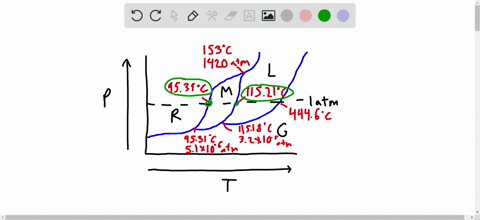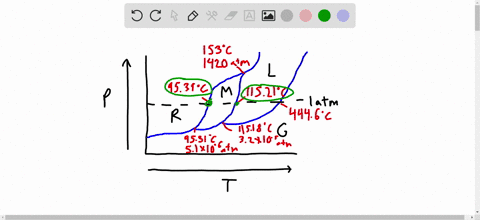
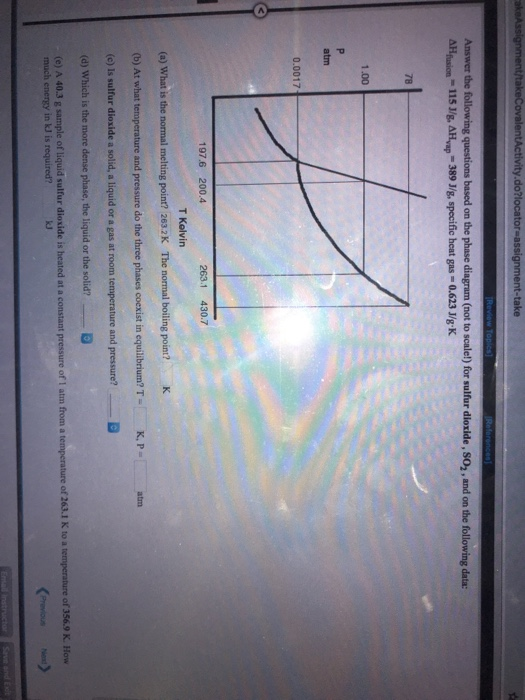
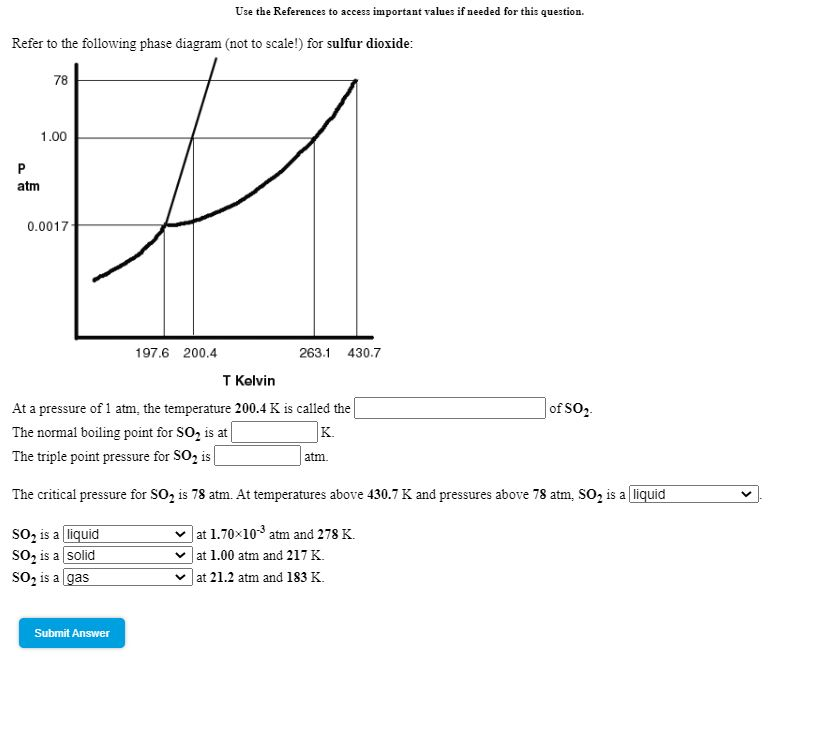
Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Refer to the following phase diagram (not to scale!) for sulfur dioxide 78 1.00 atm 0.0017 197.6 200.4 263.1 430.7 T Kelvin A sample of sulur dioxide at a pressure of 1.70 10-3 atm and a temperature of 267 K is compressed at constant temperature to a pressure of 85.3 atm.
How to draw the Lewis Structure of SO2 - with explanationCheck me out: http://www.chemistnate.com
Sulfur dioxide is a colorless gas with a pungent odor. It is a liquid when under pressure, and it dissolves in water very easily.Sulfur dioxide in the air comes mainly from activities such as the burning of coal and oil at power plants or from copper smelting. In nature, sulfur dioxide can be released to the air from volcanic eruptions.
14.3.1 Sulfur Dioxide. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a nonflammable, colorless gas, which may be liquefied to a colorless liquid with a specific pungent odor [69]. The main difference between chlorine and SO 2 is the lower vapor pressure of SO 2 (at 21°C the SO 2 vapor pressure is ∼240 kPa) compared with chlorine (at 21°C the chlorine vapor ...
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ...
by BC Spall · 1963 · Cited by 17 — At higher temperatures the phase diagrams are of simple shape, and above the critical point of sulphur dioxide the liquid-vapor inhomogeneous regions become ...
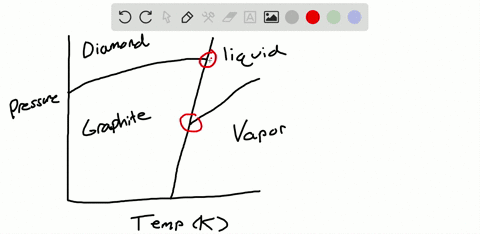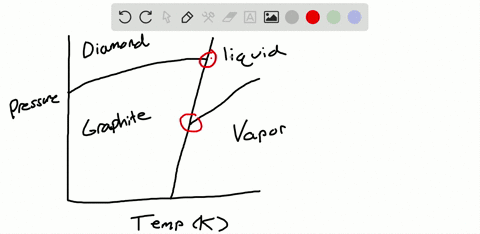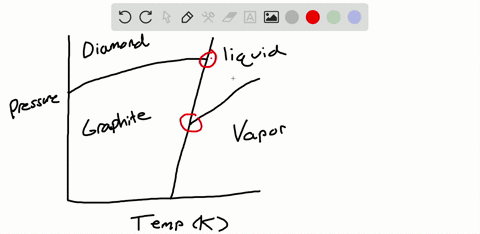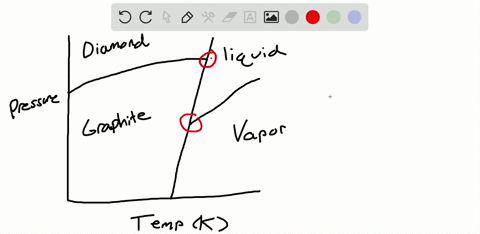
Solved Sulfur Exhibits Two Solid Phases Rhombic And Monoclinic Use The Accompanying Phase Diagram For Sulfur To Answer The Following Questions The Phase Diagram Is Not To Scale A How Many Triple Points
Sulfur dioxide SO2 - Sulfur oxide, Sulfurous anhydride, Sulfurous oxide, Bisulfite - UN1079 - 7446-09-5.
The boiling point and freezing point of sulfur dioxide (SO2) are –10 ... phase diagram of SO2. Label your axes. Place the following points on your graph.2 pages
Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Refer to the following phase diagram (not to scale!) for sulfur dioxide: 78 1.00 P atm f 0.0017 197.6 200.4 263.1 430.7 T Kelvin A sample of sulfur dioxide at a pressure of 1.70x10-3 atm and a temperature of 268 K is compressed at constant temperature to a pressure of 83.5 atm.
high, sulfur dioxide can easily be condensed by compression to give a colorless, ... vapor phase diagram (Figure 9), shown for reasons of expediency here, ...21 pages
7 Jun 2012 — The phase diagram for sulfur dioxide, SO2, is shown below. Marks. 4. Io, the innermost of the four Galilean moons orbiting Jupiter, ...1 page
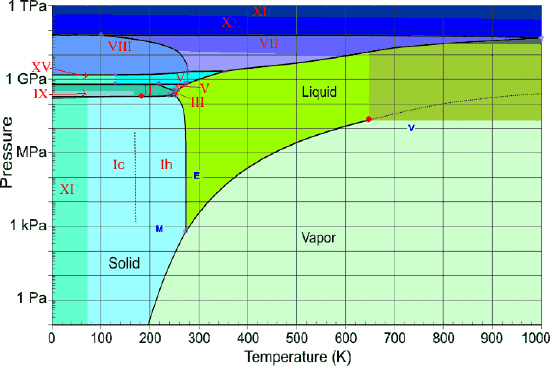
The pressure-temperature (P-T) phase diagram for sulfur is complex (see image). The region labeled I (a solid region), is α-sulfur. High pressure solid allotropes. In a high-pressure study at ambient temperatures, four new solid forms, termed II, III, IV, V have been characterized, where α-sulfur is form I. Solid forms II and III are polymeric, while IV and V are metallic (and are ...
Figure A-14EP-h diagram for refrigerant-134a Table A-16EProperties of the atmosphere at high altitude Table A-17EIdeal-gas properties of air Table A-18EIdeal-gas properties of nitrogen, N 2 Table A-19EIdeal-gas properties of oxygen, O 2 Table A-20EIdeal-gas properties of carbon dioxide, CO 2 Table A-21EIdeal-gas properties of ...
Determining the State of Carbon Dioxide Using the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in , determine the state of CO 2 at the following temperatures and pressures: (a) −30 °C and 2000 kPa (b) −60 °C and 1000 kPa (c) −60 °C and 100 kPa (d) 20 °C and 1500 kPa (e) 0 °C and 100 kPa (f) 20 °C and 100 kPa. Solution
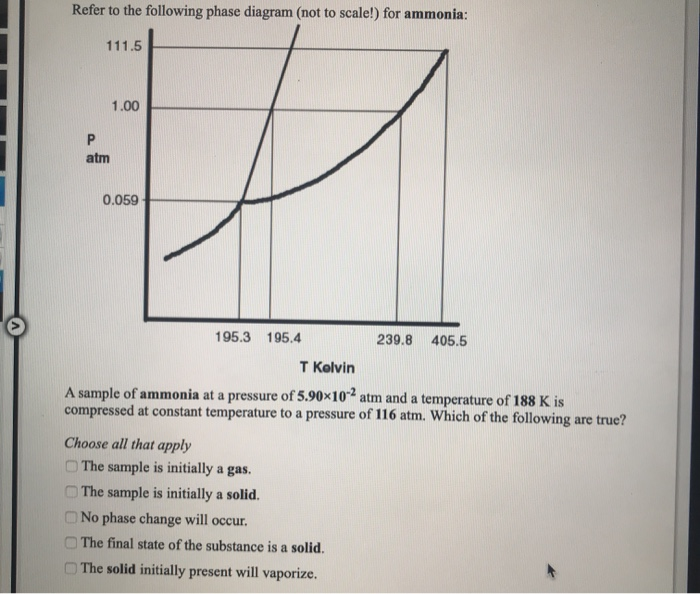
Related Topics . Material Properties - Material properties for gases, fluids and solids - densities, specific heats, viscosities and more ; Related Documents . Acetone - Thermophysical Properties - Chemical, physical and thermal properties of acetone, also called 2-propanone, dimethyl ketone and pyroacetic acid. Phase diagram included. Ammonia - NH 3 - Thermodynamic Properties - Thermodynamic ...
Calculation of vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) and drawing of phase diagrams. Name of substance. CAS-nr. Formula. Type of substance. acetone. 67-64-1. C 3 H 6 O. ketone.
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ...
1) The boiling point and freezing point of sulfur dioxide (SO2) are -10 oC and -72.7 oC (at 1 atm), respectively. The triple point is -75.5oC and 1.65 x 10-3 atm, and its critical point is at 157 oC and 78 atm. On the basis of this information draw a rough sketch of the phase diagram of SO2. Label your axes.
Phase Diagrams: Problem 10.82: Look at the phase diagram of CO 2 in Figure 10.29 and tell what phases are present under the following conditions: Before answering the questions below, we first bring up the phase diagram. ... Sulfur dioxide: T c = 157.8°C and P c = 77.7 atm
Solved The Boiling Point And Freezing Point Of Sulfur Dioxide Are 10 Circ Mathrm C And 72 7 Circ Mathrm C At 1 Atm Respectively The Triple Point Is 75 5 Circ Mathrm C And 1 65 Times 10 3 Atm And Its
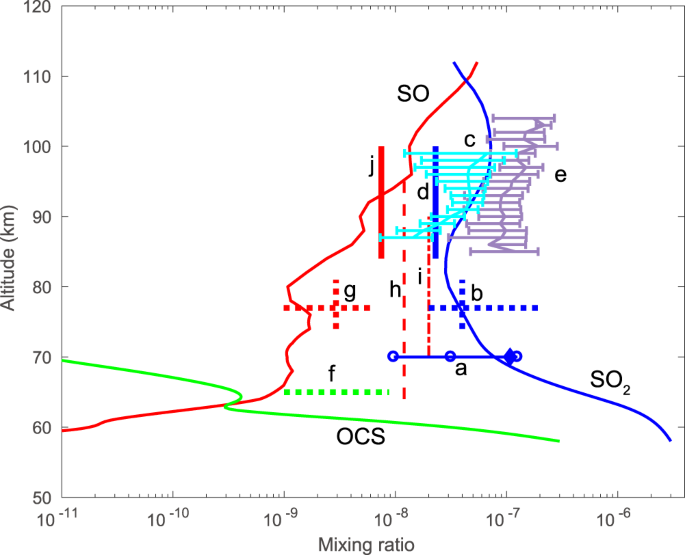
Sulfur Monoxide Dimer Chemistry As A Possible Source Of Polysulfur In The Upper Atmosphere Of Venus Nature Communications

Pdf Sulfur Isotopic Fractionation In The Gas Phase Oxidation Of Sulfur Dioxide Initiated By Hydroxyl Radicals Semantic Scholar















0 Response to "41 sulfur dioxide phase diagram"
Post a Comment